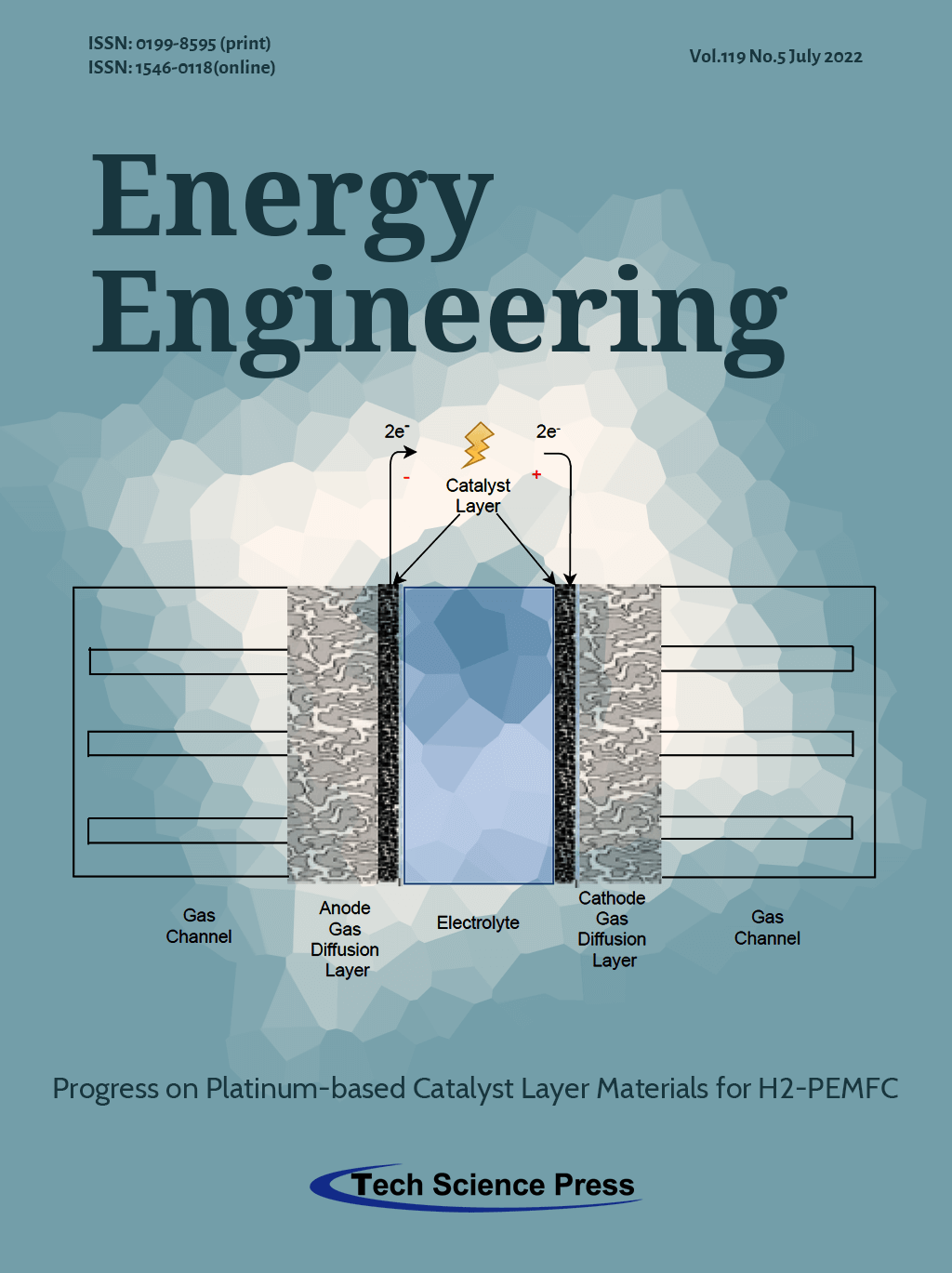
This image provides a schematic representation of a Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC) and the corresponding components of which it is composed. The path the reactant gases follow can be easily illustrated, beginning from the gas channels of the anode/cathode, where hydrogen and oxygen flow to the gas diffusion layers and finally end up in the catalyst layers. The electrochemical reactions of hydrogen oxidation HOR on the anode catalyst layer and oxygen reduction ORR on the cathode catalyst layer occur. At the same time, hydrogen positive ions are flowing through the electrolyte. Considering the aforementioned operating procedure, it is concluded that catalyst layers are one of the most crucial components of a PEMFC in terms of overall efficiency and performance. For achieving high reaction rates in the catalyst layers usually, platinum is employed. However, the usage of platinum implies drawbacks such as the significantly high cost and the low durability in CO tolerance when the supplied hydrogen isn’t 100% pure. To this extent, several materials have been examined to minimize the percentage of platinum with cost efficient and durable materials without decreasing the overall performance of the PEMFC.
View this paper