 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Enhancing Autonomy Capability in Regional Power Grids: A Strategic Planning Approach with Multiple Autonomous Evaluation Indexes
1 Planning and Assessment Center Department, State Grid Henan Economic Research Institute, Zhengzhou, 450000, China
2 Key Laboratory of Modern Power System Simulation and Control & Renewable Energy Technology, Ministry of Education, Northeast Electric Power University, Jilin, 132012, China
3 Development Planning Department, State Grid Henan Electric Power Company, Zhengzhou, 450000, China
4 Innovation Development Research Center, State Grid Shanghai Energy Internet Research Institute Co., Ltd., Shanghai, 201210, China
5 State Grid Simulation Center, China Electric Power Research Institute Co., Ltd., Beijing, 100192, China
* Corresponding Author: Junhui Li. Email:
Energy Engineering 2024, 121(9), 2449-2477. https://doi.org/10.32604/ee.2024.051244
Received 01 March 2024; Accepted 24 May 2024; Issue published 19 August 2024
Abstract
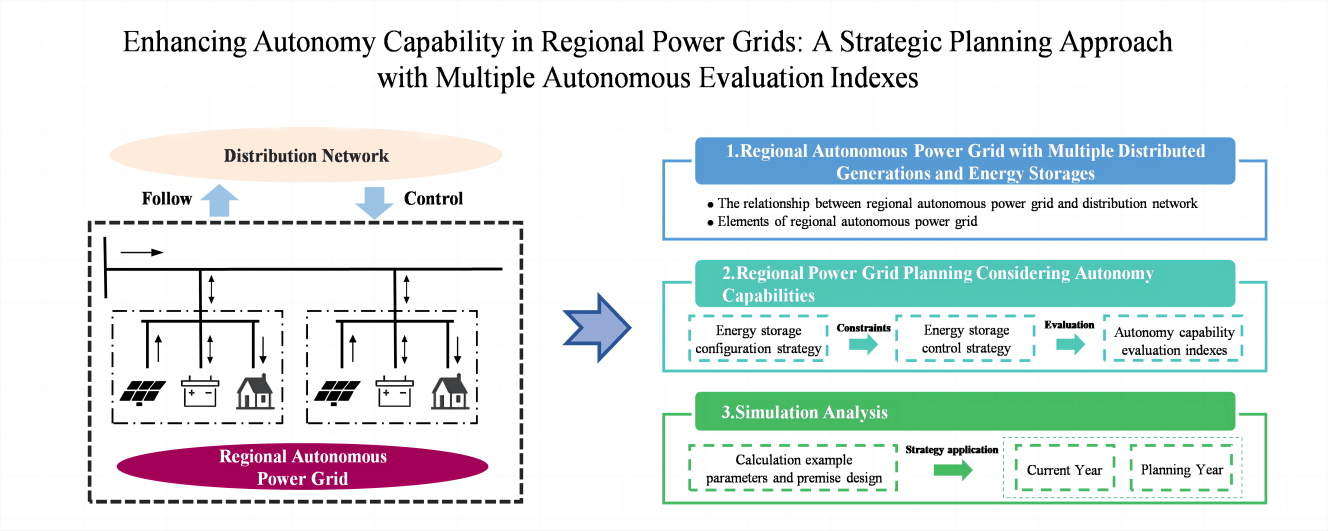
After the integration of large-scale Distributed Generation (DG) into the distribution network, the randomness and volatility of its output result in a reduction of spatiotemporal alignment between power generation and demand in the distribution network, exacerbating the phenomenon of wind and solar power wastage. As a novel power system model, the fundamental concept of Regional Autonomous Power Grids (RAPGs) is to achieve localized management and energy autonomy, thereby facilitating the effective consumption of DGs. Therefore, this paper proposes a distributed resource planning strategy that enhances the autonomy capabilities of regional power grids by considering multiple evaluation indexes for autonomy. First, a regional Energy Storage (ES) configuration strategy is proposed. This strategy can select a suitable reference value for the upper limit of ES configuration based on the regional load and DG output to maximize the elimination of source load deviations in the region as the upper limit constraint of ES capacity. Then, a control strategy for regional ES is proposed, the charging and discharging reference line of ES is set, and multiple autonomy and economic indexes are used as objective functions to select different proportions of ES to control the distributed resources of the regional power grid and establish evaluation indexes of the internal regional generation and load power ratio, the proportion of power supply matching hours, new energy consumption rate and tie line power imbalance outside the region to evaluate changes in the regional autonomy capabilities. The final simulation results show that in the real regional grid example, the planning method in the planning year in the region of the overall power supply matching hour ratio and new energy consumption rate increased by 3.9% and 4.8% on average, and the power imbalance of the tie line decreased by 7.8% on average. The proposed planning approach enables the maximization of regional autonomy while effectively smoothing the fluctuation of power exchange between the regional grid and the higher-level grid. This presents a rational and effective planning solution for the regional grid, facilitating the coordinated development between the region and the distribution network.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools