 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Dispersed Wind Power Planning Method Considering Network Loss Correction with Cold Weather
1 Hulunbeier Power Supply Company, State Grid Inner Mongolia East Power Co., Ltd., Hulunbeier, 021100, China
2 College of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, North China Electric Power University, Beijing, 102206, China
* Corresponding Author: Yihong Jiao. Email:
Energy Engineering 2024, 121(4), 1027-1048. https://doi.org/10.32604/ee.2023.045358
Received 24 August 2023; Accepted 28 November 2023; Issue published 26 March 2024
Abstract
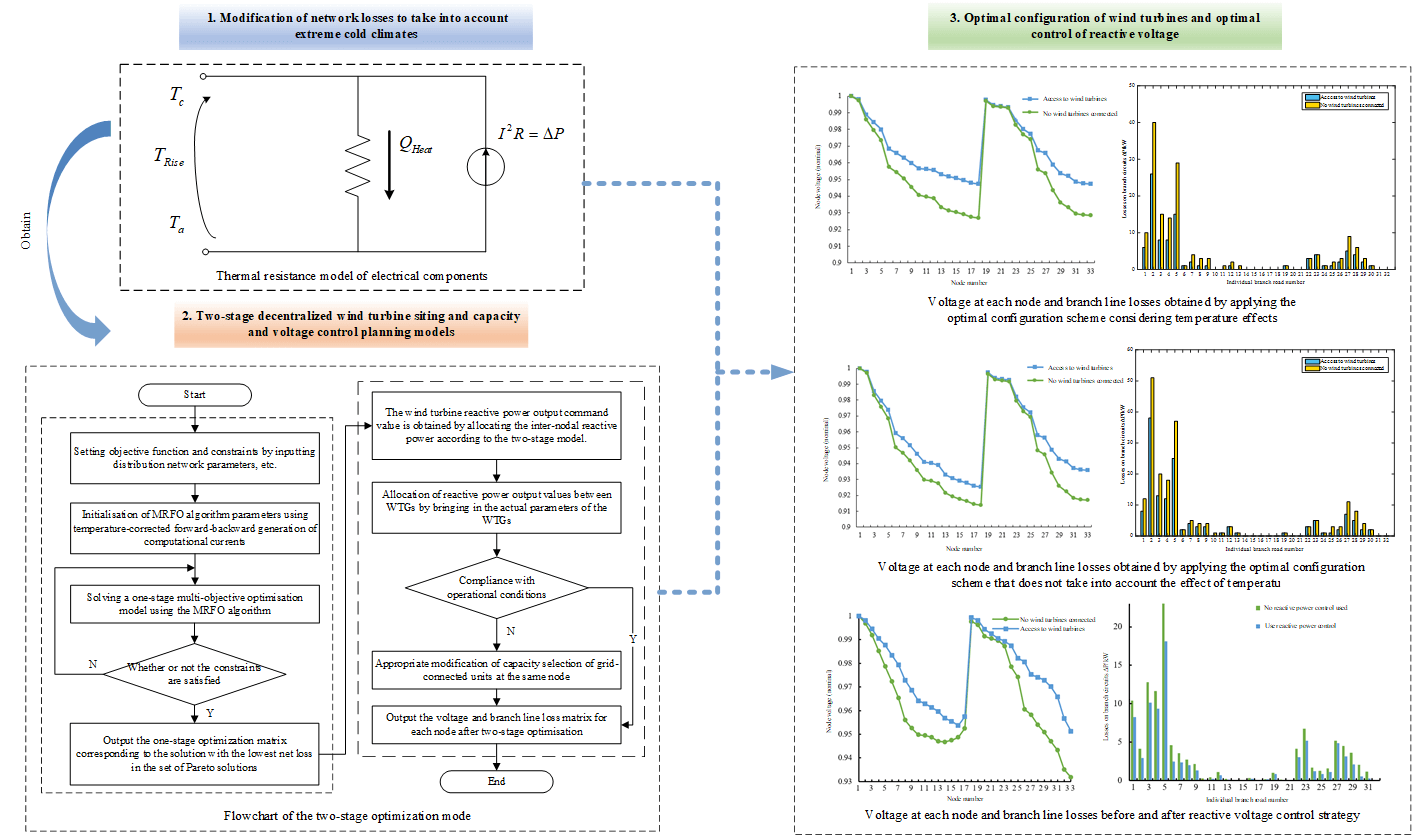
In order to play a positive role of decentralised wind power on-grid for voltage stability improvement and loss reduction of distribution network, a multi-objective two-stage decentralised wind power planning method is proposed in the paper, which takes into account the network loss correction for the extreme cold region. Firstly, an electro-thermal model is introduced to reflect the effect of temperature on conductor resistance and to correct the results of active network loss calculation; secondly, a two-stage multi-objective two-stage decentralised wind power siting and capacity allocation and reactive voltage optimisation control model is constructed to take account of the network loss correction, and the multi-objective multi-planning model is established in the first stage to consider the whole-life cycle investment cost of WTGs, the system operating cost and the voltage quality of power supply, and the multi-objective planning model is established in the second stage. planning model, and the second stage further develops the reactive voltage control strategy of WTGs on this basis, and obtains the distribution network loss reduction method based on WTG siting and capacity allocation and reactive power control strategy. Finally, the optimal configuration scheme is solved by the manta ray foraging optimisation (MRFO) algorithm, and the loss of each branch line and bus loss of the distribution network before and after the adoption of this loss reduction method is calculated by taking the IEEE33 distribution system as an example, which verifies the practicability and validity of the proposed method, and provides a reference introduction for decision-making for the distributed energy planning of the distribution network.
Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools