 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yixuan Wang1, Yanchao Li1, Qiang Feng1, Haicheng Sun2, Guchang Zhang3, Zhiming Zhao1, Jianfeng Xiao1, Jingyun Huang1, Tiankui Guo3,*
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2026.076849
Abstract Achieving uniform proppant distribution among multiple perforation clusters is essential for the effectiveness of horizontal well fracturing, yet remains challenging due to complex solid-liquid transport mechanisms. This study presents a comprehensive numerical investigation using Computational Fluid Dynamics to analyze proppant transport heterogeneity in a full-scale 90-m horizontal wellbore with five perforation clusters. An Eulerian-Eulerian multiphase model is employed to simulate proppant transport and settling in the wellbore and perforations. The effects of key operational and geometric parameters—including injection rate, proppant concentration and size, fluid viscosity and phase angle—are systematically evaluated. Results demonstrate that flow rate… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Fabiano Thulu, Zeyun Wu*
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2026.076328
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Neutronic and Thermal-Hydraulic Analysis of Advanced Nuclear Reactors)
Abstract Real-time prediction of temperature distribution in the pressurizer walls of Pressurized Water Reactors (PWRs) during severe accidents, such as Station Blackout (SBO) and Loss-of-Coolant Accident (LOCA) is vital for structural integrity assessment. However, conventional thermal-hydraulic simulations used for such predictions are computationally intensive, limiting their applicability for real-time analysis. This study develops and compares three surrogate models: Polynomial Regression, Deep Neural Network (DNN), and a Physics-Informed Neural Network (PINN). Thermal-hydraulic simulation data generated by RELAP5-3D are integrated with physics-constrained learning techniques to model transient heat conduction in the pressurizer wall. The internal wall temperature evolution… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Zhongjin Shi#, Zhe Zang#, Chong Wang#, Yue Yang*
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2026.074923
Abstract To address the critical challenges of power fluctuations and the imperative for efficient reactive power optimization in distribution networks with high photovoltaic (PV) penetration, this study proposes an innovative solution: a robust reactive power optimization approach that integrates VMD-LSTM-based PV power forecasting with the advanced Lion Swarm Optimization (LSO) algorithm. The methodology commences by employing Variational Mode Decomposition (VMD) to decompose the PV power sequence into distinct modal components in a seamless manner. Each modal component is subsequently modeled using a dedicated forecasting framework built on Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks, with the LSO algorithm… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Hongbo Liu, Jingzhou Zhu, Li Sun*, Fanjun Zeng
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2026.075768
Abstract This paper tackles the challenge of balancing computational efficiency with analytical rigor in Probabilistic Power Flow (PPF) analysis for power systems with integrated wind power. We propose an enhanced steady-state security region (SSR) assessment method based on PPF theory. The methodology first employs a hybrid Monte Carlo technique that integrates Latin Hypercube Sampling (LHS) with Importance Sampling (IS) to compute and analyze the probabilistic power flow distribution. This hybrid strategy ensures comprehensive global coverage while intensively sampling critical risk regions, thereby improving both computational efficiency and accuracy. Subsequently, a fast-search model for the SSR is… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Melita Srpak1, Darko Pavlovic2, Predrag Brlek3,*, Nikola Kozul3
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2026.075211
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Energy Transition in the Transport Sector: Challenges and Opportunities)
Abstract Discussions about the future of energy sources and environmental sustainability are becoming critical on a global scale. The energy sector plays a central role in the economy, as the availability and cost of energy influence the competitiveness of economies, while the level of energy consumption impacts the standard of living for individuals. This paper aims to examine environmental challenges and steps for a sustainable transition towards a hydrogen economy, focusing on its potential as an alternative to fossil fuels and the importance of developing the hydrogen paradigm. The research methodology is based on a combination… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Xiaoming Yu1, Peng Wang1, Jun Wang1, Zhijun Chen1, Ke Zhang1, Duicheng Zhao2, Jiapeng Shen2, Chuyang Wang2,*, Li Zhang2
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2026.073475
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Innovations and Challenges in Smart Grid Technologies)
Abstract Electrolytic capacitors in Modular Multilevel Converter-based Unified Power Flow Controllers (MMC-UPFC) are prone to parameter degradation, significantly affecting system reliability. Accurate identification of their degradation parameters—capacitance (C) and equivalent series resistance (ESR)—is essential for equipment health management. This study proposes a non-intrusive degradation parameter identification method for electrolytic capacitors in MMC-UPFC full-bridge submodules based on digital twin technology and an improved intelligent optimization algorithm. First, the degradation mechanism of electrolytic capacitors under long-term operational conditions is systematically analyzed. Second, a high-fidelity digital twin model integrating the main circuit, sampling circuit, and modulation circuit of the… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yihua Zhu1, Chao Luo1, Yuxia Tang1, Renxin Yang2,*
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2026.075636
Abstract With the rapid development of renewable energy, the proportion of wind power generation in modern power systems has been steadily increasing. Benefiting from the high controllability of power electronic converters, wind energy can be efficiently transmitted to the grid through power conversion stages. However, the reliability of wind turbine systems is closely related to the thermal stress and degradation of power semiconductor devices. The diversity of actual operating conditions and the rapid fluctuations of grid load bring significant challenges to their safe and stable operation. To address these issues, this paper establishes an online electro-thermal… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Xuefeng Yang1,2, Chunyu Ren1,2, Deliang Zhang1,2, Huaicai Fan1,2, Yue Chen1,2, Yue Yang1,2, Yan Zhang1,2, Shuai Wu1,2, Baoyun Zhang3,*, Xin Zhao3
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.074956
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Progress and Prospects of Hydraulic Fracture Network Morphology Characterization, Flow Simulation and Optimization Technology for Unconventional Oil and Gas Reservoirs)
Abstract In southern Sichuan’s deep shale gas development, multi-stage fractured horizontal wells are commonly used. Evaluating fracturing results is challenging due to complex fracture networks. This study classifies fracture systems into four types: single-wing, bi-wing, branched, and serial fractures. A discrete fracture model (DFM) combined with matrix-fracture flow is used to establish a single-stage well testing interpretation model. To address multi-solution issues in well testing, an equivalent fracture network model based on a trilinear flow model is proposed, adjusting crossflow coefficients and the fracture network volume ratio. The study finds significant differences in the pressure derivative More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Kewen Li, Xiaoyong Yu, Shifeng Ou*, Jueming Pan
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.073825
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advanced Analytics on Energy Systems)
Abstract The increasing integration of renewable energy sources (e.g., wind and solar power) into distribution grids and the development of new, source–grid–load–storage coordinated power systems have led to a substantial expansion in the volume of situational awareness data in the distribution networks. Moreover, the transmission of low-voltage distribution measurement data via a power line carrier (PLC) is often susceptible to packet loss and, consequently, data gaps. To address these issues, this paper proposes a data completion method using a conditional generative adversarial network (CGAN) integrated with a three-dimensional convolutional neural network (3D-CNN). This approach leverages the… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Xiang Xiao, Peng Zhang*, Yuan Yuan, Zhiyuan Feng, Kui Hu, Yuan Xu, Yunhuang Zhang, Guoming Liu
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2026.073741
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Neutronic and Thermal-Hydraulic Analysis of Advanced Nuclear Reactors)
Abstract As a promising solution to the challenges of future clean and reliable energy supply, the Gas-Cooled Micro-Reactor (GCMR) has attracted increasing attention due to its potential for decentralized power generation, carbon-free operation, and flexible deployment in remote or extreme environments. As a novel reactor concept, the GCMR offers advantages such as compact size, inherent safety, and high thermal efficiency. However, conventional core calculation methods face significant challenges due to the complex geometric configurations, heterogeneous material distribution, and pronounced neutron leakage characteristics of the GCMR. This study proposes a diffusion-based homogenization method for GCMR analysis. First,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yinfeng Ma1, Kuan Zhang1,*, Youxin Chen1, Nian Liu1, Zhi Xu2, Min Ren2
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2026.077169
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Next-Generation Distribution System Planning, Operation, and Control)
Abstract With the advancement of the Rural Revitalization Strategy and the “Dual Carbon” goals, rural energy systems are exhibiting pronounced multi-energy coupling, a high penetration of renewable energy, and strong load randomness, placing higher demands on the construction of source-load scenarios across multiple time scales. Addressing the limitations of traditional statistical models in generating high-quality short-term source-load scenarios and the tendency of deep learning methods to overlook medium- to long-term seasonal evolution patterns, this paper proposes a hybrid data- and model-driven method for constructing multi-energy source-load scenarios in rural systems. This method establishes a multi-time-scale generation… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Rongyi Niu1,2, Chong Li1,2,*, Gang Gu1,2, Qunhui Hu1,2
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2026.076567
Abstract To address the operational complexity caused by the high proportion of new energy integration into distribution networks, a multilevel resource-coordinated operation strategy based on an improved whale optimization algorithm (improved WOA) is proposed for active distribution networks (ADNs). A bilevel optimization model is established to ensure the economic and safe operation of ADNs. The upper level is used to minimize the total system operation cost, while the lower level is used to optimize the power balance. Subsequently, the improved WOA, integrated with an adaptive weight and chaotic disturbance mechanisms, is used to solve the bilevel… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Xintong Mao1, Yechi Xu1, Yaowen Sun2, Zhihan Liu1, Yumeng Wang1, Chuyang Wang2,*
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2026.076436
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Operation and Control of Grid-connected New Energy and Emerging Loads)
Abstract The self-adaption STATCOM and line commutation converter (SLCC) system based on the static var generator and filter (SVF) utilizes the compensation capability of the SVF to reduce the commutation process’s dependence on the AC grid, thereby enhancing the SLCC’s ability to resist commutation failure. However, existing SLCC control strategies have not fully considered the boundary conditions for the safe and stable operation of the SVF (i.e., the SVF withstand capability), which limits or even deteriorates the ability of the SVF to provide commutation support for the SLCC under AC grid voltage fault conditions. To address… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yuanxiang Luo, Xinmeng Pan*, Xuyang Gao
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2026.076019
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Grid Integration and Electrical Engineering of Wind Energy Systems: Innovations, Challenges, and Applications)
Abstract The integration of a high proportion of renewable energy sources via power electronic devices poses significant challenges to power systems. Their grid-connection characteristics differ considerably from those of synchronous generators, leading to a reduction in system inertia. Furthermore, the complex interactions between renewable energy units and the power grid substantially impact the transient stability of the system. Based on the virtual synchronous control characteristics of grid-forming wind turbines (GWT), this paper proposes an adaptive control method to enhance system transient stability. Firstly, a transient stability model for integrating GWT into conventional power systems is established,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Zhan Lv*, Lan Lan, Zijian Hu, Honghua Xu, Hong Zhu, Jiehua Hou
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2026.075769
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Digital and Intelligent Planning and Operation Technologies for Flexible Distribution Network)
Abstract To fully utilize the diverse source-grid-load-storage flexible resources integrated in new distribution networks, this paper proposes an optimal load transfer strategy that coordinates distributed generator island operation with network reconfiguration. Following a fault event, the strategy prioritizes the black-start capability of distributed generators and establishes island operation model to maximize and locally restore critical loads while respecting island operational constraints. To solve this model, the actual topology of the new distribution network is abstracted as a tree structure, and an improved Kruskal algorithm is employed to derive the minimum spanning tree, achieving optimal island partition… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Wenqiang Xie*, Xiaolong Xiao, Fangfang Zhu, Ziran Guo, Xiaoxing Lu
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.075298
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Artificial Intelligence-Driven Collaborative Optimization of Electric Vehicle, Charging Station and Grid: Challenges and Opportunities)
Abstract In the framework of the comprehensive energy transition, the proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) powered by renewable energy emerges as a promising alternative, particularly with relevance to applications like electric vehicles (EVs), where clean and efficient power sources are crucial. However, the accurate prediction of PEMFC performance degradation poses significant challenges due to the combined effects of complex and variable aging mechanisms and operational conditions, which are especially critical in the context of EV applications where reliability and durability directly impact vehicle performance and user safety. These challenges pose notable constraints on the feasibility… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yunlong Du1, Shuyi Zhuang2,*, Zhigang Ye2, Qiangsheng Bu2, Yun Chai1, Yuanbing Wang3
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.074702
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advanced Analytics on Energy Systems)
Abstract Under the dual challenges of global warming and energy transition, improving the short-term forecasting accuracy of surface solar radiation is of great practical importance for photovoltaic (PV) power integration. In this study, a short-term solar radiation forecasting model based on the XGBoost machine learning algorithm was developed for Jiangsu Province by integrating multispectral data from the Fengyun-4A (FY-4A) geostationary satellite with ground-based meteorological observations. The model incorporated 18 input features—including satellite reflectance, solar zenith angle, normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI), elevation, and land-cover data—to dynamically predict ground horizontal irradiance (GHI) with 0–4 h lead times.… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Meng Zhang1, Lijuan Zhang2, Jie Zhang1, Shiliang Miao2, Jiangong Yang2, Yajun Zhao1,*, Feifei Bu1
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.074465
Abstract Conventional electric servo drive systems suffer from high common-mode voltage (CMV) due to the use of zero vectors in Space Vector Pulse Width Modulation (SVPWM). To mitigate this issue, this paper proposes an inverted SVPWM (I-SVPWM) strategy. By simply inverting the switching actions of a specific phase, this strategy avoids the use of zero vectors and achieves an effect similar to Active Zero-State PWM (AZSPWM), thereby effectively suppressing common-mode voltage. Compared with AZSPWM, the proposed method eliminates the need to recalculate vector action times or design new switching sequences. It can be seamlessly implemented by… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Mahboobeh Attaei1,2, Maria Vieira1, Cinthia Maia Pederneiras3,4,*, Filipa Clara Coimbra1, David Bastos1, Rosário Veiga3
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2026.074246
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advancing Carbon Mitigation Strategies for a Sustainable Future)
Abstract The construction industry is a significant contributor to global CO2 emissions, and urgent innovation is needed to mitigate its environmental impact. This paper provides a comprehensive review of scalable approaches for CO2 uptake in construction materials, including the injection of CO2 into fresh concrete, the CO2 curing of precast concrete, and the use of ceramics as CO2 sinks. Among these three approaches, CO2 curing methods for concrete represent the most advanced and widely adopted strategies within industrial practice, with substantial research supporting their effectiveness and scalability. The comparison of carbonation mineralisation across three distinct material groups reveals that… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Wulfran Fendzi Mbasso1,2, Idriss Dagal3, Manish Kumar Singla4,5,*, Muhammad Suhail Shaikh6, Aseel Smerat7
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2026.072899
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Global Intelligent Optimization and Advanced Control of Photovoltaic Systems Under Complex Operating Conditions)
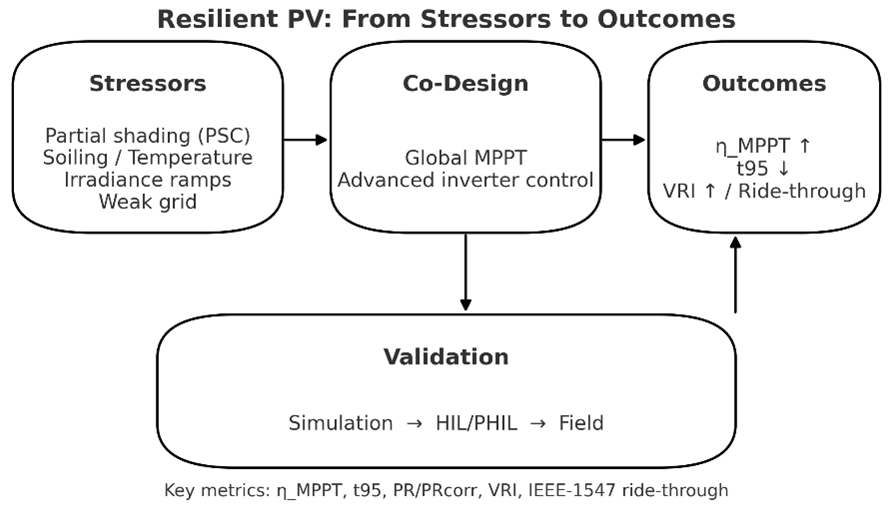
Abstract Utility-scale PV plants increasingly operate under partial shading, soiling, temperature swings, and rapid irradiance ramps that depress yield and challenge stability on weak grids. This critical review addresses those conditions by (i) unifying a stressor-to-method taxonomy that links field stressors to global intelligent MPPT (metaheuristics and learning-based trackers) and to advanced inverter controls (adaptive/MPC and grid-forming), (ii) standardizing metrics and reporting aligned with IEC 61724-1 and IEEE 1547/1547.1 to enable fair, reproducible comparisons, and (iii) framing MPPT and grid support as a co-design problem with a DT→HIL→Field validation pathway and seedable scenarios. We identify persistent… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Xinhao Lin1, Lei Yu1, Shuyin Duan1, Yinliang Liu1, Lvzerui Yuan1, Xiao Chen1,*, Yiqing Lian2
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2026.072845
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Next-Generation Distribution System Planning, Operation, and Control)
Abstract To address the operational challenges posed by renewable energy generation uncertainty and load fluctuations in DC microgrids, this paper proposes a hierarchical coordinated optimization control strategy for electricity-hydrogen hybrid DC microgrids (EH-DC-MG). The strategy aims to leverage the synergistic advantages of hybrid electricity-hydrogen energy storage to simultaneously achieve multiple objectives, including economic system operation, efficient utilization of renewable energy, and reliable power supply. The upper optimization scheduling layer formulates a mixed-integer linear programming model with the objective of minimizing the total system cost, which incorporates equipment operation and maintenance expenses, battery depreciation, penalties for renewable… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Hongsheng Su, Dan Li*, Yuwei Du
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.072397
Abstract When the three-phase grid-connected inverter system is in operation, there are problems of significant switching losses and power losses. At the same time, if the switching frequency is not fixed, it will lead to problems such as a high content of low-order harmonics in the current on the grid side. This paper takes the three-phase grid-connected inverter as the research object and proposes a solution. Establish a mathematical model for the inverter system and analyze the transformation relationships of relevant electrical quantities across different coordinate systems. First, the paper proposes an improved three-vector model predictive… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Huajie Zhang1, Xiaopeng Li1, Hanlin Xiao2,*, Lifeng Xing2, Wenyue Zhou1
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2026.071768
Abstract The integration of a high proportion of renewable energy introduces significant challenges for the adaptability of traditional fault nature identification methods. To address these challenges, this paper presents a novel fault nature identification method for renewable energy grid-connected interconnection lines, leveraging wavelet packet decomposition and voltage waveform time-frequency morphology comparison algorithms. First, the paper investigates the harmonic injection mechanism during non-full-phase operation following fault isolation in photovoltaic renewable energy systems, and examines the voltage characteristics of faulted phases in renewable energy scenarios. The analysis reveals that substantial differences exist in both the time and frequency… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Long Yu1,*, Xianghua Pan2, Rui Sun1, Yuan Li3, Wenjia Hao4
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.070023
Abstract Distribution transformers play a vital role in power distribution systems, and their reliable operation is crucial for grid stability. This study presents a simulation-based framework for active fault diagnosis and early warning of distribution transformers, integrating Sample Ensemble Learning (SEL) with a Self-Optimizing Support Vector Machine (SO-SVM). The SEL technique enhances data diversity and mitigates class imbalance, while SO-SVM adaptively tunes its hyperparameters to improve classification accuracy. A comprehensive transformer model was developed in MATLAB/Simulink to simulate diverse fault scenarios, including inter-turn winding faults, core saturation, and thermal aging. Feature vectors were extracted from voltage,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Polina A. Tretyakova*, Alexey P. Belkin, Alexander A. Rumyantsev, Anna A. Menshikova
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.075393
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advancements in Energy Resources and Their Processes, Systems, Materials and Policies for Affordable Energy Sustainability)
Abstract Limited adoption of solar energy in the Northwestern region of Russia is associated with insufficient data on annual solar radiation indicators and on the potential of solar collectors for water heating. The study aims to evaluate the potential of solar water heating for domestic use in Northwestern Russia, using Tyumen city as the case. In this region, the number of cloudy days ranges from 5% to 50%, with cloud cover increasing in winter. New data on the total solar radiation, availability duration, and cloud cover have been collected. Solar irradiance could reach 900 MJ/m2 during summer… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Mirna Omar1,*, Sarah Omar1, Kamaruzzaman Sopian1,2, Taib Iskandar Mohamad1
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2026.072583
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Green Hydrogen Technologies)
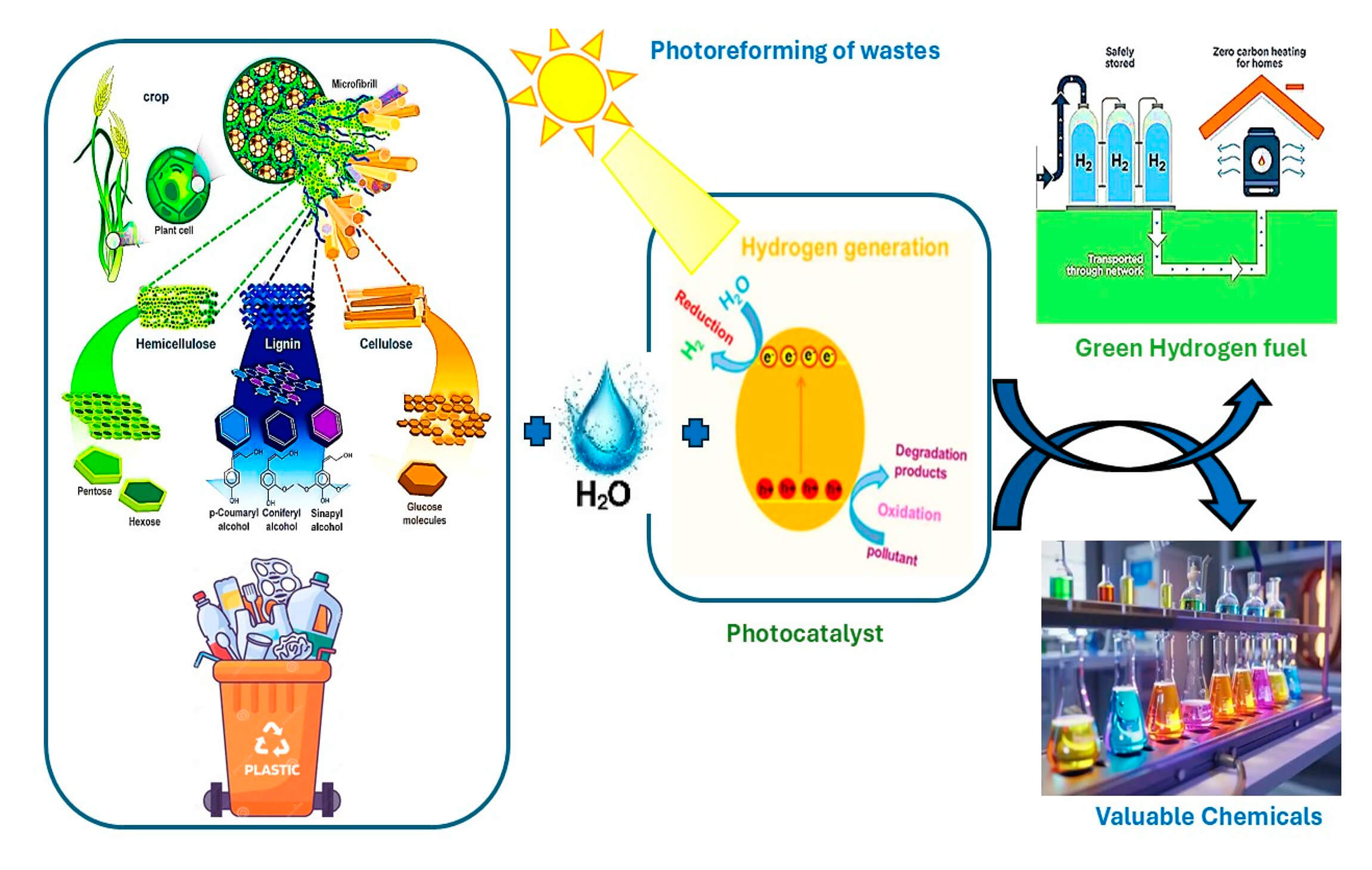
Abstract Photoreforming is an emerging photocatalytic process that converts organic waste into hydrogen H2 using solar energy, offering a dual solution for waste valorization and sustainable fuel production. This review comprehensively examines the fundamental mechanisms of photoreforming, emphasizing the critical role of photocatalyst design in optimizing hydrogen evolution. Key criteria for effective photocatalysts including suitable band edge positions, broad spectrum solar absorption, and photostability are systematically analyzed alongside advances in heterojunction engineering and defect modulation. The review further explores diverse waste-derived feedstocks, such as biomass: alcohols, saccharides, lignin and plastics: PET, PLA, polyolefins, highlighting substrate, specific challenges More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Zhen Pan1, Lijuan Huang1, Kaiwen Huang1, Feipeng Huang1, Bo Yang2,*
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2026.077000
Abstract With the global pursuit of carbon neutrality and the rapid development of marine renewable energy, offshore power transmission has become a key link in the integration of offshore power into onshore power grids. This paper summarizes the current advanced offshore transmission technologies, including high voltage alternating current transmission, high voltage direct current transmission, multi-terminal high voltage direct current transmission, hybrid high voltage direct current transmission, frequency division transmission, offshore overhead line transmission and energy storage transmission system. The application scenarios of various technologies are analyzed in detail: High voltage alternating current transmission is suitable for More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
He Wang, Yuyan Wang, Jing Bian*, Huanan Yu
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2026.076766
Abstract Addressing the challenges of peak shaving and curtailment caused by integrating a large amount of renewable energy into the grid, this paper proposes an optimized operation method for microgrid electricity-hydrogen hybrid energy storage (EH-HES), which considers electrolyzer arrays and an energy management strategy (EMS). Firstly, the time span of the energy-rich season and the energy-poor season is determined through time series decomposition, and a hydrogen energy storage (HES) operation mode based on seasonal typical scenarios is proposed. Secondly, the key equipment for EH-HES is modeled, including the hybrid electrolyzer arrays model that considers rotation strategy… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Xiaolan Li1,2,*, Jinyu Shen1,2, Jinhuang Liang1,2, Yanting Wang1,2
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2026.076521
Abstract The intrinsic volatility and stochasticity of large-scale wind power generation pose significant challenges to grid stability. To address the limitations of conventional models in capturing strong non-stationarity, this study proposes a novel Multi-Stage Adaptive Forecasting Network (MSAF-Net). The framework features a hierarchical signal refinement strategy coupled with an intelligently optimized hybrid predictor. Initially, input redundancy is minimized via Pearson Correlation Coefficient (PCC) analysis to isolate significant meteorological variables. A two-phase decomposition-reconstruction mechanism is then implemented: the wind power series is first decomposed using Complete Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition with Adaptive Noise (CEEMDAN). To optimize the… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Naveen Guguloth1, Bishwajit Dey2, Fausto Pedro García Márquez3,*, Prasenjit Dey1, Isaac Segovia Ramírez4
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.073971
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advanced Analytics on Energy Systems)
Abstract The increasing integration of electric vehicle (EV) loads into power systems necessitates understanding their impact on stability. Small-magnitude perturbations, if persistent, can cause low-frequency oscillations, leading to synchronism loss and mechanical stress. This work analyzes the effect of voltage-dependent EV loads on this small-signal stability. The study models an EV load within a Single-Machine Infinite Bus (SMIB) system. It specifically evaluates the influence of EV charging through the DC link capacitor of a Unified Power Flow Controller (UPFC), a key device for damping oscillations. The system’s performance is compared to a modified version equipped with More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Thanyapisit Buaprakhong1, Varintorn Sithisint1, Awirut Phusaensaart1, Sinthon Wilke1, Thatsamaphon Boonchuntuk1, Thittaporn Ganokratanaa1,*, Mahasak Ketcham2
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2026.069004
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: AI in Green Energy Technologies and Their Applications)
Abstract The rapid digitalization of the energy sector has led to the deployment of large-scale smart metering systems that generate high-frequency time series data, creating new opportunities and challenges for energy anomaly detection. Accurate identification of anomalous patterns in building energy consumption is essential for optimizing operations, improving energy efficiency, and supporting grid reliability. This study investigates advanced feature engineering and machine learning modeling techniques for large-scale time series anomaly detection in building energy systems. Expanding upon previous benchmark frameworks, we introduce additional features such as oil price indices and solar cycle indicators, including sunset and… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Leonid Plotnikov1,*, Leonid Osipov1, Danil Davydov1, Dmitry Krasilnikov1, Alexander Ryzhkov2
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2026.076278
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Thermal Engineering Technology Innovation and Sustainable Development)
Abstract The use of alternative fuels to generate mechanical and thermal energy in engines is a promising and sought-after technological area with its own unique advantages and characteristics. Consequently, enhancing the technical, economic, and environmental efficiency of gas engines fueled by propane-butane mixture and syngas through optimized operating cycle parameters (including valve timing, ignition timing angle, fuel mixture composition, and compression ratio) is a pressing imperative for scientific and energy sectors. The aim of the study was to investigate and compare the performance of an engine with different compression ratios running on a propane-butane mixture and… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Wanxing Sheng1, Xiaoyu Yang1, Dongli Jia1, Keyan Liu1, Zewei Chen2,*
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2026.075810
Abstract Accurate forecasting of electricity consumption patterns is a fundamental task of power demand-side management (DSM), particularly for industrial and commercial users who significantly influence market supply-demand balance and price fluctuations. Traditional forecasting methods, including statistical models and deep learning approaches, often struggle to capture the complex multi-factor, non-linear, and spatio-temporal dependencies inherent in power load data. To address these limitations, this paper introduces GBCTT (GAT-TBA-CNN-TCN), a novel multi-factor load forecasting model. The model integrates a Graph Attention Network (GAT) to dynamically learn spatial dependencies among heterogeneous influencing factors (e.g., temperature, humidity, electricity prices), a Time… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Weijia Tang, Qiang Li*, Ningyu Zhang
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2026.074698
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Research and Application of Marine Renewable Energy Technologies)
Abstract Large-scale offshore wind farm clusters (OWFCs) have been increasingly connected to the power grid, and requires advanced forecasting models to enhance the prediction accuracy of OWFC’s power output. This paper proposes a multi-source fusion with patch-guided multi-task learning for power prediction of offshore wind farm clusters. Unlike traditional graph-based approaches that rely on predefined topological relationships, which are limited in capturing the highly similar but rapidly changing meteorological conditions among closely spaced offshore farms, the proposed model employs a parameter-sharing multi-task learning network to achieves both independence and correlation among offshore wind farm clusters, followed More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Wulfran Fendzi Mbasso1,2, Idriss Dagal3, Manish Kumar Singla4,5,*, Muhammad Suhail Shaikh6, Aseel Smerat7, Abdullah Mohammed Al Fatais8,9, Ali Saeed Almufih8,9, Rabia Emhamed Al Mamlookol10,11
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2026.072751
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Global Intelligent Optimization and Advanced Control of Photovoltaic Systems Under Complex Operating Conditions)
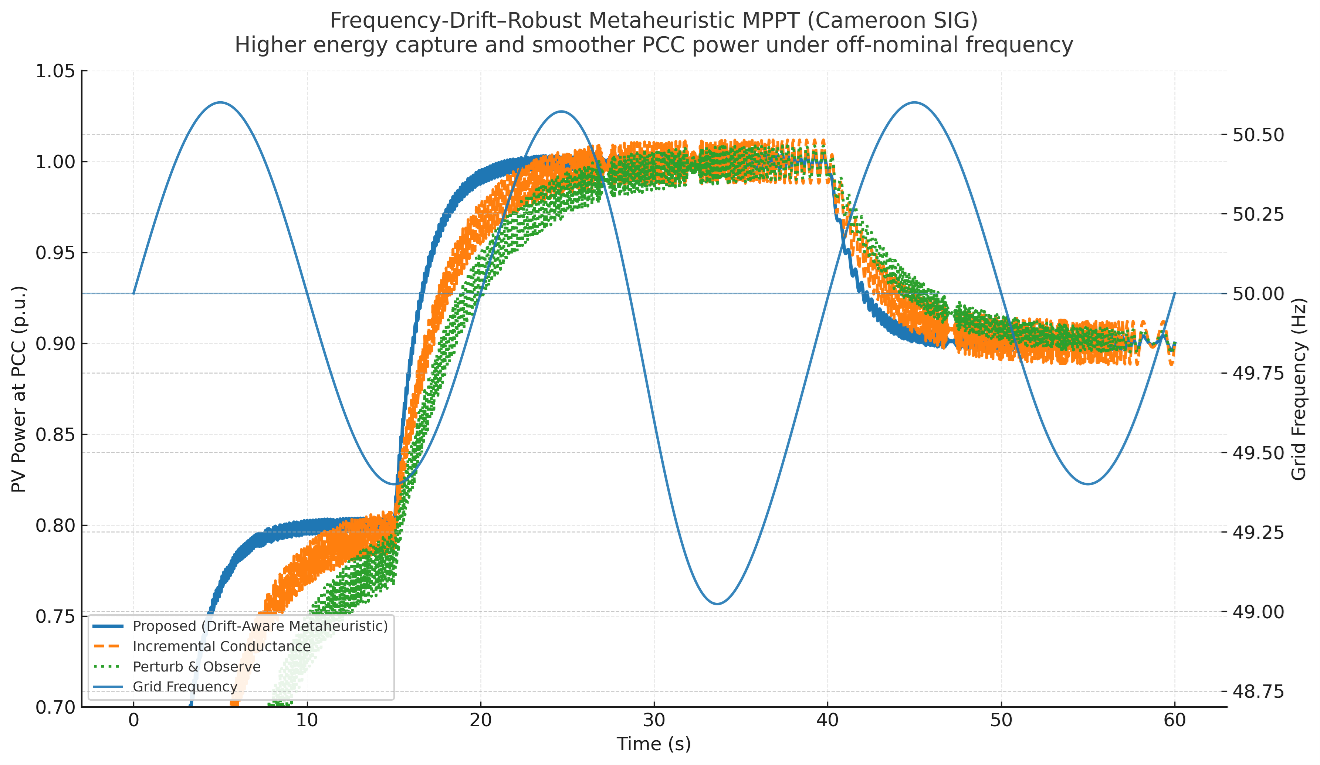
Abstract Photovoltaic (PV) systems in the field operate under complex, uncertain conditions rapid irradiance ramps, partial shading, temperature swings, surface soiling, and weak-grid disturbances including off-nominal frequency and voltage distortion that degrade energy yield and power quality. We propose a drift-aware, power-quality-constrained MPPT framework that co-optimizes MPPT, PLL, and current-loop gains under stochastic frequency drift, while enforcing IEEE-519 limits (per-order Ih/IL and TDD) during optimization. Unlike energy-only or THD-only methods, the design target integrates PQ constraints into the objective and is validated across calibrated drift scenarios with explicit per-order and TDD reporting. Operating scenarios are calibrated to… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Shu Zhou, Wenfeng Yang, Guoxing Wu*, Xinming Jiang, Qingmiao Guo
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.072997
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Renewable Energy and Storage: Harnessing Hydrocarbon Prediction and Polymetric Materials for Enhanced Efficiency and Sustainability)
Abstract The integration of high-penetration distributed photovoltaic (PV) systems in low-voltage (LV) distribution networks introduces significant challenges, including voltage violations, power quality degradation, and coordination difficulties among multiple distributed energy resources. Grid-forming converters with droop control offer autonomous voltage and frequency regulation capabilities, yet conventional fixed-parameter droop strategies perform poorly in resistance-dominant LV networks under variable PV generation conditions. This paper proposes an adaptive droop control method that dynamically adjusts control parameters to address these challenges. The proposed strategy incorporates three key innovations: (1) power-flow-aware adaptive voltage droop coefficients specifically designed for resistance-dominant networks, (2) a… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Zichang Meng, Na Chen, Qi Li, Qingyi Liu, Hongfei Jiang*
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.072848
Abstract Heliostat field design for tower solar thermal plants must jointly address solar geometry, optical losses,and layout optimization under engineering constraints. We develop an end-to-end workflow that (i) adopts a consistentEast–North–Up (ENU) convention for all plant- and sun-related vectors; (ii) integrates cosine efficiency, projectionbased
shading and blocking (SB), atmospheric transmittance, and an HFLCAL (heliostat field local calculation)truncation model into a single optical chain; and (iii) couples an Eliminate-Blocking (EB) layout prior with an improved“Cheetah” metaheuristic to search ring topology, mirror sizes, and heights while enforcing spacing, kinematics, andrated-power requirements. Projection-based SB is calibrated against Monte-Carlo ray… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Rajanand Patnaik Narasipuram1,*, Md M. Pasha2, Suresh Badugu3, Saleha Tabassum4, Attuluri R.Vijay Babu5, Bharath Kumar N5, Amit Singh Tandon6
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2026.076542
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Renewable Energy and Storage: Harnessing Hydrocarbon Prediction and Polymetric Materials for Enhanced Efficiency and Sustainability)
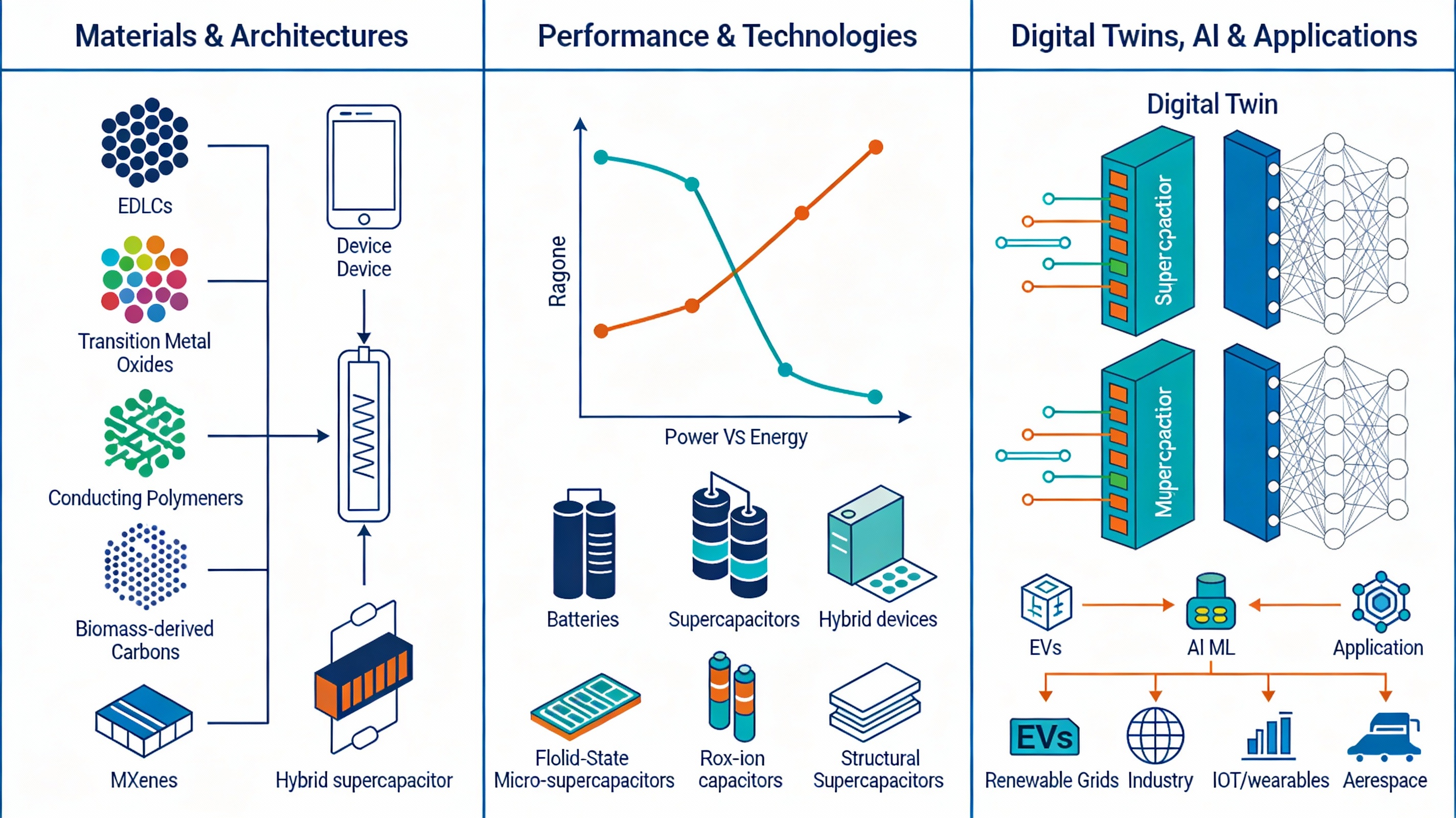
Abstract Supercapacitors are increasingly deployed as high power buffers in modern energy systems, yet their broader impact is constrained by limited energy density, fragmented testing practices, and incomplete understanding of lifecycle implications. This article presents a critical, method driven review based on a structured literature survey and explicit inclusion criteria, aggregating quantitative performance data for major electrode families (carbon materials, transition metal oxides, conducting polymers, biomass derived carbons, MXenes, and hybrid composites), electrolytes (aqueous, organic, ionic liquid, and gel/solid state), and device architectures (flexible, micro, solid state, lithium ion capacitors, and structural supercapacitors) under harmonized metrics… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Mingqi Liu, Ying Wang*, Wujiang Li, Juyong Cao, Fuyong Yang
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2026.074783
Abstract Accurately predicting battery life is essential for performance management and system safety. Due to the complexity and diversity of internal mechanisms in lithium-ion batteries, their nonlinear characteristics directly give rise to uncertainty in the battery degradation process. However, most existing prediction methods do not fully account for the uncertainty caused by various factors and only provide a point estimate finally. To address this issue, this paper proposes a new framework that combines Random Forest and Conformal Prediction to predict battery life and quantify the uncertainty of the results. This approach leverages the efficiency of Random… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Mingxuan Ji1, Jing Gao1,*, Dantian Zhong1, Yingqi Xu1, Shuxiang Yang1, Zhongxiao Du1, Yingming Liu2
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2026.074643
Abstract The intermittency of wind power poses severe challenges to the safe and stable operation of power grids, while conventional forecasting models are deficient in prediction accuracy and adaptability to variable weather conditions. To address these issues, this study proposes an adaptive short-term wind power forecasting model integrating affinity propagation (AP) clustering and a black-winged kite algorithm (BKA)-optimized temporal convolutional network-bidirectional long short-term memory (TCN-BiLSTM) hybrid architecture. First, mutual information was employed to screen key meteorological features, and AP clustering categorized historical data into six distinct weather scenarios. A scenario-specific TCN-BiLSTM model was then constructed for… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Shaymaa Husham Abdulmalek1, Ali Ahmed Gitan2,*, Israa Sami Farhan2, Oras Fadhil Khalaf1, Sayf Waleed Albayati1
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2026.074018
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advancements in Energy Resources and Their Processes, Systems, Materials and Policies for Affordable Energy Sustainability)
Abstract The utilisation of waste in green sustainable technology can provide a clean environment and support energy demand. This work aims to design and analyse the performance of a developed indirect flat-plate Solar Air Heater (SAH) integrated with an internal thermal storage unit using Waste Automotive Oil (WAO). The SAH was designed based on the circulation of confined air around the internal thermal storage unit due to the updraft effects of hot air. Two SAHs were tested to compare the performance of WAO and water, with the results being compared to previous work that utilised phase… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Nan Li1,2,*, Yinan Wang2, Liang Huang3, Yabin Zhu4, Guangyao Zhang5
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.073712
Abstract The large-scale integration of new energy into power systems significantly elevates the risk of instability. To achieve an accurate assessment of power system transient stability, a multi-classification assessment model based on an improved TCN-ResNeXt is proposed. The core of this model lies in a dual-branch structure, which enables the extraction and interactive fusion of dynamic temporal features and spatial features at multiple scales. By integrating the Triplet Attention mechanism, the model enhances focus on key features across the three dimensions of channel, space, and time—effectively boosting the assessment performance of the transient stability multi-classification model.… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Abdin Abdin1, Nicola Bianchi1,*, Andrea Voltan2, Walter Faedo2, Piero Cazzavillan2, Alessandro Biason2
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.073434
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Energy Transition in the Transport Sector: Challenges and Opportunities)
Abstract Synchronous reluctance motors (SynRM) are widely employed in industrial applications due to their high robustness, low cost, and absence of permanent magnets. In recent years, significant research efforts have focused on improving the controllability and efficiency of SynRM. Accurate rotor position information is essential for the controller to generate appropriate current and voltage references corresponding to the desired speed and load torque. Shaft-mounted position sensors are generally undesirable because of their high cost, sensitivity to harsh operating conditions, maintenance requirements, and reduced reliability in environments characterized by high vibration. Consequently, sensorless control techniques that estimate… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Qianfeng Wu1, Dabo Xie1, Wenhua Ni2, Junjie Zhou1, Xuantong Lu1, Chengying Ma1, Rongqiang Li2,*, Yang Li2,*
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2026.073197
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Innovations and Challenges in Smart Grid Technologies)
Abstract With the deepening of the power system reform, an increasing number of microgrids are being integrated into the distribution network. In traditional centralized optimization algorithms, the optimal power flow model of the distribution network and the optimal scheduling model of microgrid clusters are directly coupled and solved simultaneously. This process involves extensive information exchange between the upper distribution network system and the lower microgrid clusters, which not only increases the communication burden but also prolongs computation time and raises computational complexity. Moreover, it requires excessive information sharing, making it difficult to achieve limited information exchange… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Zhengrong Chen1,2,*, Yu Qi2, Maojun Fang2, Bo Wang2, Xin Xie2, Le Sun2, Wei Liu1
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.064770
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Integrated Geology-Engineering Simulation and Optimizationfor Unconventional Oil and Gas Reservoirs)
Abstract The migration, accumulation, and high yield of hydrocarbons in tight sandstone reservoirs are closely tied to the natural fracture systems within the reservoirs. Large-scale fracture networks not only enhance reservoir seepage capacity but also influence effective productivity and subsequent fracturing reconstruction. Given the diverse mechanical behaviors, such as migration, penetration, or fracture arrest, traditional assumptions about fracture interaction criteria fail to address this complexity. To resolve these issues, a global cohesive element method is proposed to model random natural fractures. This approach verifies intersection models based on real-time stress conditions rather than pre-set criteria, enabling… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Guanghua He1, Jinlong Qi1,*, Yao Feng1, Jiayi Han1, Heng Chen2, Baoming Huang3, Jiangtao Li3
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2026.076354
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advanced Analytics on Energy Systems)
Abstract The identification of the traveling wave head is an important factor affecting the accuracy of fault traveling wave positioning. In practice, in addition to the attenuation of traveling wave amplitude and rising speed caused by distribution line factors, various traveling wave sensors can also cause transmission distortion of high-frequency traveling wave signals, which in turn affects the calibration of traveling wave arrival time and the accuracy of fault distance measurement. The inversion technology of sensor transmission characteristics using analytical methods has limited ability to reflect factors such as stray capacitance and sensor differences. In comparison,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yi Pan, Mingshen Wang, Ye Xue, Huiyu Miao, Kemin Dai, Xiaodong Yuan*, Fei Zeng
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.074882
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Sustainable Transport Technologies and Strategies: Impacts on Energy and Environment)
Abstract Electric vehicles (EVs), characterized by their large-scale deployment and flexible charging–discharging scheduling, represent a growing form of transportation. However, their widespread adoption poses considerable challenges to the security and stability of the power grid during peak charging periods, highlighting the need for effective management of the coupled traffic–grid system. To address this issue, this paper proposes a blockchain-driven optimization model for charging scheduling in dynamic traffic networks. Blockchain technology is introduced to ensure data transparency and security in decentralized decision-making. First, a queuing model integrating the Bureau of Public Roads (BPR) function with the M/M/c/K… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Qiang Liu1, Yongqiang Zhou1, Chaoyang Lu2, Zhen Yan1, Yanwen Li1, Gangui Yan2, Yupeng Wang2,*
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.074766
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: New Energy and Energy Storage System)
Abstract Hybrid photovoltaic and energy storage systems play a critical role in enhancing grid stability; however, the sub-synchronous oscillation issues induced by their power electronic interfaces cannot be overlooked. This study proposes a graphical block-based modeling method for a hybrid power generation system composed of grid-following (GFL) photovoltaic and grid-forming (GFM) energy storage units. The method abstracts each system component into graphical modules with clearly defined interfaces, enables intuitive construction in the Matlab/Simulink environment, and utilizes built-in functions to automatically generate global system equations. While ensuring model accuracy, it significantly improves modeling intuitiveness, efficiency, and scalability,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Nantian Huang*, Jingyuan Zhang, Shicheng Ren, Hao Zhang, Bingling Li, Yaoyao Wang
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.072993
Abstract User electricity consumption behavior analysis and multi-load forecasting in integrated energy systems are crucial for system operation and scheduling. Traditional user electricity consumption behavior analysis fails to adequately incorporate meteorological factors, limiting the accuracy of characterizing user electricity consumption patterns. Traditional multi-load forecasting models do not consider the differentiated coupling relationships with meteorological factors across different seasons, which restricts the improvement of forecasting accuracy. To address the above issues, a method integrating data cleaning and meteorological correlation for electricity consumption behavior and multi-dimensional forecasting analysis is proposed. First, the Akima interpolation method is used to… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Lizhong Lu1, Guangze Li2, Zheng Yang2,*, Yunjing Liu1,2, Xiaozhuo Guan1, Tiebin Guo1
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.075585
Abstract With the substantial advancement of the manufacturing industry, a large number of new types of loads are being connected to the distribution network via power electronic devices, exacerbating the deterioration of power quality at the Point of Common Coupling and making harmonic problems increasingly severe. Currently, most researchers focus on improving harmonic suppression performance from the perspective of the controller, but they overlook the fact that excessive performance enhancement may lead to issues such as resonance in the distribution network. To address this, this paper proposes an adaptive harmonic compensation strategy for scenarios with limited… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Jiyuan Liao1, Jiangyan Zhao2,*, Xin Li3, Changmao Liu1, Banghong Tang1, Zihan Ling3
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.074667
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advanced Energy Management and Process Optimization in Industrial Manufacturing: Towards Smart, Sustainable, and Efficient Production Systems)
Abstract To address the uncertainty and volatility of renewable energy while meeting the requirements of low-carbon economic operation, this paper proposes a two-stage robust optimal dispatch model for an integrated wind-solar-hydro-thermal-storage energy system with coupled power-to-gas (P2G) and carbon capture system (CCS). First, a mathematical model of the integrated wind-solar-hydro-thermal-storage energy system with P2G-CCS coupling is developed to promote internal carbon cycling and enhance the capability to accommodate renewable energy. Second, the scheduling problem is formulated as a two-stage robust optimization model. A cardinality-based uncertainty set is adopted to model deviations in renewable energy output, and… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Peng Wang1,2, Zhiying Gao1,2,*, Yongyan Chen1, Rina Su1,2, Yefei Bai2, Jianlong Ma1,2, Tianhao Zhang1
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.073862
Abstract We propose a novel procedure, Time-Domain De-Dopplerized Orthogonal Matching Pursuit deconvolution approach for the mapping of acoustic sources (TD-OMP-DAMAS), for separating aerodynamic noise sources distributed across wind turbine blades (WTB), a task that is typically hindered by mutual interference and spatial mixing. The proposed procedure is a two-stage, hybrid de-Doppler/sparse-reconstruction algorithm based on time-domain de-Doppler (TD, Stage 1) and an orthogonal matching pursuit (OMP)-based deconvolution scheme (Stage 2), enabling sparse-reconstruction techniques to be effectively applied in rotating-source scenarios. The method is validated using both simulated rotating-source data and wind-tunnel measurements, and its performance is systematically… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Zhenjie Yuan, HaiLong Yu*, Hongjun Cao
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.076483
Abstract Low-NOx combustion of natural gas is essential for cleaner industrial heat supply under increasingly strict emission regulations. However, many existing low-NOx swirl burners still rely on single-mechanism control and suffer trade-offs between temperature suppression, combustion stability, and mixing uniformity. This work develops and numerically optimizes a structurally integrated cyclonic-impingement natural-gas burner that combines four rows of impinging secondary-air jets with four axially deflected main fuel nozzles, realizing a coupled swirl-impingement-staging mechanism that differs fundamentally from conventional swirl burners employing only geometric swirl or simple air staging. Validated three-dimensional RANS CFD simulations (realizable k-ε turbulence model,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Lin Chen1, Anqi Zhao2, Yunpei Zhang1, Sai-Mi-La XiaFuKaiTi1, Yao Qin1, Chuan Wang1, Gang Chen2, Jiqiang Li2, Shilai Hu2,*
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.075878
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Progress and Prospects of Hydraulic Fracture Network Morphology Characterization, Flow Simulation and Optimization Technology for Unconventional Oil and Gas Reservoirs)
Abstract The shale oil resources in the Permian Fengcheng Formation of the Mahu Sag exhibit significant potential but are characterized by strong heterogeneity and complex production dynamics, posing challenges for development. This study conducts a comprehensive analysis of the reservoir characteristics and production performance of the shale oil reservoir in the second member of the Fengcheng Formation within the MX Block. Utilizing data from three appraisal wells (M1X, M2X, M3H), we systematically evaluated the geological structural features, sedimentary characteristics, complex mineralogy, and petrophysical properties of the reservoir. The production dynamics of all wells display a multi-stage… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Junwei Zhang1, Pei Liu1, Huihang Li1, Guokang Huang1, Bozheng Yuan1, Wenjing Wei1, Xiaoshun Zhang2,*
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.072462
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Low-Carbon Situational Awareness and Dispatch Decision of New-Type Power System Operation)
Abstract Addressing global climate challenges necessitates urgent low carbon transitions in high energy consuming enterprises (HECEs). This study proposes a comprehensive framework to assess their carbon reduction potential (CRP) by integrating electricity usage behavior analysis and dynamic carbon emission factor (DCEF) prediction. HECEs are classified into “electricity reduction” and “electricity transfer” categories based on load characteristics, enabling tailored optimization strategies. The framework employs machine learning to predict DCEFs, capturing real time variations in grid carbon intensity. A low carbon optimization model is then formulated to minimize emissions while adhering to production requirements and grid constraints, solved… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yueyang Ji1, Yaohui Peng1, Haoran Ji1,*, Xinran Na1, Yuxuan Chen1, Wei Li2, Shengbin Chen2
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.074599
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Digital and Intelligent Planning and Operation Technologies for Flexible Distribution Network)
Abstract With the increasing penetration of distributed generations and continuous growth of loads, traditional rural distribution networks face severe challenges in both hosting capacity and reliability. Addressing these issues requires planning approaches that strike a balance between economic efficiency in infrastructure development and resilience in operation. Considering the dynamic growth of distributed generations and rural loads over the planning horizon, this paper presents a multi-stage expansion planning approach that coordinates flexible interconnection devices (FIDs) with substation and line construction to improve both economic performance and system reliability. The proposed method account for the time-varying growth of… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Xiutai Cao1, Yuxin Sun1, Bowen Shi1, Hao Zhang1, Hongli Tang1, Yongbin Bi1,2, Huiying Zhong1,3,*
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.074439
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Enhanced Oil and Gas Recovery in Unconventional Reservoirs)
Abstract With the steady advancement of China’s “Dual-Carbon” goals, CO2 huff-and-puff technology has become one of the mainstream methods for enhancing oil recovery (EOR) in oilfields. However, differences in sweep radius of CO2, CO2-oil interaction mechanisms, injection parameters, and huff-and-puff modes between conventional heavy-oil and light-oil reservoirs still require further investigation. The NP oilfield consists of an upper heavy-oil zone and a lower light-oil zone, with the reservoir inclined at a certain angle. Taking this oilfield as the study area, a positively rhythmic reservoir geological model was established. A compositional numerical simulation approach was employed to analyze the… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yangjun Zhou1, Chenying Yi1, Wei Zhang1, Juntao Pan2,*, Ke Zhou1, Weixiang Huang1, Like Gao1, Shan Li1, Yuanchao Zhou3, Ling Li2, Liwen Qin1, Hongwen Wu4, Lijuan Yan2
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.073787
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Next-Generation Distribution System Planning, Operation, and Control)
Abstract The increasing integration of distributed generation (DG) and energy storage systems (ESS) has significantly enhanced the flexibility and efficiency of distribution networks. However, the growing frequency of extreme weather events has exposed the vulnerability of distribution lines, posing serious challenges to the reliability and resilience of such systems. Existing DG and ESS planning models often neglect this vulnerability dimension, leading to suboptimal siting decisions and reduced system robustness. To address this issue, this paper proposes a comprehensive multi-objective optimization framework that coordinates the allocation of DG and ESS and explicitly incorporates line vulnerability under extreme… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Xing Wen1, Huan Chen1, Ning Wang1,*, Yu Song1, Zhuqiao Qiao2, Bin Zhang1
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.073567
Abstract High voltage direct current (HVDC) systems play a pivotal role in long-distance, high-capacity, and cross-regional power transmission. However, their complex structure, wide-ranging impact of faults, and stringent safety requirements pose significant challenges to operational stability. Conventional model-based and data-driven methods for tasks such as text classification, fault diagnosis, and operation and maintenance support suffer from limited scalability and interpretability. Recent advances in large language model (LLM) provide new opportunities to address these issues. This paper provides a systematic review of LLM applications in HVDC systems. Firstly, it introduces the core architecture and training mechanisms of… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yingjie Su1, Yubin Qiu2, Zhuojun Dong1, Jiying Liu2,*, Bo Gao1,3,*
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.074454
Abstract In response to the high energy consumption, large load fluctuations, and insufficient adaptability associated with conventional control strategies in industrial park heating and hot water systems, this paper studies a 15,000 m2 factory office building in Jinan as its object of study. A photovoltaic-thermal integrated air-source heat pump system (PVT-ASHP) is developed. This system leverages its hardware parameter co-optimization and intelligent operational strategy control to perform cost reduction and efficiency increase, while focusing on the novel innovative high effectiveness of its operational strategies. The study first employs the Hooke-Jeeves algorithm to optimize key hardware parameters so… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Junjian Wu, Jingliao Sun*, Yejun Xiang, Zhenyu Zhou, Zhengchai Shi
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.073042
Abstract The inherent unpredictability of renewable energy generation poses significant challenges to the reliable and economic dispatch of grid-connected microgrids. In response, this paper proposes a novel robust optimization strategy grounded in uncertain boundary decision-making and enhanced through innovations in the multi-objective cross-entropy method. An uncertainty budget-aware environmental economic dispatch model is first established, integrating photovoltaic and wind power generation. By employing mathematical sophistication—particularly Lagrangian transformation—the proposed method effectively resolves embedded uncertainties, transforming the original model into a deterministic multi-objective optimization framework robust against renewable energy volatility. Furthermore, by incorporating the dynamic operational demands of microgrids, More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Junmin Tang1,*, Yi Ding2, Juzheng Zhu3, Hongbo Zhong3, Yanliang Long4, Shuo Dong5
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.074489
Abstract With the rapid growth of the electric vehicle (EV) population and the development of active distribution networks (DN), the optimal scheduling of power systems that incorporate EVs has become increasingly important. electric vehicle battery swap stations (EVBSS), leveraging their substantial battery resources and suitability for centralized scheduling, offer a new approach for enhancing DN flexibility. Accordingly, this paper proposes a two-stage optimal scheduling method for DN that considers low-carbon demand response and the battery life of EVBSS. The method employs dynamic carbon emission factors as penalty components in time-of-use electricity pricing, thereby transmitting carbon signals… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Ebtehal Chasseb Jbary*, Alaa R. Al-Badri
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.074415
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advancements in Energy Resources and Their Processes, Systems, Materials and Policies for Affordable Energy Sustainability)
Abstract Despite significant advancements in solar collector technology, persistent challenges remain in improving the overall efficiency of solar systems. This paper investigates the use of mini-channel aluminum tubes mounted on the reflective surface as preliminary heating stages to enhance the overall system thermal performance. Experimental assessments were conducted with flow rates ranging from 0.1 to 0.8 LPM and tilt angles of 180° South and 225° Southwest in Al-Kut, Iraq, from 9:00 AM to 2:00 PM. Fluid flows sequentially through five flat aluminum tubes totaling 50 channels, named stage-1, then flows through four aluminum tubes totaling 40… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Lihua Zhong1, Feng Pan1, Yuyao Yang1, Lei Feng1, Jinghe Jiang2, Guo Lin2, Xiaoshun Zhang3,*
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.073240
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Low-Carbon Situational Awareness and Dispatch Decision of New-Type Power System Operation)
Abstract This paper addresses the challenge of efficiently calculating dynamic carbon emission factors (CEFs) in large-scale power systems. Traditional methods that rely on direct matrix inversion are computationally intensive and become impractical for networks with thousands of nodes. To overcome this limitation, a fast and scalable computational framework is proposed based on the incomplete LU (ILU) preconditioned biconjugate gradient stabilized (BiCGSTAB) iterative solver. The proposed approach formulates the nodal CEF model as a sparse linear system and employs Krylov subspace acceleration with ILU preconditioning to enhance convergence and numerical stability. The method is applied to synthetic… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Ximing Zhang1,*, Zhuohuan Li2, Xuexia Quan1, Kai Cheng2, Yang Yu2
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.073912
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Digital and Intelligent Planning and Operation Technologies for Flexible Distribution Network)
Abstract The “N-1” criterion represents a fundamental principle for assessing the reliability of power systems in static security analysis. Existing studies mainly rely on centralized single-agent reinforcement learning frameworks, where centralized control is difficult to cope with regional autonomy and communication delays. In high-dimensional state–action spaces, these approaches often suffer from low efficiency and unstable policies, limiting their applicability to large-scale grids. To address these issues, this paper proposes a Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning (MADRL) method enhanced with Curriculum Learning (CL) and Prioritized Experience Replay (PER). The proposed framework adopts a Centralized Training with Decentralized Execution… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Zemin Liang, Songyu Gao, Qi Yao*
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.072877
Abstract For mixed-integer programming (MIP) problems in new power systems with uncertainties, existing studies tend to address uncertainty modeling or MIP solution methods in isolation. They overlook core bottlenecks arising from their coupling, such as variable dimension explosion, disrupted constraint separability, and conflicts in solution logic. To address this gap, this paper focuses on the coupling effects between the two and systematically conducts three aspects of work: first, the paper summarizes the uncertainty optimization methods suitable for addressing uncertainty-related issues in power systems, along with their respective advantages and disadvantages. It also clarifies the specific forms… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Jiguang Wu1, Qing Zhi2,*, Jin Guan2, Ruopeng Zhang2, Lixia Wu2, Shuhui Zhang2, Caifeng Wen3,4
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.073914
Abstract This paper proposes a hybrid energy storage control method that coordinates the minimum output of the wind–storage system and the SOC self-recovery capability, applied to stand-alone energy storage stations. Under the premise of meeting the wind power smoothing requirements, model predictive control (MPC) is employed to rapidly regulate the SOC and output of the energy storage system during the smoothing process, thereby enhancing its sustained and stable operation capability, and decomposing the original wind power into a direct grid-connected component and a hybrid energy storage smoothing component. Subsequently, the Northern Goshawk Algorithm-Improved Complete Ensemble Empirical… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Hong Zhang1, Bin Xu1, Jinzhong Li1, Xiaoxiao Meng2,*, Cheng Qian2, Wei Ma1, Yuguang Xie1
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.073542
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Operation and Control of Grid-connected New Energy and Emerging Loads)
Abstract The increasing integration of distributed renewable energy sources in the distribution network leads to unbalanced load rates in the distribution network. The traditional load balancing methods are mainly based on network reconfiguration, which have problems such as a long time scale and poor adaptability. In response to these issues, this paper proposes a distributed iterative learning control (ILC) strategy for load balancing in flexible AC/DC hybrid distribution systems. This method combines the consensus algorithm with the ILC mechanism to construct a multi-terminal AC/DC flexible interconnection system model. It is only necessary to measure the load… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Guoqing Li, Jian Lou, Shouqi Jiang*, Yechun Xin, Yanxu Wang, Tuo Wang
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.074947
Abstract To mitigate the frequency stability challenges arising from insufficient system inertia and inadequate damping capacity, a phased active frequency support control strategy for the sending-end grid with collaborative participation of wind power and modular multilevel converter-based high-voltage direct current (MMC-HVDC) is proposed, which realizes flexible mutual support and efficient utilization of multiple frequency regulation units. For wind power, a macro-variable considering frequency and power deviations is constructed based on cooperative control theory, then an adaptive frequency cooperative control method is designed based on rotor speed and pitch angle adjustment, which realizes differentiated utilization of rotor… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Wei Chen, Zhi Wei*, Tingting Pei, Jianghao Zhu, Yang Wu
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.073843
Abstract Wind turbine gearboxes are critical components in large-scale power generation systems, and their unexpected failures often result in significant economic losses, long downtime, and decreased energy efficiency. Accurate prediction of their Remaining Useful Life (RUL) is therefore vital for enhancing operational reliability, implementing condition-based maintenance, and optimizing lifecycle management. However, existing approaches often neglect the memory effect in degradation processes and fail to establish an effective interaction between stochastic degradation modeling and RUL prediction. To address these challenges, this study proposes a novel fusion method that integrates a stochastic degradation model with an intelligent prediction framework.… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Samar Taha Yousif1,2, Firas Basim Ismail1,3,*, Ammar Al-Bazi4, Alaa Abdulhady Jaber5, Sivadass Thiruchelvam1
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.073955
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advancements in Energy Resources and Their Processes, Systems, Materials and Policies for Affordable Energy Sustainability)
Abstract Thermal power plants are the main contributors to greenhouse gas emissions. The prediction of the emission supports the decision makers and environmental sustainability. The objective of this study is to enhance the accuracy of emission prediction models, supporting more effective real-time monitoring and enabling informed operational decisions that align with environmental compliance efforts. This paper presents a data-driven approach for the accurate prediction of gas emissions, specifically nitrogen oxides (NOx) and carbon monoxide (CO), in natural gas power plants using an optimized hybrid machine learning framework. The proposed model integrates a Feedforward Neural Network (FFNN)… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Sheng Lei1,2,3, Guanglong Sheng1,2,3,*, Hui Zhao1,2,3
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.073788
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Progress and Prospects of Hydraulic Fracture Network Morphology Characterization, Flow Simulation and Optimization Technology for Unconventional Oil and Gas Reservoirs)
Abstract Multi-stage fractured horizontal wells are among the most prevalent technologies in contemporary shale oil development. This article provides a comprehensive overview of several prevalent issues by examining pertinent simulation methods applicable to existing fractured horizontal wells. First, traditional methods primarily concentrate on individual stages of fracturing, shut-in, and production. These stages are relatively isolated and lack continuity. Second, the effects of reservoir stimulation vary under different operational conditions. The conventional dual (or multiple) porosity model is overly idealized, while analytical (or semi-analytical) models often struggle to accurately represent actual fracture geometries and internal fracture-grid characteristics,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yun Yu1, Li Lin2,*, Ximing Zhang1, Yang Yu3, Wei Zhang2, Kai Cheng3
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.073445
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Innovations and Challenges in Smart Grid Technologies)
Abstract Traditional transient stability preventive control calculation methods suffer from low computational efficiency, struggling to meet the real-time decision demands of increasingly large-scale power systems. Meanwhile, reinforcement learning-based preventive control approaches, which adopt an “offline training, online application” framework, show greater promise in preventive control. However, they still face challenges such as low computational efficiency in electromechanical transient simulation and insufficient decision robustness. Therefore, this paper proposes a power system predictive control strategy based on Generative Adversarial Proximal Policy Optimization (GA-PPO). Firstly, considering multiple constraints in transient stability operation, a power system preventive control model is… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Chunting Liu1, Xiaozhi Shi1, Juhui Zhu1, Bin Guan1, Subing Wang1, Le He1, Tianjun Qi1, Wenjun Xu2,3,4, Shun Qiu2,3,4,*
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.073233
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Enhanced Oil and Gas Recovery in Unconventional Reservoirs)
Abstract To investigate the long-term fracture conductivity behavior of propped fractures under the high-temperature and high-pressure conditions of deep shale gas reservoirs in the Sichuan Basin, this study systematically analyzed the effects of closure stress, proppant concentration, formation temperature, and proppant size combination. Conductivity experiments were conducted using the HXDL-2C long-term proppant conductivity evaluation system under simulated reservoir conditions to determine the time-dependent evolution of fracture conductivity. The results showed that the 50-h conductivity retention of the rock-plate experiments ranged from 22% to 28%. With increasing closure stress, fracture conductivity exhibited a rapid decline. Under a… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Xingzuo Pan1, Yi Ding2, Zhilong Wei3, Tonglin Liu4, Jianxin Ni5, Yupeng He1,*
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.072849
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Innovative Energy Engineering for Resilient and Green Systems)
Abstract Wind and photovoltaic generation integration into power systems has steadily increased in recent years. To mitigate increasing renewable curtailment and deteriorating operational economics associated with high penetrations of wind and PV, this paper develops a robust optimal scheduling framework for integrated energy systems that integrates waste-heat recovery from power-to-ammonia (P2A) processes and ammonia cofiring as a substitution strategy. First, the energy transfer pathways of electricity–heat, ammonia, and the heat release characteristics of the entire P2A process are analyzed, enabling waste heat recovery throughout the conversion process. Second, considering the low-carbon characteristics of ammonia cofiring in… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Cheng Yang1, Xiuyu Yang1,*, Gangui Yan1, Hongda Dong2, Chenggang Li2
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.072773
Abstract The integration of renewable energy introduces significant uncertainty into daily power system operation scenarios. Traditional deterministic unit commitment methods struggle to adapt to these conditions, often resulting in poor economic performance and high curtailment rates in planning outcomes. To address these challenges, this paper proposes a coordinated thermal power-energy storage planning methodology for managing renewable energy uncertainty. First, the operational effectiveness of daily unit commitment under uncertain renewable energy scenarios is analyzed, with quantitative assessment of how different commitment strategies impact supply-demand balance and economic performance. Subsequently, by conducting flexibility evaluation under multiple renewable energy… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Chenying Yi1, Yangjun Zhou1,2, Wei Zhang1, Like Gao1, Hongwen Wu3, Yuanchao Zhou4,*, Ke Zhou1, Weixiang Huang1, Juntao Pan5, Shan Li1, Bin Feng5
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.073805
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Innovations and Challenges in Smart Grid Technologies)
Abstract Ensuring reliability in distribution networks is essential under increasing operational and economic constraints. Traditional planning models rely on power flow calculations, leading to high computational costs and poor scalability. This study proposes a quantitative decomposition framework that establishes a direct linkage among reliability improvement measures, reliability parameters, and reliability indices, enabling fast and analytical reliability evaluation without power flow analysis. A bi-objective optimization model is developed to minimize both reliability indices (SAIDI) and investment costs, solved using Pareto-based multi-objective PSO combined with the TOPSIS method. Case studies on a 519-node distribution network demonstrate that the More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yifeng Wang1,*, Wei Cui1, Zhihui Wang2, Yanning Xue2, Bing Wang2
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.074707
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Innovative Renewable Energy Systems for Carbon Neutrality: From Buildings to Large-Scale Integration)
Abstract This paper proposes a photovoltaic (PV) output prediction and trading strategy based on fractal theory. Firstly, rescaled range analysis (R/S analysis) is employed to quantify the fractal characteristics of PV output sequences under different weather conditions. By calculating the Hurst exponent and fractal dimension, the self-similarity patterns and complexity differences are revealed. Secondly, a fractal interpolation prediction method based on the iterated function system is constructed to achieve high-precision fitting of typical daily output curves. Finally, by integrating the fractal prediction results, a trading decision-making model aimed at minimizing daily electricity procurement costs is established, More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Tao Wang1, Ze Feng1,*, Jinghao Ma2, Shenhui Chen2, Jihui Zhang2, Tong Wang2
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.074054
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances and Emerging Trends in Photovoltaic Technologies, Energy Storage, and Green Hydrogen)
Abstract This paper develops an MPPT control strategy utilizing the particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm to enhance the tracking accuracy of photovoltaic arrays under complex operating conditions and to mitigate the transient effects on energy storage batteries during grid-connected and off-grid transitions. Initially, the operational principle of the three-phase voltage source PWM converter and the bidirectional DC/DC converter within solar power generation and energy storage systems is carefully examined, leading to the establishment of the appropriate mathematical model. Secondly, a voltage and current double closed-loop control structure utilizing feedforward decoupling is devised to meet the cooperative… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yi Qi1, Yuhao Xie2,*, Zhibing Hu1, Fan Ding1, Junxian Ma3, Liang Zhao3, Shouqi Jiang2
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.073663
Abstract To address the challenges of low inertia support capability and poor frequency stability encountered in the process of power system electronification, this paper designs a coordinated inertia support control strategy for offshore wind power connected to the grid via Modular Multilevel Converter Based High Voltage Direct Current (MMC-HVDC), which enhances the system inertia level and accounts for secondary frequency drop. In terms of inertia support, building on the existing coupling relationship between grid frequency and DC voltage, the influence of wind turbine (WT) rotor speed is further integrated, leading to the proposal of a virtual… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Li Sun, Fanjun Zeng, Hongbo Liu, Chenglian Ma*, Qiting Zhang, Jingzhou Zhu
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.073405
Abstract The widespread integration of large-scale wind power has resulted in decreased equivalent inertia in power systems, thereby compromising their frequency regulation (FR) capabilities. Conventional synthetic inertia control faces challenges under stochastic wind conditions, including inadequate utilization of rotor kinetic energy in high wind condition regions and the risk of triggering rotor speed stability limits in low wind condition regions. To overcome these limitations, in this paper, a parameter adaptive synthetic virtual inertial control (SVIC) framework based on wind speed partition is proposed. The control mechanisms are designed differently across partitioned wind condition intervals: in high-wind-speed More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Xincheng Han1, Hongyan Ma1,2,3,*, Shuo Meng1, Chengzhi Ren1
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.072906
Abstract Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries stand as the dominant energy storage solution, despite their widespread adoption, precisely determining the state of charge (SOC) continues to pose significant difficulties, with direct implications for battery safety, operational reliability, and overall performance. Current SOC estimation techniques often demonstrate limited accuracy, particularly when confronted with complex operational scenarios and wide temperature variations, where their generalization capacity and dynamic adaptation prove insufficient. To address these shortcomings, this work presents a PSO-TCN-Transformer network model for SOC estimation. This research uses the Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) method to automatically configure the architectural parameters of… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Qiang Xu1,*, Leyao Cong1, Jianing Wang1, Xingyu Zhu1, Shaojun Cui1, Guoqiang Sun2, Xueheng Shi2
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.073947
Abstract Power system faults can trigger a massive influx of complex alarm signals to the operation and maintenance center, posing significant challenges for dispatchers in accurately identifying the underlying faults. To address the issues of sample imbalance and low accuracy in traditional power grid monitoring alarm event identification methods, a power grid monitoring alarm event identification method based on BERT large language model is proposed. Firstly, information entropy is employed to filter effective monitoring alarm signals, and the k-means clustering algorithm is used to group all alarm signals into different event types, forming the initial power… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yansen Sun1,2, Yi Ding3, Hualei Cui4, Yuanchao Hui5, Yupeng He1,2,*
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.072860
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Revolution in Energy Systems: Hydrogen and Beyond)
Abstract Integrated energy systems (IES) are pivotal for achieving low-carbon transitions, yet their optimization under carbon constraints remains challenging. This paper proposes an optimal scheduling model for IES that synergistically combines power-to-gas coupled with carbon capture systems (P2G-CCS) and hydrogen-blended natural gas under a tiered carbon trading mechanism. The model innovatively refines the P2G process into two stages (electrolysis and methanation), utilizing methanation reaction heat to enhance efficiency. It further incorporates hydrogen blending into gas turbines and boilers and implements a tiered carbon trading mechanism to constrain emissions. The objective is to minimize total costs, including… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Xian Shi1,2,*, Botao Zhang1,2, Weidong Zhang1,2, Zenghua Ma3, Bo Zhang3, Ahmad Ramezanzadeh4, Bin Li5, Jian Mao5
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.073586
Abstract To investigate the mechanism governing the continuous decline in fracture conductivity of unconsolidated sandstone reservoirs post-hydraulic fracturing, this study centers on the synergistic effects of two key mechanisms—particle migration and proppant embedment. Through the integration of laboratory experiments and computational fluid dynamics-discrete element method (CFD-DEM) coupled numerical simulations, this study systematically examines the influence patterns of varying closure pressures, particle concentrations, fluid properties, and proppant parameters on fracture conductivity. The experimental results demonstrate that particle migration induces pore blockage within the proppant packing layer. When the fines mass concentration reaches 10%, fracture conductivity is almost… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Taotao Zhu, Pai Pang, Yang Wang*
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.073516
Abstract Frequent extreme weather events and the increasing popularity of renewable energy have exacerbated the frequency spatiotemporal imbalance in the new power system. To address these issues, this paper proposes a collaborative optimization strategy for virtual inertia spatiotemporal distribution replenishment, aiming to enhance nodal frequency stability through targeted virtual inertia allocation. This strategy integrates the nodal inertia characteristics with frequency response dynamics to establish a spatiotemporal quantitative model for evaluating the equivalent inertia distribution across nodes, thereby overcoming the limitations of conventional global inertia assessments. Furthermore, by implementing differentiated virtual inertia supplementation from renewable energy power More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Jian Wang1, Gongqiang Yang1,*, Yufeng Sun2, Gangui Yan1, Jie Long3
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.072828
Abstract Given that the power grid partitioning method relying mainly on line reactive power flow information sees frequent changes in partitioning results with reactive power flow fluctuations under high-proportion fixed-power-factor PV-connected distribution networks, and traditional distributed PV collaborative optimization fails to adapt due to such changes, a stable partitioning and distributed PV collaborative optimization method for this scenario is proposed. Firstly, the Gaussian mixture model (GMM) is used to characterize the characteristics of PV reactive power output, obtaining the typical curve of PV reactive power output. Secondly, the Monte Carlo Simulation (MCS) probabilistic power flow calculation… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Wenfei Yi1, Mingzhong Zheng1, Jiayi Wang2, Hao Yang2,*, Zhenglong Sun2
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.072770
Abstract With the growing integration of renewable energy sources (RESs) and smart interconnected devices, conventional distribution networks have turned to active distribution networks (ADNs) with complex system model and power flow dynamics. The rapid fluctuation of RES power may easily result in frequent voltage violation issues. Taking the flexible RES reactive power as control variables, this paper proposes a two-layer control scheme with Koopman wide neural network (WNN) based model predictive control (MPC) method for optimal voltage regulation and network loss reduction. Based on Koopman operator theory, a data-driven WNN method is presented to fit a… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Hongbo Sun1, Xingyu Jiang1,*, Wenyao Sun1, Yi Zhao1, Jifeng Cheng2, Xiaoyi Qian1, Guo Wang3
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.073012
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Renewable Energy Systems: Integrating Machine Learning for Enhanced Efficiency and Optimization)
Abstract The accuracy of photovoltaic (PV) power prediction is significantly influenced by meteorological and environmental factors. To enhance ultra-short-term forecasting precision, this paper proposes an interpretable feedback prediction method based on a parallel dual-stream Temporal Convolutional Network-Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (TCN-BiLSTM) architecture incorporating a spatiotemporal attention mechanism. Firstly, during data preprocessing, the optimal historical time window is determined through autocorrelation analysis while highly correlated features are selected as model inputs using Pearson correlation coefficients. Subsequently, a parallel dual-stream TCN-BiLSTM model is constructed where the TCN branch extracts localized transient features and the BiLSTM branch captures long-term… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Zhixiang Zhang1, Chao Luo2, Chen Zhang1,*, Zheng Li1, Yihua Zhu2, Xu Cai1
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.072678
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Trends of Offshore Wind Technologies: Support Structure Design, Health monitoring, HVDC transmission, Control and Optimization)
Abstract Fatigue loads on wind turbines are critical factors that significantly influence operational lifespan and reliability. The passive yaw control of wind turbines often fails to capture the dynamic gradient changes of wind speed and direction in the wind field, leading to an increased risk of load overload, severely affecting operational lifespan and reducing power generation efficiency. This impact is even more pronounced during the passage of a cold front. To address this issue, this paper proposes an independent variable-pitch control method that optimizes predictions by utilizing the spatiotemporal relationship between pre-observed cold front patterns and… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Huiyong Yu1, Haifu Li1, Liwei Zhang1, Yong Chen1, Rui Wang1, Qiyong Xiong1, Xuyang Guo2, Shijie Shen2,*
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.072416
Abstract Re-fracturing horizontal wells is a critical strategy for enhancing recovery from tight oil reservoirs, but its success depends on the evaluation of candidate wells and locations. This process is complicated by production-induced alterations in reservoir pressure and geomechanical responses. This study introduces a workflow to evaluate re-fracturing potential by integrating coupled fluid flow and geomechanical modeling for the production of initial hydraulic fractures. We developed a numerical model that simulates the poroelastic response of a tight oil reservoir to depletion from an initial set of hydraulic fractures. To quantify the re-fracturing potential along the horizontal… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Qiang Liu1, Yongqiang Zhou1, Chaoyang Lu2, Zhen Yan1, Gangui Yan2, Cheng Yang2,*, Yupeng Wang2
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.073028
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: New Energy and Energy Storage System)
Abstract The increasing proportion of power generated by new energy has meant that grid-forming energy storage has become a key method for improving power grid flexibility. However, the small disturbance stability problem has become an important challenge. The issue is that grid-forming energy storage is prone to low-frequency oscillation under strong grid conditions. Therefore, this study proposes a multi damping torque model to analyze the small signal stability of grid-forming energy storage converters. The impact of grid strength, operating conditions, and control parameters on the damping characteristics of the low-frequency oscillation by the system was quantitatively More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Haifeng Li1, Xiao Li1, Yuchen Hao1, Tao Jin1, Yi Cao1, Yan Yang2, Zheng Wang2, Yuze Zhou2, Yao Zou3,*
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.072787
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Operation and Control of Grid-connected New Energy and Emerging Loads)
Abstract The increasing penetration of renewable energy sources (RES) imposes stringent flexibility requirements on thermal power units (TPUs). Integrating molten salt thermal storage systems (MSTS) and thermal-electric coupling technologies into TPUs has the potential to improve their operational flexibility and regulation capability. However, existing research seldom investigates the combined effects of MSTS retrofitting and thermal-electric output coupling on short-term dispatchability, especially under rapid load variation conditions. This study proposes a comprehensive modeling and multi-timescale optimization framework for MSTS-retrofitted TPUs with rapid load variation capability, enabling coordinated thermal and electrical dispatch in both day-ahead and real-time stages.… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Cuihong Wen1, Jingjing Wen1, Qinyue Zhang1, Yeting Wen2, Fanyong Cheng3,*
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.071911
Abstract Air conditioning is a major energy-consuming component in buildings, and accurate air conditioning load forecasting is of great significance for maximizing energy utilization efficiency. However, the deep learning models currently used in the field of air conditioning load forecasting often suffer from issues such as distribution bias in load data and insufficient expression ability of nonlinear features in the model, which affect the accuracy of load forecasting. To address this, this paper proposes a novel load forecasting model. Firstly, the model employs the Dish-TS (DS) module to standardize the input window data through self-learning standardized… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Qian Yang1, Shenglei Du1,2, Boyang Chen1, Yalu Sun1, Ding Li1, Zhiheng Zhang3,*
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.073720
Abstract In recent years, as the core infrastructure of the digital economy, data centers have witnessed increasingly prominent issues of energy consumption and carbon emissions. To achieve the goals of “carbon peak” and “carbon neutrality”, data centers have gradually introduced new energy power such as wind and photovoltaic power. However, the randomness and volatility of their output pose challenges to efficient absorption. Based on the spatiotemporal complementary characteristics of new energy output in multiple data centers and the spatiotemporal migration capability of computing tasks, this paper proposes a new energy-aware adaptive collaborative scheduling strategy for computation… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Man Zhang1, Cheng Chen1, Hai-Xia Guo1, Yi-Ming Xiao1, Xin-Jian Zhao2,*
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.071943
Abstract Traditional oilfields face increasing extraction challenges, primarily due to reservoir quality degradation and production decline, which are further exacerbated by volatile international crude oil prices—illustrated by Brent Crude’s trajectory from pandemic-induced negative pricing to geopolitically driven surges exceeding USD 100 per barrel. This study addresses these complexities through an integrated methodological framework applied to medium-permeability sandstone reservoirs in the Xinjiang oilfield by combining advanced numerical simulations with multivariate regression analysis. The methodology employs Latin Hypercube Sampling (LHS) to stratify geological parameter distributions and constructs heterogeneous reservoir models using Petrel software, rigorously validated through historical production… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Xuming Hu1, Nan Hu1, Na Li1, Xinsong Zhang2, Xiaocen Xue2, Xiuyong Yu2,*
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.071728
Abstract The dense integration of residential distributed photovoltaic (PV) systems into three-phase, four-wire low-voltage (LV) distribution networks results in reverse power flow and three-phase imbalance, leading to voltage violations that hinder the growth of rural distributed PV systems. Traditional voltage droop-based control methods regulate PV power output solely based on local voltage measurements at the point of PV connection. Due to a lack of global coordination and optimization, their efficiency is often subpar. This paper presents a centralized coordinated active/reactive power control strategy for PV inverters in rural LV distribution feeders with high PV penetration. The… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Zezhong Liu, Jinyu Guo, Xingxu Zhu*, Junhui Li
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.072679
Abstract With the increasing penetration of renewable energy, the coordination of energy storage with thermal power for frequency regulation has become an effective means to enhance grid frequency security. Addressing the challenge of improving the frequency regulation performance of a thermal-storage primary frequency regulation system while reducing its associated losses, this paper proposes a multi-dimensional cooperative optimization strategy for the control parameters of a combined thermal-storage system, considering regulation losses. First, the frequency regulation losses of various components within the thermal power unit are quantified, and a calculation method for energy storage regulation loss is proposed,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Xu Liu*, Hongsheng Su
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.072246
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Integration of Hybrid Renewable Energy Systems for Sustainable Development)
Abstract Further investigation is warranted into the collaborative function of carbon capture and electrolysis-to-gas conversion technologies within integrated electro-gas energy systems, as well as optimized scheduling that addresses the variability of wind and solar energy, to promote multi-energy complementarity and energy decarbonization while enhancing the capacity to absorb new energy. This work presents an optimized scheduling model for electro-gas integrated energy systems that include hydrogen storage, utilizing information gap decision theory (IGDT). A model is constructed that integrates the synergistic functions of carbon capture and storage (CCS), power-to-gas (P2G), and gas turbine units through electrical coupling.… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yutao Xu1, Zukui Tan1, Xiaofeng Gu1, Zhuang Wu2, Jikai Li2,*, Qihui Feng1
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.071243
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Construction and Control Technologies of Renewable Power Systems Based on Grid-Forming Energy Storage)
Abstract Flexibly interconnected distribution networks (FIDN) offer improved operational efficiency and operational control flexibility of power distribution systems through DC interconnection links, and have gradually become the main form of distribution networks. Aiming at the impact of constant power loads and converter transmission power variations in FIDN system stability, this paper presents an impedance reshaping based stability analysis and stabilization control to enhance the stability of the interconnected system and improve the system’s dynamic load response capability. Firstly, a small-single based equivalent impedance model of FIDN system, which consists flexibly interconnected equipment, energy storage, PV units,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Song Zhang, Yang Yu*, Shuguang Li, Xue Li
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.072333
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Grid Integration of Intermittent Renewable Energy Resources: Technologies, Policies, and Operational Strategies)
Abstract Thermal storage electric heating (TSEH), as a prevalent variable load resource, offers significant potential for enhancing system flexibility when aggregated into a cluster. To address the uncertainties of renewable energy and load forecasting in active distribution networks (ADN), this paper proposes a multi-timescale coordinated optimal dispatch strategy that incorporates TSEH clusters. It utilizes the thermal storage characteristics and short-term regulation capabilities of TSEH, along with the rapid and gradual response characteristics of resources in active distribution grids, to develop a coordinated optimization dispatch mechanism for day-ahead, intraday, and real-time stages. It provides a coordinated optimized… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Lei Su1,2,3, Wanli Feng1,2,3, Cao Kan1,2,3, Mingjiang Wei1,2,3, Jihai Wang4, Pan Yu4, Lingxiao Yang5,*
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.071006
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Grid Integration of Intermittent Renewable Energy Resources: Technologies, Policies, and Operational Strategies)
Abstract To address the high costs and operational instability of distribution networks caused by the large-scale integration of distributed energy resources (DERs) (such as photovoltaic (PV) systems, wind turbines (WT), and energy storage (ES) devices), and the increased grid load fluctuations and safety risks due to uncoordinated electric vehicles (EVs) charging, this paper proposes a novel dual-scale hierarchical collaborative optimization strategy. This strategy decouples system-level economic dispatch from distributed EV agent control, effectively solving the resource coordination conflicts arising from the high computational complexity, poor scalability of existing centralized optimization, or the reliance on local information… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yibin Guo1, Lingxiao Ye1,*, Xiang Wang1, Di Wu1, Zirong Wang1, Hao Wang2
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.072163
Abstract Accurate forecasting of crude oil futures prices is crucial for understanding global energy market dynamics and formulating effective macroeconomic and energy strategies. However, the strong nonlinearity and multi-scale temporal characteristics of crude oil prices pose significant challenges to traditional forecasting methods. To address these issues, this study proposes a hybrid CEEMDAN–HOA–Transformer–GRU model that integrates decomposition, complexity analysis, adaptive modeling, and intelligent optimization. Specifically, Complete Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition with Adaptive Noise (CEEMDAN) is employed to decompose the original series into multi-scale components, after which entropy-based complexity analysis quantitatively evaluates each component. A differentiated modeling strategy… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Xuan Ruan1, Han Yan2, Donglin Hu1, Min Zhang2, Ying Li1, Di Hai1, Bo Yang3,*
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.071166
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Grid Integration of Intermittent Renewable Energy Resources: Technologies, Policies, and Operational Strategies)
Abstract An optimized volt-ampere reactive (VAR) control framework is proposed for transmission-level power systems to simultaneously mitigate voltage deviations and active-power losses through coordinated control of large-scale wind/solar farms with shunt static var generators (SVGs). The model explicitly represents reactive-power regulation characteristics of doubly-fed wind turbines and PV inverters under real-time meteorological conditions, and quantifies SVG high-speed compensation capability, enabling seamless transition from localized VAR management to a globally coordinated strategy. An enhanced adaptive gain-sharing knowledge optimizer (AGSK-SD) integrates simulated annealing and diversity maintenance to autonomously tune voltage-control actions, renewable source reactive-power set-points, and SVG output.… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Xueting Cheng1, Rui Xu2,*, Liming Bo1, Cheng Liu2, Huiping Zheng1, Zhichong Cao2
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.072350
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Renewable Energy Systems: Integrating Machine Learning for Enhanced Efficiency and Optimization)
Abstract To address the issue of transient low-voltage instability in AC-DC hybrid power systems following large disturbances, conventional voltage assessment and control strategies typically adopt a sequential “assess-then-act” paradigm, which struggles to simultaneously meet the requirements for both high accuracy and rapid response. This paper proposes a transient voltage assessment and control method based on a hybrid neural network incorporated with an improved snow ablation optimization (ISAO) algorithm. The core innovation of the proposed method lies in constructing an intelligent “physics-informed and neural network-integrated” framework, which achieves the integration of stability assessment and control strategy generation.… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yongjun Xiao1, Yuduo Sun2,*, Jian Zheng1, Xiaojin Zhou3, Wang Liu1, Cheng Shen2, Qi Deng2, Hao Zhao4
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.070942
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Enhanced Oil and Gas Recovery in Unconventional Reservoirs)
Abstract The shale gas development in China faces challenges such as complex reservoir conditions and high development costs. Based on the pore pressure and geostress coupling theory, this paper studies the geostress evolution laws and fracture network characteristics of shale gas infill wells. A mechanism model of CN platform logging data and geomechanical parameters is established to simulate the influence of parent well’s production on the geostress in the infill well area. It is suggested that with the increase of production time, normal fault stress state and horizontal stress deflection will occur. The smaller the parent… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Xiaoya Chen1, Chao Zhang1,*, Xufeng Yuan1, Wei Xiong1, Zhiyang Lu1, Huajun Zheng1, Yutao Xu2, Zhukui Tan2
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.070996
Abstract To address the issues of high costs and low component utilization caused by the independent configuration of hybrid DC circuit breakers (HCBs) and DC power flow controllers (DCPFCs) at each port in existing DC distribution networks, this paper adopts a component sharing mechanism to propose a composite multi-port hybrid DC circuit breaker (CM-HCB) with DC power flow and fault current limitation abilities, as well as reduced component costs. The proposed CM-HCB topology enables the sharing of the main breaker branch (MB) and the energy dissipation branch, while the load commutation switches (LCSs) in the main… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Jian Wu*, Xiaowei Hao, Chao Han
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.071023
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Innovations and Challenges in Smart Grid Technologies)
Abstract Owing to the development of communication technologies and control systems, the integration of numerous Internet of Things (IoT) nodes into the power grid has become increasingly prevalent. These nodes are deployed to gather operational data from various distributed energy sources and monitor real-time energy consumption, thereby transforming the traditional power grid into a smart grid (SG). However, the openness of wireless communication channels introduces vulnerabilities, as it allows potential eavesdroppers to intercept sensitive information. This poses threats to the secure and efficient operation of the IoT-driven smart grid. To address these challenges, we propose a… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Min Liu1,*, Zhengxiong Lu2,*
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.071144
Abstract The accurate state of health (SOH) estimation in lithium-ion batteries represents a critical technological challenge with profound implications for electric vehicle performance and user experience. Precise SOH assessment not only enables reliable mileage prediction but also ensures operational safety. However, the complex and non-linear capacity fading process during battery cycling poses a challenge to obtaining accurate SOH. To address this issue, this study proposes an effective health factor derived from the local voltage range during the battery charging phase. First, the battery charging phase is divided evenly with reference to voltage intervals, and an importance… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Wan Chen1, Zhi Liu1, Yingxue Ma1, Cuicui Wang2, Xinfa Gu1, Baolian Liu1, Lei Shen3, Hui Huang1, Jie Ji1,*
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.069764
Abstract In order to solve the problems of slow dynamic response and difficult multi-source coordination of solar electric vehicle charging stations under intermittent renewable energy, this paper proposes a hardware-algorithm co-design framework: the T-type three-level bidirectional converter (100 kHz switching frequency) based on silicon carbide (SiC) MOSFET is deeply integrated with fuzzy model predictive control (Fuzzy-MPC). At the hardware level, the switching trajectory and resonance suppression circuit (attenuation resonance peak 18 dB) are optimized, and the total loss is reduced by 23% compared with the traditional silicon-based IGBT. At the algorithm level, the adaptive parameter update… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Zhukui Tan1, Dacheng Zhou1, Song Deng1, Jikai Li2,*, Zhuang Wu2, Qihui Feng1, Xuan Zhang1
Energy Engineering, DOI:10.32604/ee.2025.069610
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Construction and Control Technologies of Renewable Power Systems Based on Grid-Forming Energy Storage)
Abstract This paper presents an optimal operation method for embedded DC interconnections based on low-voltage AC/DC distribution areas (EDC-LVDA) under three-phase unbalanced compensation conditions. It can optimally determine the transmission power of the DC and AC paths to simultaneously improve voltage quality and reduce losses. First, considering the embedded interconnected, unbalanced power structure of the distribution area, a power flow calculation method for EDC-LVDA that accounts for three-phase unbalanced compensation is introduced. This method accurately describes the power flow distribution characteristics under both AC and DC power allocation scenarios. Second, an optimization scheduling model for EDC-LVDA… More >