DOI:10.32604/cmc.2022.026197

| Computers, Materials & Continua DOI:10.32604/cmc.2022.026197 |  |
| Article |
Embedded Coded Relay System for Molecular Communications
1Department of Electrical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Minia University, Minia, Egypt
2Department of Electronics and Electrical Communications, Faculty of Electronic Engineering, Menoufia University, Menoufia, Egypt
3Department of Informatics, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences, University of Oslo (UiO), Norway
4Computer Science Department, Community College, King Saud University, Riyadh, 11437, Saudi Arabia
5Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Engineering & Technology, Peshawar, 814, Pakistan
6Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, 34134, Korea
*Corresponding Author: Ki-Il Kim. Email: kikim@cnu.ac.kr
Received: 17 December 2021; Accepted: 24 January 2022
Abstract: With the emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic, the World Health Organization (WHO) has urged scientists and industrialists to explore modern information and communication technology (ICT) as a means to reduce or even eliminate it. The World Health Organization recently reported that the virus may infect the organism through any organ in the living body, such as the respiratory, the immunity, the nervous, the digestive, or the cardiovascular system. Targeting the abovementioned goal, we envision an implanted nanosystem embedded in the intra living-body network. The main function of the nanosystem is either to perform diagnosis and mitigation of infectious diseases or to implement a targeted drug delivery system (i.e., delivery of the therapeutic drug to the diseased tissue or targeted cell). The communication among the nanomachines is accomplished via communication-based molecular diffusion. The control/interconnection of the nanosystem is accomplished through the utilization of Internet of bio-nano things (IoBNT). The proposed nanosystem is designed to employ a coded relay nanomachine disciplined by the decode and forward (DF) principle to ensure reliable drug delivery to the targeted cell. Notably, both the sensitivity of the drug dose and the phenomenon of drug molecules loss before delivery to the target cell site in long-distance due to the molecules diffusion process are taken into account. In this paper, a coded relay NM with conventional coding techniques such as RS and Turbo codes is selected to achieve minimum bit error rate (BER) performance and high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), while the detection process is based on maximum likelihood (ML) probability and minimum error probability (MEP). The performance analysis of the proposed scheme is evaluated in terms of channel capacity and bit error rate by varying system parameters such as relay position, number of released molecules, relay and receiver size. Analysis results are validated through simulation and demonstrate that the proposed scheme can significantly improve delivery performance of the desirable drugs in the molecular communication system.
Keywords: Molecular communication; nanonetwork; internet of bio-nano things; coded relay scheme; coding
Nanoscale communication is a new research area in communications engineering. It is considered a new communication network paradigm between macro, micro, and/or nanodevices (namely nanomachines). Inherent to the communications scenario, the concept of nanomachines is introduced in the communication world. The nanonetwork consists of interconnected nanomachines performing the information exchange work. Nano-machines are capable of implementing simple functions like computing, storage, and driving data. The concept of nanonetwork-based nanomachines has appeared in medical applications, wherein nanomachines can be used to deliver drugs to cells through emission, propagation, and reception of drug information molecules in the Advanced Targeted Nanomedicine (ATN) system [1]. Additionally, they can perform more complex tasks such as encoding, decoding, and error correction/detection according to cooperative property. Moreover, nanotechnology has recommended that nanoscale communication can be performed by molecular communica-tions technology. Molecular communication (MC) system utilizes molecules (bio-chemical signals over multiple scales), to encode, transmit and receive molecular information among a group of macro, micro, and nanodevices [2]. Thereby, it is bio-inspired communication that enables macro, micro, and nanodevices to interconnect. The importance of the MC system aims to gain new insights into modeling the biological systems as well as introducing the interface with the macro networks such as the Internet. More importantly, targeting the development of techniques to control the nanodevices performing specific functions. A very widely-used paradigm, which represents the network engineering, is the Internet of bio-nano things (IoBNT). This paradigm stems from the artificial biology and nanotech¬nology tools that allows the engineering of biologically-embedded devices [3]. It can sustain novel Internet of Things (IoT) applications, such as intra-body sensing, actuation networks, health monitoring, health-care and targeted therapy [4]. The IoBNT also enables an interface to the electrical domain of the Internet.
Molecular Communication via Diffusion (MCvD), is one of the most popular methods explored in the literature. In MCvD, the molecules released by the transmitter nanomachine in a fluid medium, randomly walk in all directions without any more infrastructure via diffusion. Therefore, a number of molecules may reach the receiver nanomachine or not due to the nature of the random diffusion process, particularly when the distance between the transmitter and the receiver is long. However, in flow-based diffusion, the molecules are confined in the microfluidic channels such as blood vessels [5]. On the other hand, the information can be conveyed from transmitter-based mobility to receiver (such as proteins) by using active molecular communications. Consequently, MC experiences high propagation delay as a proportion to the square of the distance between the transmitter and the receiver nanomachines. Additionally, the molecular concentration is inversely proportional to the cubic power of the distance between the transmitter and the receiver nanomachines. Such characte¬ristics result in communication deterioration and unreliability between the transmitter and the receiver nanomachines. Such challenges can be mitigated by adopting the relay capability in wireless communication. Particularly the relay signaling can be found in biological systems such as the nervous system and quorum sensing in bacteria [6].
Some research efforts have been devoted to MC with relays. In [7], the authors use the relay node to decode the incoming signal and forward it to the receiver. Different types of molecules are used and the Maximum a Posteriori (MAP) detection method is employed at the receiver. The authors of [8] used relay schemes in MCVD communication systems using different types of molecules twofold. In the former case, the receiver uses only molecules which originate from the relay node and ignores molecules from the transmitter. In the latter, the receiver considers both molecules received from the transmitter and the relay node. An estimate and forward (EF) relaying scheme was adopted in [9] to enhance the system performance between two hops under the influence of both residual and counting noise. Quadruple Concentration Shift Keying (QCSK) modulation is employed. In this scheme, the signal is encoded into the four-level concentrations of molecules emitted by nano-machines. Amplify and forward relay scheme are investigated in [10], accompanied by performance analysis of signal detection schemes, by mean square error detection, maximum posterior probability detection, and minimum error probability (MEP) detection. In [11], another relay scheme was presented on the foundation of the DF strategy to ensure a high transmission rate in addition to enhanced BER performance by means of analytical equation. For the benefits of coding techniques, the coding protocols in [12] have been adopted in diffusion-based MC systems with energy consumption constraints and a relevant mathematical framework. Different Error correction codes were considered to improve the transmission performance of molecular communications, An RS coding technique has been used in [13] to improve the system BER performance and derive an analytical solution for the bit error probability of the diffusion-based MC system with the full absorption receiver. In addition, the Hamming code is exploited in [14] to enhance the MC system performance taking into account the energy budget of error correction codes.
With the emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic, WHO has urged scientists and industrialists to use modern information and ICT to find appropriate solutions that may help eliminate this epidemic. The WHO recently reported that the virus may taint/enter any organ in the living body, such as the respiratory system, immune system, nervous system, digestive system, and cardiovascular system. On the grounds of the previous, we envision an implanted nanosystem inside the intra living-body network. The main function of the nanosystem may be diagnosis and mitigation of infectious diseases or targeted drug delivery (i.e., delivery of the therapeutic drug to the diseased tissue or targeted cell). The nanosystem consists of a group of bio-nanomachines. The bio-nanomachine is able to perform specific tasks such as sensing, storing, computing and encoding, error detection and correction. We can employ a modern technology such as IoBNT to enable the interconnection among such bio-nanomachines, and thus perform complex tasks. The illustration example of the IoBNT is given in Fig. 1. Moreover, the IoBNT is able to perform the connectivity control among the nanomachines inside the nanosystem as well as perform control for the therapeutic drug side effects. The interconnection between the IoBNT and the nanosystems is accomplished by the promising MC technology. On the other hand, the applications of targeted drug delivery and health monitoring require robust and reliable communication channels. In order to improve the reliability of the transmitted data among the nanomachines and over the biological network, coding techniques should be utilized within the MC system. Additionally, the MC is only suitable for very short transmission ranges (in nanometer), as in microtubule or via diffusion from the extracellular to intracellular through the cytosol of the cell. Therefore, increasing the distance between the bio-nanomachines increases the propagation delay, and thus deteriorates the performance of the proposed nanosystem. Additionally, the variations of inter-arrival times of receiving molecules at the DX, cause ISI between the received bit information. Therefore, the IoBNT makes use of the relay theory to enable MC for medium to large transmission ranges in (micrometer).

Figure 1: The illustration of internet of biological nano things-based nano-system
In this paper, unlike other papers, an embedded coded relay scheme with Turbo or RS code is used for extending the communication distance in reliable diffusion-based MC. It is introduced as a treatment method for effectively delivering drug molecules to diseased cells by using IoBNT technology. This is accomplished by an embedded nanomachine network near the diseased cell to avoid the distribution of drugs in the whole body. The main contributions of this paper are as follows:
• Establishing a channel model of diffusion-based DF relay scheme in MC systems with CSK
• Using an Error Correction Code (ECC) scheme to ensure reliable channel communication
• Considering the ISI from previous time slots and channel noise
• Deriving an analytical expression for BER with ML, and MEP for the diffusion-based DF relay in MC systems
• Studying the effect of key factors, such as the number of released molecules, the receiving radius, and the relay position on channel performance.
The remainder of this article is organized as follows. The system model is presented in Section 3. The proposed coded relay scheme is presented in Section 4. Detection schemes and corresponding theoretical performance analysis are studied in Section 5. Numerical results are analyzed in Section 6 whereas in the final Section 7 conclusions are drawn.
We consider a nanosystem consisting of three bio-nanomachines, namely nanotransmitter (TX), nanorelay (RX) and nanoreceiver (DX). It is implanted inside the living body close to the targeted tissue (diseased cell) as shown in Fig. 1. We assumed that the TX is a point source, while the DX is a full absorber sphere with radius rr. Additionally, we assume that the RX is an intermediate nanomachine located between TX and DX in a three-dimensional (3D) medium. The structure of the proposed nanosystem is illustrated in Fig. 2. TX releases the therapeutic drug molecules (information molecule), IM, into the medium immediately after receiving a command from the IoBNT through the biocyber interface. The IMs move according to the Brownian motion, and thus IMs diffuse randomly in the medium. The noise coming from the variation of the Temperature (Tp) and PH inside the human body or from the chemical reactions, is taking into consideration. The IMs, represented by bit symbols, are encoded by TX with different concentration levels, i.e., concentration shift keying (CSK) scheme. According to the Brownian motion of IMs, the symbol may arrive in a delayed fashion, and thus may cause incorrect symbol detection i.e., ISI issue. Also, we consider two levels of molecule concentration represented in a binary form of 0's and 1's, and it is referred to as On-Off keying (OOK). Moreover, we consider the RX includes an Error correction code (ECC) memory, and thus uses a Decode-and-Forward (DF) discipline to reduce the bit error rate in the received signal over such a noisy and ISI channel.

Figure 2: Proposed nanosystem model-based relaying scheme
The drug molecules (i.e., IM) released from TX start to randomly diffuse inside a medium according to Fick's law of diffusion. After certain period of time, some drugs are absorbed by DX, while others not. Therefore, we can express the concentration of drug molecules starting from the origin at distance d and time t as follows [15]:
where d represents the distance from the TX to the destination node. d is equal to
As soon as the IMs hit the RX, the molecule is received and removed from the medium. This process is referred to as the hitting or capture process. The capture probability density function (PDF) can be expressed as:
where
where erfc (.) is the complementary error function.
In the following subsection, inspired by conventional communication systems, we present the analysis of the proposed nanosystem model.
3.1 Modulation and Demodulation Scheme
As illustrated in Fig. 2, the TX transmits molecular information in the medium. It may be encoded based on a specific structure of molecules, or on a specific composition of the information molecules (e.g., DNA sequence), or on the concentration of information molecules. In the proposed model, we consider that the molecular information (IM) is encoded according to the amount of concentration. The TX adopts the On-Off Keying (OOK) modulation scheme to transmit molecular information (therapeutic drugs), which represents the amplitude of the signal. We consider that the molecular information, IM is sent by using a sequence of binary symbols noted by (
A binary concentration shift keying (BCSK), which is defined by the number of molecules per unit volume
Due to the movement of drug molecules that follow a Brownian motion, the molecules move randomly and some of them cannot be captured by the DX. Moreover, the received molecules in a time slot may be captured in another one, which may cause ISI [19]. We consider that there is no equalizer to mitigate ISI owning to the fact that the performance of the proposed nanosystem is influenced by the number of received molecules. In consequence, the number of molecules that are sent at the previous time slot but arrived at the current time slot which can be defined as the ISI which absorbed during (
where I is the ISI length and
where the noise power is defined as the variance of the normal distribution
3.3 Encoding and Decoding Scheme
In the context of MC for transmission over a reliable channel, encoding techniques are very important for protecting data as (drugs molecules) when performing a serious surgery for a sick man through an advanced technology, which is called IoBNT, as we can envisage in our paper. Coding techniques are generally based on the addition of redundant bits into the source coding representations, followed by the transfer of these bits into the channel, where noise is present. At the Rx, an appropriate decoding method is used whereby the redundant bits can be used to check whether or not the information is corrupted. The use of coding and protocol techniques is still in its infancy at the nano-scale with many outstanding challenges, especially in this crucial technology as IoBNT. The BER can often be reduced and improved by choosing a slow and robust modulation scheme or coding scheme or by using channel ECC schemes, which can be employed to detect and possibly correct a certain number of errors that occur when information symbols are transmitted in a communication system. The study of the coding techniques and their abilities for manufacturing is still being researched.
Turbo coder and RS coder are used as ECC in the proposed relay scheme. The ECCs are used as block codes or convolutional codes. Block codes are very simple codes. They produce n-bit code-words by adding (n-k) extra bits to the k-bit message or information data [22]. Usually, these codes are called (n, k) block codes (abbreviation from Reed & Solomon codes). On the other hand, in the convolutional code as Turbo code, the whole data is converted onto a single code word. The encoding data depends on the previously (past) used input bits and on the present (current) input data which is called constraint length. So it is a memory coding technique.
The proposed nanosystem is utilized to deliver the desired therapeutic drug molecules dose via molecular communication-based diffusion to the targeted cell with the control from the IoBNT technology. However, the molecular communications suffer from severe attenuation of molecular concentration results with high errors at the DX, especially when it is far away from the TX. Consequently, the communication principles and the approaches in conventional communication systems such as relay discipline, information theory and coding techniques, can be employed to enhance the performance of the proposed nanosystem. Inspired by the biological system, the notion of the relay can be traced back in the nervous system, wherein there are various types of neurons such as motor, sensory and relay neurons. In such a system, the relay neuron is intermediated between motor and sensory neuron, used to relay the electrical impulse from sensory to the motor neuron. Moreover, due to the sensitivity of the transmission of the therapeutic drug over the IoBNT, a coding method must be employed to accomplish the data integrity/protection and thus achieve the complex goal of reliability over the molecular channel. Therefore, in the proposed nanosystem, not only do we employ a relay discipline but also a coding technique. We develop an intermediate DF nanorelay (RX) between TX and DX as illustrated in Fig. 3. It is able to ensure delivery of drugs effectively and thus improve the performance of the nanosystem to attain a minimum bit error rate. Also, we provide solutions for the position of the nanorelay, which can be served. Additionally, we use a widely experimented coding technique such as an RS coder and a Turbo coder to improve the performance of transmission over the proposed nanosystem.

Figure 3: Proposed molecular communication model
The developed DF scheme demonstrated in Fig. 3 works as follows:
• The TX releases a type of drug molecule using a CSK modulation scheme. The modulation scheme is adopted to encode the input signal, which represents the binary signals ‘1’ and ‘0’ at the start of each bit interval. If the current bit is encoded as ‘1’, Ntx molecules are emitted from the transmitter at a distance d1 from the center of the RX. Otherwise, the transmitter emits no molecules to transmit bit 0.
• Due to the ISI source, which comes from the arrival of molecules in a time slot, it may be captured in another one.
• In addition, noise sources as mentioned before may degrade the channel reliability.
So, the coding techniques must be utilized within our relaying scheme, especially when we deal with the life of the man through advanced technology such as IoBNT. The RX decodes the signal received from the TX.
• The DF relay is able to deduce and select the best transmission signal in the first hop between TX and RX nodes by calculating the BER metric and then, re-encode and re-transmit it again by RS or Turbo coder.
• At the RX or DX, detection of the signal can be carried out by assuming that the receiver nodes are able to count the net number of drug molecules that are captured by the receiver at any sampling period interval.
• The RX decodes the received signal by comparing it with the detection threshold values. Then, it selects the received signal with minimum bit error rate, and after, re-encoding and re-transmitting again along a diffusion channel between the RX and DX, which is attained by re-transmitting from the RX at a distance
The proposed MC system-based coded nano-relay procedures are represented in the following Algorithm 1

The RX detects the received (

Figure 4: Representation of the diffusion channel
The total number of molecules absorbed by the relay node or receiver node at the
The arrival of molecules
where
The last term adheres to the pattern of a normal distribution, expressed in Eq. (5). With large
where
where the mean and variance are derived as follows:
The RX decodes the received signal and chooses the signal with the minimum BER to re-transmit again by one of the detection methods: ML or MEP as explained in the next section. The signal will undergo the same attenuation process as the transmitter to the relay node. A similar calculation can be applied to the next-hop between RX and DX at (j + 1)th time slot.
After receiving molecules, the receiver RX or DX is able to decode the signal by a suitable decoder as in our model by MATLAB code simulation as RS (255, 239) or Turbo decoder, whose constraint length is 4 and generator polynomials are 13 and 15. There are several algorithms that exist for decoding convolutional codes such as sequential decoding, Viterbi decoding, and majority logic decoding. Threshold decoding is a simple solution to the decoding problem based on a special subset of parity checks as maximum likelihood detector or minimum error probability.
5.1 Maximum Likelihood Detector
The receiver uses the ML detection scheme to detect signal which means that 1 and 0 are equal probability transmission events
Therefore, the decoded relay satisfies:
The BER is deduced as:
From Fig. 4, the bit transition probability is formulated as P(y|x):
So, the BER probability can be reevaluated as:
The deviation of ML decoding compared to other schemes is that it permits use of the statistical information regarding the received bits available at the receiver in contrast to purely algebraic decoding techniques.
5.2 Minimum Error Probability (MEP)
A detection method based on the MEP is proposed in this subsection. The threshold can be adjusted adaptively, according to the number of released molecules to yield to/converge on the optimal reception, as long as the detection criteria are satisfied:
Receiver detection can adjust adaptively the detection threshold according to the mean value and variance. The number of released molecules is different and the corresponding detection threshold is directly determined, based on the former.
Also, from Fig. 4, we can obtain:
The corresponding channel bit error probability from TX to RX or RX to DX is calculated by:
According to the above description, we can deduce that the bit error probability of the whole channel can be expressed as:
From the information theory, mutual channel information can be obtained as:
where H (Y) is considered as the amount of minimum information that should be received at the receiver and H (Y|X) accounts for the actual amount of information received by the receiver.
Thereafter, the channel capacity can be expressed as:
According to the channel capacity and each time slot length, the channel information transmission rate can be obtained as:
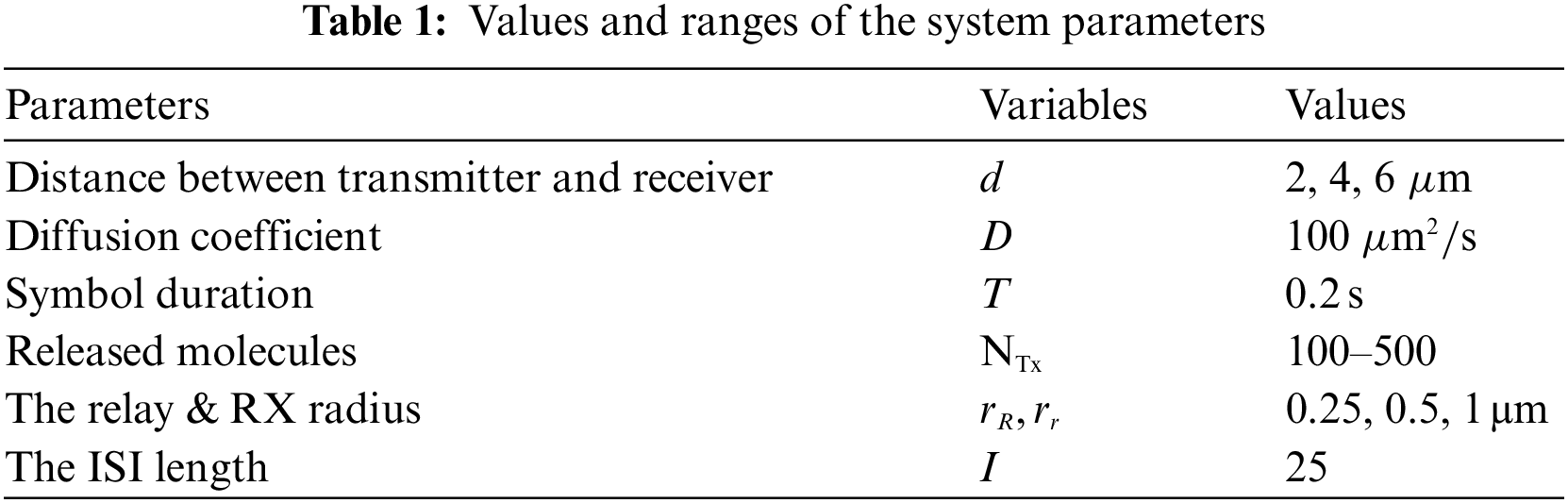
In this section, we study the performance of the proposed coded relay scheme by using simulation and empirical results to evaluate the channel performance of the proposed diffusion MC system based on the coded nano relay scheme. We have conducted specific simulations using MATLAB. All our simulation results are provided using parameters summarized in Tab. 1. We present the procedures for simulating the MC system based on coded nano relay system in Algorithm 1. We study the performance of the proposed scheme by evaluating certain important metrics such as BER, SNR, and channel capacity. Also, the influence of receiver, relay radius, diffusion coefficient, and a number of transmitted molecules are explored. Comparison results and analysis with previous work are further explored. For each figure, ‘Anal’ and ‘Sim’ are used to abbreviate ‘Analytical’ and ‘Simulation’, respectively. Also, the units for all parameters are as denoted in Tab. 1.
6.1 Influence of the Proposed Coded Relay
Exploring human body, entails ensuring the reliability of delivering drugs to the affected cell. In that context, BER metric should be taken into account in IoBNT, which is often employed to assess the performance of communication system as in Fig. 5.

Figure 5: Error probability of coded relay scheme as a function of detection threshold at d = 6 μm,
Fig. 5 depicts the BER performance of the proposed nanonetwork-based relay nanomachine vs. detection threshold for different values
Figs. 6 and 7 represents the coded relay system performance. These figures illustrate matching between the analytical (ML-MEP) and simulation results. From those results, the ability of decoded relay scheme to extend the distance between TX and DX is justified This in contrast to other papers which provide the optimal position of the relay in the middle between TX and DX.

Figure 6: Error probability of coded RS relay scheme as a function of detection threshold at d = 6 μm

Figure 7: Error probability of coded turbo relay scheme as a function of detection threshold at d = 6 μm
Fig. 8 demonstrates the efficiency of the DF relay scheme (BER) vs. the detection threshold. We have validated the statement that by using the DF strategy with a relay scheme can significantly improve the BER of the system concerning the direct transmission (un-coded) with the same transmission distance. Also, it can be noted that the Turbo coder system with a relay scheme can provide better performance than the RS due to a better processing strategy that utilizes the past and present data (due to the fact that it is a memory coding scheme which attains to minimize the bit error rate). In comparison, Turbo code takes a long time for processing and more truncation period than RS code.

Figure 8: Error probability of DF relay scheme as a function of detection threshold at d = 4 μm,
On the other hand, SNR is defined as the ratio between the average received signal power and the average noise power [5]. The transmission power is defined as the average number of drug molecules sent by the transmitter and the noise power is the variance of the noise. Fig. 9 depicts BER, where SNR varies from −5 to 15 dB. There is a clear improvement in channel performance with coded relay schemes. Also, the Turbo coder provides good performance at a low signal to noise ratio and high performance at a high signal to noise ratio than RS code, due to the better processing units in order to minimize the error rate as mentioned before.

Figure 9: Bit error rate performance vs. SNR (dB) based DF relaying scheme at d = 4 μm
Another significant metric that examines the channel performance is the channel capacity. Despite the traditional communication, the capacity for molecular communication is limited and it depends on the circumstances of the channel model which is clear from the number of molecules received and captured by the receiver nodes. Figs. 10 and 11 represent the benefits of using the RS or Turbo coder system. Channel capacity elevates with RS coder or Turbo coder when increasing the number of molecules transmitted or SNR as clear from the figure. Also, the Turbo coder represents a better performance than the un-coded or RS coder under the same slot length.

Figure 10: The channel capacity under coded and un-coded channel at T = 0.2 s

Figure 11: The channel capacity vs. SNR (dB) channel T = 0.2 s
From the figures, we can conclude that the coded signal has a higher channel capacity than the un-coded one. The turbo code has a higher capacity than RS within the same slot length.
6.2 Influence of RX and DX Radius `
Another vital factor that affects the delivery of drugs to affect the cell is the radius of the receiving nanomachine rr and RX rR as shown in Fig. 12. When the radius of the receiving nodes is larger, more captured drug molecules affect the cell, which entails more molecules as observed by the receiving nanomachine resulting from increasing reception areas. Subsequently, this minimizes the BER probability which in turn improves the channel performance.

Figure 12: Error probability of DF relay scheme as a function of detection threshold at d = 6 μm,
6.3 Influence of TX Released Molecules‘
To improve the performance of the system, we should study the number of released molecules from the TX. Due to the random motion of molecules adhering to the Brownian motion and the nature of propagation medium in a nano-machine network, the number of drugs molecules captured by DX (received signal) is very small compared with the traditional communication. To obtain a satisfactory performance for the system, we need to release a large number of drugs molecules on the TX side. Also, by increasing the number of molecules released by the TX give much clearer boundaries at the DX side, perfect detection is achieved due to the large gap between zero and the one, released by the TX. So, the BER probability can be enhanced as demonstrated in Fig. 13 since as the number of released molecules is increased, this yields to better performance, particularly for coded relay scheme.

Figure 13: Error probability of coded relay scheme as a function of number of transmitted molecules at d = 4 μm
6.4 Influence of Diffusion Coefficient ‘D’
Fig. 14 demonstrates the effect of the diffusion coefficient on the performance of the system with BER and the number of received molecules at DX. As previously mentioned, the diffusion coefficient depends on the temperature, viscosity and radius of the solvent molecules. So, D increases as temperature increases, viscosity, and radius of molecules decreases. It can be seen that the BER performance increases as the value of diffusion coefficient increases depending on the nature of solvent molecules.

Figure 14: Bit error rate performance vs. detection threshold with DF relaying scheme at d = 6 μm,
Fig. 15 represents the BER performance vs. detection threshold as denoted in previous work compared to the proposed encoding relay scheme when using RS or Turbo coder. The proposed scheme enhances bit error performance giving the best position of the relay when it is the nearest to TX as to decrease the provoking of affected tumor cells.

Figure 15: Bit error rate performance vs. detection threshold at d = 40 μm
In simulation terms, BER performance of the coded relay scheme vs. the number of released molecules, compared with previous work is depicted in Fig. 16. The coded relay strategy significantly improves system reliability as compared to previous work. It is directly concluded from Fig. 16 that the performance improves with the increase of the number of released molecules. From the simulation results, it can be seen that the analysis and simulation can achieve a coincident performance.

Figure 16: The channel BER performance of the diffusion-based coded relay in MC systems vs. the number of released molecules in comparison DF relay and previous work [20]
In this paper, bit error probability, SNR, and channel capacity qualitative results of the DF relaying scheme have been analyzed and evaluated. Simulation results have demonstrated that the performance of the proposed DF relaying scheme is better than that of the direct transmit scheme within the same transmission distance, and it has a significantly higher channel capacity. In addition, the simulation experiments show how the parameters affect the performance of the system. Simulation results show that the convolution code (Turbo code) has better error controlling and correction performance in comparison to block code (RS code). However, Turbo code is very difficult to implement than RS code in nanomachine manufacturing.
Acknowledgement: This study was supported by the Institute for Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation (IITP) grant funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (No. 2019-0-01343, Training Key Talents in Industrial Convergence Security).
Funding Statement: This work was funded by the Researchers Supporting Project No. (RSP-2021/102) King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to report regarding the present study.
1. I. C. Okonkwo, R. Malekian, B. T. Maharaj and A. V. Vasilakos, “Molecular communication and nanonetwork for targeted drug delivery: A survey,” IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, vol. 19, no. 4, pp. 3046–3096, 2017. [Google Scholar]
2. A. Jamshidi, A. K. Haddad and G. Ardeshiri, “MAP detector performance analysis in diffusion-based relaying molecular communication,” Nano Communication Networks, vol. 19, no. 4, pp. 81–91, 2019. [Google Scholar]
3. P. He, X. Han and H. Liu, “Chain modeling of molecular communications for body area network,” Sensors Journal, vol. 19, no. 2, pp. 1–18, 2019. [Google Scholar]
4. P. Pramanik, A. Solanki, A. Debnath, A. Nayyar and K. Kwak, “Advancing modern healthcare with nanotechnology, nanobiosensors, and internet of nanothings: Taxonomies, applications, architecture, and challenges,” IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 65230–65266, 2020. [Google Scholar]
5. H. Fouad, M. Hashem and A. Youssef, “A nano-biosensors model with optimized bio-cyber communication systems based on internet of bio-nano things for thrombosis prediction,” Journal of Nanoparticle Research, vol. 22, no. 7, pp. 1–17, 2020. [Google Scholar]
6. A. Abdellah, O. Mahmood, R. Kirichek, A. Paramonov and A. Koucheryavy, “Machine learning algorithm for delay prediction in iot and tactile internet,” Future Internet, vol. 13, no. 12, pp. 1–13, 2021. [Google Scholar]
7. A. Ghazaleh, A. Jamshidi and K. Haddad, “Performance analysis of decode and forward relay network in diffusion based molecular communication,” in Iranian Int. Conf. on Electrical Engineering (ICEE), Esfihan, Iran, pp. 782–788, 2017. [Google Scholar]
8. N. Tavakkoli, P. Azmi and N. Mokari, “Optimal positioning of relay node in cooperative molecular communication networks,” IEEE Transactions on Communications, vol. 65, no. 12, pp. 5293–5304, 2017. [Google Scholar]
9. S. Tiwari and P. Upadhyay, “Estimate-and-forward relaying in diffusion-based molecular communication networks: Performance evaluation and threshold optimization,” IEEE Transactions on Molecular, Biological and Multi-Scale Communications, vol. 3, no. 8, pp. 183–193, 2017. [Google Scholar]
10. J. Wang, M. Peng, Y. Liu, X. Liu and M. Daneshmand, “Performance analysis of signal detection for amplify-and-forward relay in diffusion-based molecular communication systems,” IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 7, no. 2, pp. 1401–1412, 2020. [Google Scholar]
11. A. Nguyen, V. Vo, C. In and D. Ha, “System performance analysis for an energy harvesting iot system using a df/af uav-enabled relay with downlink noma under nakagami-m fading,” Sensors Journal, vol. 21, no. 1, pp. 1–18, 2021. [Google Scholar]
12. M. Femminella and G. Reali, “A simple queuing model for molecular communication receivers,” Sensors Journal, vol. 21, no. 22, pp. 1–16, 2021. [Google Scholar]
13. M. Dissanayake, Y. Dang, A. Nallanathan, E. Ekanayake and M. Elkashlan, “Reed Solomon codes for molecular communication with a full absorption receiver,” IEEE Communications Letters, vol. 21, no. 6, pp. 1245–1248, 2017. [Google Scholar]
14. L. Mark and H. Matthew, “Error correction for molecular communications,” Nano Communication Networks, vol. 3, no. 3, pp. 161–167, 2012. [Google Scholar]
15. M. Barros, M. Veletic, M. Kanada, M. Pierobon, S. Vainio et al., “Molecular communications in virtual infections research: Modeling, experimental data, and future directions,” IEEE Transactions on Molecular, Biological and Multi-Scale Communications, vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 121–141, 2021. [Google Scholar]
16. E. Lipiec, K. Sofinska, S. Seweryn, N. Wilkosz and M. Szymonski, “Revealing dna structure at liquid/solid interfaces by afm-based high resolution imaging and molecular spectroscopy,” Molecules Journal, vol. 26, no. 21, pp. 1–17, 2021. [Google Scholar]
17. S. Chopra, J. Kaur and H. Monga, “Comparative performance analysis of block and convolutional codes,” Indian Journal of Science and Technology, vol. 9, no. 45, pp. 971–983, 2016. [Google Scholar]
18. Y. Deng, A. Noel, M. Elkashlan, A. Nallanathan and K. C. Cheung, “Modeling and simulation of molecular communication systems with a reversible adsorption receiver,” IEEE Transactions on Molecular, Biological and Multiscale Communications, vol. 1, no. 4, pp. 347–362, 2015. [Google Scholar]
19. M. Mahfuz, M. Upal, D. Makrakis and T. Mouftah, “Performance analysis of convolutional coding techniques in diffusion-based concentration-encoded pam molecular communication systems,” BioNanoScience, vol. 3, no. 3, pp. 270–284, 2013. [Google Scholar]
20. A. Nair, P. Chauhan, B. Saha and K. Kubatzky, “Conceptual evolution of cell signaling,” International Journal of Molecular Sciences, vol. 20, no. 13, pp. 1–17, 2019. [Google Scholar]
21. L. Siukstaite, F. Rosato, A. Mitrovic, P. Muller, K. Kraus et al., “The two sweet sides of janus lectin drive crosslinking of liposomes to cancer cells and material uptake,” Toxins Journal, vol. 13, no. 11, pp. 1–13, 2021. [Google Scholar]
22. A. Einolghozati, M. Sardari, A. Berirami and F. Fekri, “Data gathering in networks of bacteria colonies: Collective sensing and relaying using molecular communication,” in IEEE INFOCOM Workshops, Orlando, USA, pp. 256–261, 2012. [Google Scholar]
 | This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. |