 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Hitesh Mohapatra*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076726
Abstract This review examines current approaches to real-time decision-making and task optimization in Internet of Things systems through the application of machine learning models deployed at the network edge. Existing literature shows that edge-based distributed intelligence reduces cloud dependency. It addresses transmission latency, device energy use, and bandwidth limits. Recent optimization strategies employ dynamic task offloading mechanisms to determine optimal workload placement across local devices and edge servers without centralized coordination. Empirical findings from the literature indicate performance improvements with latency reductions of approximately 32.8% and energy efficiency gains of 27.4% compared to conventional cloud-centric models.… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Ying Yao1, Le Tian1,2,3, Yuxiang Hu1,2,3,*, Pengshuai Cui1,2,3
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075747
Abstract In the process of programmable networks simplifying network management and increasing network flexibility through custom packet behavior, security incidents caused by human logic errors are seriously threatening their safe operation, robust verification methods are required to ensure their correctness. As one of the formal methods, symbolic execution offers a viable approach for verifying programmable networks by systematically exploring all possible paths within a program. However, its application in this field encounters scalability issues due to path explosion and complex constraint-solving. Therefore, in this paper, we propose NetVerifier, a scalable verification system for programmable networks. To… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Wenchao Shi1, Tao Wei2, Chuan Yang3, Qichao Fan3, Hongxi Liu4, Bin Shao5,*, Peng Jing4,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075293
Abstract Enhancing the strength of nanotwinned aluminum (Al) is essential for the development of next-generation high-end chip technology. To better understand the detwinning behavior of nanotwinned Al under conditions with no resolved shear stress acting on the twin boundaries, we conducted molecular dynamics simulations of uniaxial tensile deformation in nanotwinned single-crystal Al at room temperature. Detwinning is observed only when the twin boundary spacing is 7.01 Å. At larger spacings, twin boundaries remain parallel to the loading direction, with no rotation or bending, indicating negligible migration. Detwinning is triggered by localized stress from dislocation interactions, with More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Qi Wang, Kelvin Amos Nicodemas*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.074305
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Time Series Analysis, Modelling and Forecasting)
Abstract Multivariate time series forecasting plays a crucial role in decision-making for systems like energy grids and transportation networks, where temporal patterns emerge across diverse scales from short-term fluctuations to long-term trends. However, existing Transformer-based methods often process data at a single resolution or handle multiple scales independently, overlooking critical cross-scale interactions that influence prediction accuracy. To address this gap, we introduce the Hierarchical Attention Transformer (HAT), which enables direct information exchange between temporal hierarchies through a novel cross-scale attention mechanism. HAT extracts multi-scale features using hierarchical convolutional-recurrent blocks, fuses them via temperature-controlled mechanisms, and optimizes More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Qian Hu, Lei Tan*, Qingjun Yuan, Zong Zuo, Yan Li
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076137
Abstract Multi-behavior recommendation methods leverage various types of user interaction behaviors to make personalized recommendations. Behavior paths formed by diverse user interactions reveal distinctive patterns between users and items. Modeling these behavioral paths captures multidimensional behavioral features, which enables accurate learning of user preferences and improves recommendation accuracy. However, existing methods share two critical limitations: (1) Lack of modeling for the diversity of behavior paths; (2) Ignoring the impact of item attribute information on user behavior paths. To address these issues, we propose a Directed Behavior path graph-based Multi-behavior Recommendation method (DBMR). Specifically, we first construct… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Dmytro Tymoshchuk1,*, Oleh Yasniy1, Iryna Didych2, Pavlo Maruschak3,*, Yuri Lapusta4
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.077062
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Machine Learning in the Mechanics of Materials and Structures)
Abstract This article presents an approach to predicting the hysteresis behavior of shape memory alloys (SMAs) using a Temporal Convolutional Network (TCN) deep learning model, followed by the interpretation of the results using Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) methods. The experimental dataset was prepared based on cyclic loading tests of nickel-titanium wire at loading frequencies of 0.3, 0.5, 1, 3, and 5 Hz. For training, validation, and testing, 100–250 loading-unloading cycles were used. The input features of the models were stress σ (MPa), cycle number (Cycle parameter), and loading-unloading stage indicator, while the output variable was strain… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yan-Hao Huang*, Yu-Tse Huang
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076800
Abstract Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) is a common microvascular complication of diabetes that progressively damages the retinal blood vessels and, without timely treatment, can lead to irreversible vision loss. In clinical practice, DR is typically diagnosed by ophthalmologists through visual inspection of fundus images, a process that is time-consuming and prone to inter- and intra-observer variability. Recent advances in artificial intelligence, particularly Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Transformer-based models, have shown strong potential for automated medical image classification and decision support. In this study, we propose a Position-Wise Attention-Enhanced Vision Transformer (PWAE-ViT), which integrates a positional attention… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Sara Tehsin1,*, Muhammad John Abbas2, Inzamam Mashood Nasir1, Fadwa Alrowais3, Reham Abualhamayel4, Abdulsamad Ebrahim Yahya5, Radwa Marzouk6
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076515
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Bridging the Gap: AutoML and Explainable AI for Industrial and Healthcare Innovations)
Abstract Globally, diabetes and glaucoma account for a high number of people suffering from severe vision loss and blindness. To treat these vision disorders effectively, proper diagnosis must occur in a timely manner, and with conventional methods such as fundus photography, optical coherence tomography (OCT), and slit-lamp imaging, much depends on an expert’s interpretation of the images, making the systems very labor-intensive to operate. Moreover, clinical settings face difficulties with inter-observer variability and limited scalability with these diagnostic devices. To solve these problems, we have developed the Efficient Channel-Spatial Attention Network (ECSA-Net), a new deep learning-based… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Rama Gautam1,*, Nikhil Marriwala1, Reeta Devi1, Dhariya Singh Arya2
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076136
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advanced Computational Modeling and Simulations for Engineering Structures and Multifunctional Materials: Bridging Theory and Practice)
Abstract In this study, the multi-scale (meso and macro) modelling was used to predict the electric response of the material. Porosity was introduced through a sugar-templating process to enhance compressibility and sensitivity. Mean-field homogenization was employed to predict the electrical conductivity of the nanocomposites, which was validated experimentally through I–V characterisation, confirming stable Ohmic behavior. The homogenised material parameters were incorporated into COMSOL Multiphysics to simulate diaphragm deflection and capacitance variation under applied pressure. Experimental results showed a linear and stable capacitance response at the force magnitude of 0–7 N. The Graphene nanoplatelets (GnP)–Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) sensor demonstrated More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Hongyu Xu1,*, Xiaofeng Liu1, Zhao Li1, Shuai Zhang2, Jintao Cui1, Zongshuai Zhou1, Longlong Chen1, Mengen Zhang1
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075413
Abstract In two-scale topology optimization, enhancing the connectivity between adjacent microstructures is crucial for achieving the collaborative optimization of micro-scale performance and macro-scale manufacturability. This paper proposes a two-scale concurrent topology optimization strategy aimed at improving the interface connection strength. This method employs a parametric approach to explicitly divide the micro-design domain into a “boundary connection region” and a “free design domain” at the initial stage of optimization. The boundary connection region is used to generate a connection layer that enhances the interface strength, while the free design domain is not constrained by this layer, thus… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Chunqian Guo*, Gang Chen
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072184
Abstract Despite the ability of the anonymous communication system The Onion Router (Tor) to obscure the content of communications, prior studies have shown that passive adversaries can still infer the websites visited by users through website fingerprinting (WF) attacks. Conventional WF methodologies demonstrate optimal performance in scenarios involving single-tab browsing. Conventional WF methods achieve optimal performance primarily in scenarios involving single-tab browsing. However, in real-world network environments, users often engage in multi-tab browsing, which generates overlapping traffic patterns from different websites. This overlap has been shown to significantly degrade the performance of classifiers that rely on… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Rafika Harrabi1,2,*, Slim Ben Chaabane1,2, Hassene Seddik2
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.072054
Abstract Securing restricted zones such as airports, research facilities, and military bases requires robust and reliable access control mechanisms to prevent unauthorized entry and safeguard critical assets. Face recognition has emerged as a key biometric approach for this purpose; however, existing systems are often sensitive to variations in illumination, occlusion, and pose, which degrade their performance in real-world conditions. To address these challenges, this paper proposes a novel hybrid face recognition method that integrates complementary feature descriptors such as Fuzzy-Gabor 2D Fisher Linear Discriminant (FG-2DFLD), Generalized 2D Linear Discriminant Analysis (G2DLDA), and Modular-Local Binary Patterns (Modular-LBP)… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Jingjing Liu1, Chuanyang Liu1,2,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075348
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Deep Learning and Neural Networks: Architectures, Applications, and Challenges)
Abstract Intelligent inspection of transmission lines enables efficient automated fault detection by integrating artificial intelligence, robotics, and other related technologies. It plays a key role in ensuring power grid safety, reducing operation and maintenance costs, driving the digital transformation of the power industry, and facilitating the achievement of the dual-carbon goals. This review focuses on vision-based power line inspection, with deep learning as the core perspective to systematically analyze the latest research advancements in this field. Firstly, at the technical foundation level, it elaborates on deep learning algorithms for intelligent transmission line inspection based on image… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Nurbek Sissenov1,*, Gulden Ulyukova1,*, Dina Satybaldina2, Nikolaj Goranin3
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075504
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Software, Algorithms and Automation for Industrial, Societal and Technological Sustainable Development)
Abstract The reliability of information systems (IS) is a key factor in the sustainable operation of modern digital services. However, existing assessment methods remain fragmented and are often limited to individual indicators or expert judgments. This paper proposes a hybrid methodology for a comprehensive assessment of IS reliability based on the integration of the international standard ISO/IEC 25010:2023, multicriteria analysis methods (ARAS, CoCoSo, and TOPSIS), and the XGBoost machine learning algorithm for missing data imputation. The structure of the ISO/IEC 25010 standard is used to formalize reliability criteria and subcriteria, while the AHP method allows for… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Trong-Thua Huynh1,*, De-Thu Huynh2, Du-Thang Phu1, Hong-Son Nguyen1, Quoc H. Nguyen3
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076623
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Deep Learning: Emerging Trends, Applications and Research Challenges for Image Recognition)
Abstract This paper introduces MobiIris, a lightweight deep network for mobile iris recognition that enhances attention and specifically addresses the balance between accuracy and efficiency on devices with limited resources. The proposed model is based on the large version of MobileNetV3 and adds more spatial attention blocks and an embedding-based head that was trained using margin-based triplet learning, enabling fine-grained modeling of iris textures in a compact representation. To further improve discriminability, we design a training pipeline that combines dynamic-margin triplet loss, a staged hard/semi-hard negative mining strategy, and feature-level knowledge distillation from a ResNet-50 teacher.… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yanming Chen1, Fuxiang Yuan2,*, Zekang Wang2
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075072
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Cyberspace Mapping and Anti-Mapping Techniques)
Abstract Network topology obfuscation is a technique aimed at protecting critical nodes and links from disruptions such as Link Flooding Attack (LFA). Currently, there are limited topology obfuscation methods for protecting critical nodes, and the existing approaches mainly achieve obfuscation by extensively modifying network links, resulting in high costs. To address this issue, this paper proposes a low-cost network topology obfuscation method dedicated to critical node protection, with its core innovation lying in a lightweight obfuscation architecture based on Fake Node Clusters (FNCs). Firstly, the protected network is modeled as an undirected graph, and an adjacency… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Hui Chen1, Mohammed A. H. Ali1,*, Bushroa Abd Razak1, Zhenya Wang2, Yusoff Nukman1, Shikai Zhang1, Zhiwei Huang1, Ligang Yao3, Mohammad Alkhedher4
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.065539
Abstract Most existing path planning approaches rely on discrete expansions or localized heuristics that can lead to extended re-planning, inefficient detours, and limited adaptability to complex obstacle distributions. These issues are particularly pronounced when navigating cluttered or large-scale environments that demand both global coverage and smooth trajectory generation. To address these challenges, this paper proposes a Wave Water Simulator (WWS) algorithm, leveraging a physically motivated wave equation to achieve inherently smooth, globally consistent path planning. In WWS, wavefront expansions naturally identify safe corridors while seamlessly avoiding local minima, and selective corridor focusing reduces computational overhead in More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Malik Al-Essa1,*, Mohammad Qatawneh2,1, Ahmad Sami Al-Shamayleh3, Orieb Abualghanam1, Wesam Almobaideen4,1
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076608
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Bridging the Gap: AutoML and Explainable AI for Industrial and Healthcare Innovations)
Abstract Machine Learning (ML) intrusion detection systems (IDS) are vulnerable to manipulations: small, protocol-valid manipulations can push samples across brittle decision boundaries. We study two complementary remedies that reshape the learner in distinct ways. Adversarial Training (AT) exposes the model to worst-case, in-threat perturbations during learning to thicken local margins; Counterfactual Augmentation (CF-Aug) adds near-boundary exemplars that are explicitly constrained to be feasible, causally consistent, and operationally meaningful for defenders. The main goal of this work is to investigate and compare how AT and CF-Aug can reshape the decision surface of the IDS. eXplainable Artificial Intelligence More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Adeel Iqbal1,#, Tahir Khurshaid2,#, Syed Abdul Mannan Kirmani3, Mohammad Arif4,*, Muhammad Faisal Siddiqui5,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075819
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Vehicular Ad-Hoc Networks (VANETs) for Intelligent Transportation Systems)
Abstract Vehicular Internet of Things (V-IoT) networks need intelligent and adaptive spectrum access methods for ensuring ultra-reliable and low-latency communication (URLLC) in highly dynamic environments. Traditional reinforcement learning (RL)-based algorithms, such as Q-Learning and Double Q-Learning, are often characterized by unstable convergence and inefficient exploration in the presence of stochastic vehicular traffic and interference. This paper proposes Adaptive Reinforcement Q-learning with Upper Confidence Bound (ARQ-UCB), a lightweight and reliability-aware RL framework, which explicitly reduces interruption and blocking probabilities while improving throughput and delay across diverse vehicular traffic conditions. This proposed ARQ-UCB algorithm extends the basic Q-updates More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Somia A. Abd El-Mottaleb1, Amira G. Mohamed2, Mehtab Singh3, Hassan Yousif Ahmed4, Medien Zeghid4, Abu Sufian A. Osman5,*, Sami Mourou5
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075669
Abstract This paper presents an image encryption scheme for underwater optical wireless communication (UOWC) systems based on dynamically generated hyperchaotic S-boxes, aiming to enhance both data security and transmission performance in underwater environments. The proposed encryption approach provides strong confusion and diffusion properties and is evaluated over five Jerlov water types with different optical attenuation characteristics. Security analysis demonstrates that the encrypted images achieve information entropy values close to the ideal value of 8 (7.9925–7.9993), with very low correlation coefficients in horizontal, vertical, and diagonal directions, as well as the system achieves high values in key… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Ho Hai Quan1,2, Le Huu Binh1,*, Nguyen Dinh Hoa Cuong3, Le Duc Huy4
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075549
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: AI-Driven Next-Generation Networks: Innovations, Challenges, and Applications)
Abstract Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) play a crucial role in numerous Internet of Things (IoT) applications and next-generation communication systems, yet they continue to face challenges in balancing energy efficiency and reliable connectivity. This study proposes SAC-HTC (Soft Actor-Critic-based High-performance Topology Control), a deep reinforcement learning (DRL) method based on the Actor-Critic framework, implemented within a Software Defined Wireless Sensor Network (SDWSN) architecture. In this approach, sensor nodes periodically transmit state information, including coordinates, node degree, transmission power, and neighbor lists, to a centralized controller. The controller acts as the reinforcement learning (RL) agent, with the… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Chih-Yung Huang*, Hong-Ru Shi, Min-Yan Xie
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075398
Abstract Quality control plays a critical role in modern manufacturing. With the rapid development of electric vehicles, 5G communications, and the semiconductor industry, high-speed and high-precision detection of surface defects on silicon carbide (SiC) wafers has become essential. This study developed an automated inspection framework for identifying surface defects on SiC wafers during the coarse grinding stage. The complex machining textures on wafer surfaces hinder conventional machine vision models, often leading to misjudgment. To address this, deep learning algorithms were applied for defect classification. Because defects are rare and imbalanced across categories, data augmentation was performed… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
HeeSeok Choi1, Joon-Min Gil2,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.074511
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Integrating Computing Technology of Cloud-Fog-Edge Environments and its Application)
Abstract Given the growing number of vehicle accidents caused by unintended acceleration and braking failure, verifying Sudden Unintended Acceleration (SUA) incidents has become a persistent challenge. A central issue of debate is whether such events stem from mechanical malfunctions or driver pedal misapplications. However, existing verification procedures implemented by vehicle manufacturers often involve closed tests after vehicle recalls; thus raising ongoing concerns about reliability and transparency. Consequently, there is a growing need for a user-driven framework that enables independent data acquisition and verification. Although previous studies have addressed SUA detection using deep learning, few have explored… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Abdallah Ghourabi1,*, Hassen Chouaib2
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.074505
Abstract In recent years, ransomware attacks have become one of the most common and destructive types of cyberattacks. Their impact is significant on the operations, finances and reputation of affected companies. Despite the efforts of researchers and security experts to protect information systems from these attacks, the threat persists and the proposed solutions are not able to significantly stop the spread of ransomware attacks. The latest remarkable achievements of large language models (LLMs) in NLP tasks have caught the attention of cybersecurity researchers to integrate these models into security threat detection. These models offer high embedding… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Lin-Hui Liu1, Dong-Jie Liu1,*, Yin-Yan Zhang1, Xiao-Bo Jin2, Xiu-Cheng Wu3, Guang-Gang Geng1
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.074253
Abstract Phishing email detection represents a critical research challenge in cybersecurity. To address this, this paper proposes a novel Double-S (statistical-semantic) feature model based on three core entities involved in email communication: the sender, recipient, and email content. We employ strategic game theory to analyze the offensive strategies of phishing attackers and defensive strategies of protectors, extracting statistical features from these entities. We also leverage the Qwen large language model to excavate implicit semantic features (e.g., emotional manipulation and social engineering tactics) from email content. By integrating statistical and semantic features, our model achieves a robust More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Atef Gharbi1, Mohamed Ayari2, Nasser Albalawi3, Ahmad Alshammari3, Nadhir Ben Halima4,*, Zeineb Klai3
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075474
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Control Theory and Application of Multi-Agent Systems)
Abstract This paper presents Dual Adaptive Neural Topology (Dual ANT), a distributed dual-network meta-adaptive framework that enhances ant-colony-based multi-agent coordination with online introspection, adaptive parameter control, and privacy-preserving interactions. This approach improves standard Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) with two lightweight neural components: a forward network that estimates swarm efficiency in real time and an inverse network that converts these descriptors into parameter adaptations. To preserve the privacy of individual trajectories in shared pheromone maps, we introduce a locally differentially private pheromone update mechanism that adds calibrated noise to each agent’s pheromone deposit while preserving the efficacy More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Dina S. M. Hassan*, Reem Ibrahim Alkanhel, Thuraya Alrumaih, Shiyam Alalmaei
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.074751
Abstract The sustainability of the Internet of Things (IoT) involves various issues, such as poor connectivity, scalability problems, interoperability issues, and energy inefficiency. Although the Sixth Generation of mobile networks (6G) allows for Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication (URLLC), enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB), and massive Machine-Type Communications (mMTC) services, it faces deployment challenges such as the short range of sub-THz and THz frequency bands, low capability to penetrate obstacles, and very high path loss. This paper presents a network architecture to enhance the connectivity of wireless IoT mesh networks that employ both 6G and Wi-Fi technologies. In this… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Rui Yao1,2, Yuye Wang1,2,*, Fei Yu1,2,3,*, Hongrun Wu1,2, Zhenya Diao1,2
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.073861
Abstract Path planning for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) in complex environments presents several challenges. Traditional algorithms often struggle with the complexity of high-dimensional search spaces, leading to inefficiencies. Additionally, the non-linear nature of cost functions can cause algorithms to become trapped in local optima. Furthermore, there is often a lack of adequate consideration for real-world constraints, for example, due to the necessity for obstacle avoidance or because of the restrictions of flight safety. To address the aforementioned issues, this paper proposes a dynamic weighted spherical particle swarm optimization (DW-SPSO) algorithm. The algorithm adopts a dual Sigmoid-based More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Rama Sugavanam*, Mythili Ramu
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.071469
Abstract When performing English-to-Tamil Neural Machine Translation (NMT), end users face several challenges due to Tamil’s rich morphology, free word order, and limited annotated corpora. Although available transformer-based models offer strong baselines, they compromise syntactic awareness and the detection and management of offensive content in cluttered, noisy, and informal text. In this paper, we present POSDEP-Offense-Trans, a multi-task NMT framework that combines Part-of-Speech (POS) and Dependency Parsing (DEP) methods with a robust offensive language classification module. Our architecture enriches the Transformer encoder with syntax-aware embeddings and provides syntax-guided attention mechanisms. The architecture incorporates a structure-aware contrastive… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Hoyoon Lee1, Jeonghoon Jee1, Hoseon Kim2, Cheol Oh1,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076980
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: AI-Driven Big Data Analytics for Sustainable Mixed Traffic and Mobility Systems)
Abstract Analyzing the driving behavior of autonomous vehicles (AV) in mixed traffic conditions at urban intersections has become increasingly important for improving intersection design, providing infrastructure-based guidance information, and developing capability-enhanced AV perception systems. This study investigated the contributing factors affecting AV driving behavior using the Waymo Open Dataset. Binarized autonomous driving stability metrics, derived via a kernel density estimation, served as the target variables for a random forest classification model. The model’s input variables included 15 factors divided into four types: intersection-related, surrounding object-related, road infrastructure-related, and time-of-day-related types. The random forest classification model was… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Mohammed M. Alenazi*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075966
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Integrating Computing Technology of Cloud-Fog-Edge Environments and its Application)
Abstract Multimodal spatiotemporal data from smart city consumer electronics present critical challenges including cross-modal temporal misalignment, unreliable data quality, limited joint modeling of spatial and temporal dependencies, and weak resilience to adversarial updates. To address these limitations, EdgeST-Fusion is introduced as a cross-modal federated graph transformer framework for context-aware smart city analytics. The architecture integrates cross-modal embedding networks for modality alignment, graph transformer encoders for spatial dependency modeling, temporal self-attention for dynamic pattern learning, and adaptive anomaly detection to ensure data quality and security during aggregation. A privacy-preserving federated learning protocol with differential privacy guarantees enables… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Randika K. Makumbura1, Hasanthi Wijesundara2, Hirushan Sajindra1, Upaka Rathnayake1,*, Vikram Kumar3, Dineshbabu Duraibabu1, Sumit Sen3
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075539
Abstract Accurate streamflow prediction is essential for flood warning, reservoir operation, irrigation scheduling, hydropower planning, and sustainable water management, yet remains challenging due to the complexity of hydrological processes. Although data-driven models often outperform conventional physics-based hydrological modelling approaches, their real-world deployment is limited by cost, infrastructure demands, and the interdisciplinary expertise required. To bridge this gap, this study developed QPred, a regional, lightweight, cost-effective, web-delivered application for daily streamflow forecasting. The study executed an end-to-end workflow, from field data acquisition to accessible web-based deployment for on-demand forecasting. High-resolution rainfall data were recorded with tipping-bucket gauges… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Xuehan Li1, Tao Jing2, Yang Wang2, Bo Gao3, Jing Ai4, Minghao Zhu5,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075426
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Integrating Computing Technology of Cloud-Fog-Edge Environments and its Application)
Abstract With the deep integration of cloud computing, edge computing and the Internet of Things (IoT) technologies, smart manufacturing systems are undergoing profound changes. Over the past ten years, an extensive body of research on cloud-edge-end systems has been generated. However, challenges such as heterogeneous data fusion, real-time processing and system optimization still exist, and there is a lack of systematic review studies. In this paper, we review a cloud-edge-end collaborative sensing-communication-computing-control (
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Hamad Ali Abosaq1, Jarallah Alqahtani1,*, Fahad Masood2, Alanoud Al Mazroa3, Muhammad Asad Khan4, Akm Bahalul Haque5
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075250
Abstract The technological advancement of the vehicular Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) into next-generation ITS. The connectivity of IoT nodes enables improved data availability and facilitates automatic control in the ITS environment. The exponential increase in IoT nodes has significantly increased the demand for an energy-efficient, mobility-aware, and secure system for distributed intelligence. This article presents a mobility-aware Deep Reinforcement Learning based Federated Learning (DRL-FL) approach to design an energy-efficient and threat-resilient ITS. In this approach, a Policy Proximal Optimization (PPO)-based DRL agent is first employed for adaptive client selection. Second, More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Chang Xu1,*, Xianbo Yin2, Zhiyong Zhou1, Bomin Liu1
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.074417
Abstract This study presents a hybrid CNN-Transformer model for real-time recognition of affective tactile biosignals. The proposed framework combines convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to extract spatial and local temporal features with the Transformer encoder that captures long-range dependencies in time-series data through multi-head attention. Model performance was evaluated on two widely used tactile biosignal datasets, HAART and CoST, which contain diverse affective touch gestures recorded from pressure sensor arrays. The CNN-Transformer model achieved recognition rates of 93.33% on HAART and 80.89% on CoST, outperforming existing methods on both benchmarks. By incorporating temporal windowing, the model enables More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Shtwai Alsubai1, Abdullah Al Hejaili2, Najib Ben Aoun3,4,*, Amina Salhi5, Vincent Karovič6,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.074057
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Action Recognition: Algorithms, Applications, and Emerging Trends)
Abstract The concept of Human Activity Recognition (HAR) is integral to applications based on Internet of Things (IoT)-enabled devices, particularly in healthcare, fitness tracking, and smart environments. The streams of data from wearable sensors are rich in information, yet their high dimensionality and variability pose a significant challenge to proper classification. To address this problem, this paper proposes hybrid architectures that integrate traditional machine learning models with a deep neural network (DNN) to deliver improved performance and enhanced capabilities for HAR tasks. Multi-sensor HAR data were used to systematically test several hybrid models, including: RF +… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Xiaocong Wang1, Jiajian Li1, Peng Zhao1, Hui Lian2, Yanjun Shi1,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075202
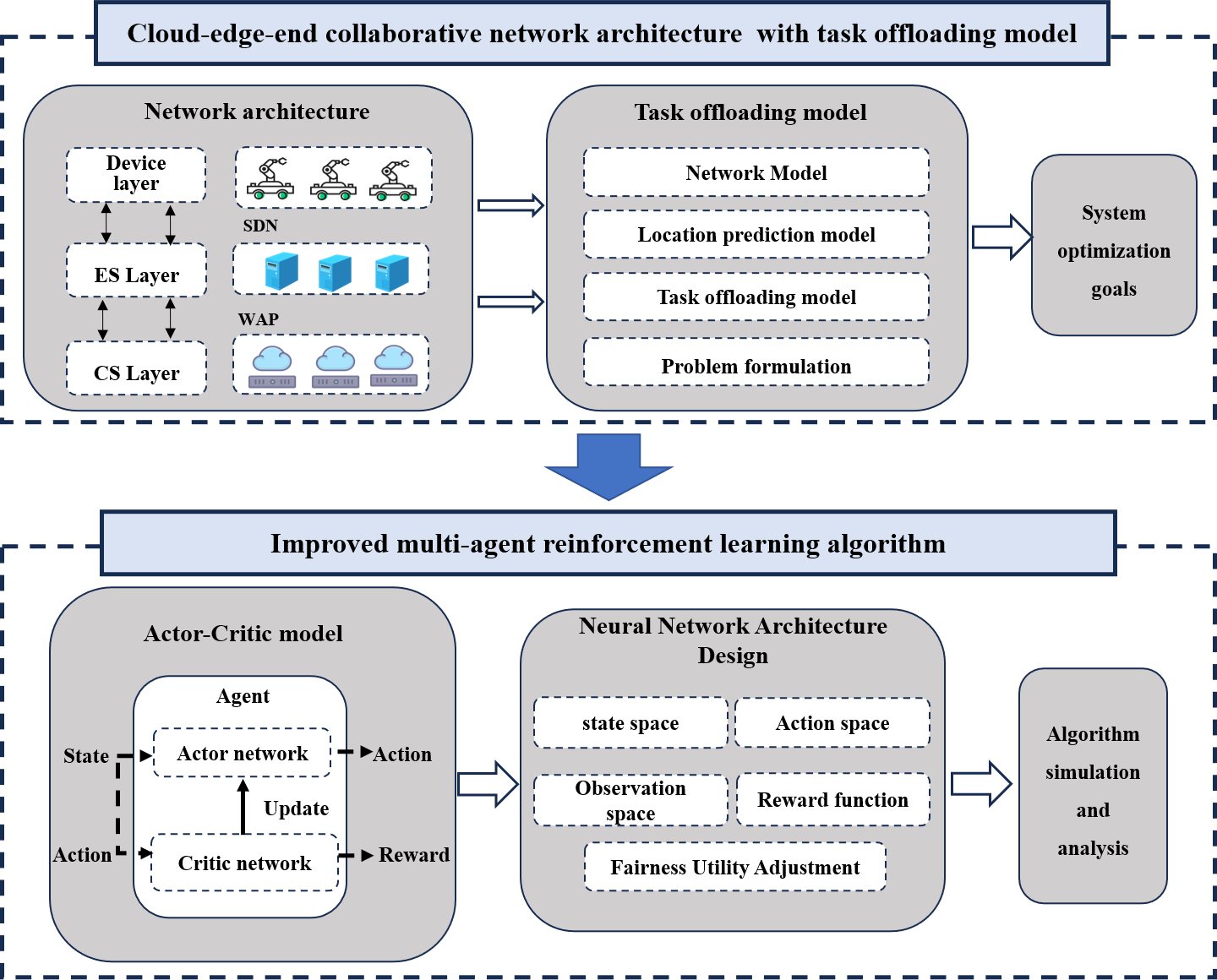
Abstract With the widespread deployment of assembly robots in smart manufacturing, efficiently offloading tasks and allocating resources in highly dynamic industrial environments has become a critical challenge for Mobile Edge Computing (MEC). To address this challenge, this paper constructs a cloud-edge-end collaborative MEC system that enables assembly robots to offload complex workflow tasks via multiple paths (horizontal, vertical, and hybrid collaboration). To mitigate uncertainties arising from mobility, the location prediction module is employed. This enables proactive channel-quality estimation, providing forward-looking insights for offloading decisions. Furthermore, we propose a fairness-aware joint optimization framework. Utilizing an improved Multi-Agent More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Gang Hou1,#, Aifeng Liu1,#, Tao Zhao1, Wenyuan Wei2, Bo Li1, Jiancheng Liu3,*, Siwen Wei4,5,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.073202
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Cooperation and Autonomy in Multi-Agent Systems: Models, Algorithms, and Applications)
Abstract Cooperative multi-UAV search requires jointly optimizing wide-area coverage, rapid target discovery, and endurance under sensing and motion constraints. Resolving this coupling enables scalable coordination with high data efficiency and mission reliability. We formulate this problem as a discounted Markov decision process on an occupancy grid with a cellwise Bayesian belief update, yielding a Markov state that couples agent poses with a probabilistic target field. On this belief–MDP we introduce a segment-conditioned latent-intent framework, in which a discrete intent head selects a latent skill every K steps and an intra-segment GRU policy generates per-step control conditioned on More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Awais Ahmad1, Fakhri Alam Khan2,3, Awais Ahmad4, Gautam Srivastava5,6,7, Syed Atif Moqurrab8,*, Abdul Razaque9, Dina S. M. Hassan10,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076104
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Complex Network Approaches for Resilient and Efficient Urban Transportation Systems)
Abstract Collision avoidance is recognized as a critical challenge in Vehicular Ad-Hoc Networks (VANETs), which demand real-time decision-making. It plays a vital role in ensuring road safety and traffic efficiency. Traditional approaches like rule-based systems and heuristic methods fail to provide optimal solutions in dynamic and unpredictable traffic scenarios. They cannot balance multiple objectives like minimizing collision risk, ensuring passenger comfort, and optimizing fuel efficiency, leading to suboptimal performance in real-world conditions. To tackle collision avoidance, this paper introduces a novel approach by defining the issue as an optimal control problem and solving it using the… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Shasha Li, Bin Ji*, Xiaodong Liu, Jun Ma, Jie Yu*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076083
Abstract Aligning natural language with operating system (OS) commands allows users to perform complex computer tasks through simple natural language descriptions. However, due to the complex nature of natural language, it still remains challenging to achieve precise alignment. In this paper, we present ComAlign, a Chinese benchmark dataset that pairs Chinese natural language descriptions with corresponding OS commands. ComAlign covers a broad range of
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Sicheng Ma1, Lixiang Zhang2,*, Guocai Chen3, Zeyu Dai3, Junru Zhu4, Wei Fang1,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073572
Abstract Community detection is a fundamental problem in network analysis for identifying densely connected node clusters, with successful applications in diverse fields like social networks, recommendation systems, biology, and cyberattack detection. Overlapping community detection refers to the case of a node belonging to multiple communities simultaneously, which is a much more meaningful and challenging task. Graph representation learning with Evolutionary Computation has been studied well in overlapping community detection to deal with complex network structures and characteristics. However, most of them focus on searching the entire solution space, which can be inefficient and lead to inadequate… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Peiying Zhang1,2, Yihong Yu1,2, Jia Luo3,4,*, Nguyen Gia Ba5, Lizhuang Tan6,7, Lei Shi8
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.076690
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: AI-Driven Next-Generation Networks: Innovations, Challenges, and Applications)
Abstract Next-Generation Networks (NGNs) demand high resilience, dynamic adaptability, and efficient resource utilization to enable ubiquitous connectivity. In this context, the Space-Air-Ground Integrated Network (SAGIN) architecture is uniquely positioned to meet these requirements. However, conventional NGN routing algorithms often fail to account for SAGIN’s intrinsic characteristics, such as its heterogeneous structure, dynamic topology, and constrained resources, leading to suboptimal performance under disruptions such as node failures or cyberattacks. To meet these demands for SAGIN, this study proposes a resilience-oriented routing optimization framework featuring dynamic weighting and multi-objective evaluation. Methodologically, we define three core routing performance metrics,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Viorel Mînzu1,*, Iulian Arama2
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075619
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Machine Learning in the Mechanics of Materials and Structures)
Abstract This work addresses optimality aspects related to composite laminates having layers with different orientations. Regression Neural Networks can model the mechanical behavior of these laminates, specifically the stress-strain relationship. If this model has strong generalization ability, it can be coupled with a metaheuristic algorithm–the PSO algorithm used in this article–to address an optimization problem (OP) related to the orientations of composite laminates. To solve OPs, this paper proposes an optimization framework (OFW) that connects the two components, the optimal solution search mechanism and the RNN model. The OFW has two modules: the search mechanism (Adaptive… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Lei Sun1,2, Jingwen Wang2,*, Peng Hu2, Xiuqing Mao1,2, Cuiyun Hu1,2, Zhihong Wang2
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.073657
Abstract Transformer models face significant computational challenges in private inference (PI). Existing optimization methods often rely on isolated techniques, neglecting joint structural and operational improvements. We propose IG-3D, a unified framework that integrates structured compression and operator approximation through accurate importance assessment. Our approach first evaluates attention head importance using Integrated Gradients (IG), offering greater stability and theoretical soundness than gradient-based methods. We then apply a three-dimensional optimization: (1) structurally pruning redundant attention heads; (2) replacing Softmax with adaptive polynomial approximation to avoid exponential computations; (3) implementing layer-wise GELU substitution to accommodate different layer characteristics. A More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Weiguo Pan1, Songjie Du2,*, Bingxin Xu1, Bin Zhang1, Hongzhe Liu1
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073599
Abstract Traffic sign detection is a critical component of driving systems. Single-stage network-based traffic sign detection algorithms, renowned for their fast detection speeds and high accuracy, have become the dominant approach in current practices. However, in complex and dynamic traffic scenes, particularly with smaller traffic sign objects, challenges such as missed and false detections can lead to reduced overall detection accuracy. To address this issue, this paper proposes a detection algorithm that integrates edge and shape information. Recognizing that traffic signs have specific shapes and distinct edge contours, this paper introduces an edge feature extraction branch More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Evgenii V. Fomin1,2, Ilya A. Bryukhanov1, Natalya A. Grachyova2, Alexander E. Mayer2,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.071952
Abstract It is well known that aluminum and copper exhibit structural phase transformations in quasi-static and dynamic measurements, including shock wave loading. However, the dependence of phase transformations in a wide range of crystallographic directions of shock loading has not been revealed. In this work, we calculated the shock Hugoniot for aluminum and copper in different crystallographic directions ([100], [110], [111], [112], [102], [114], [123], [134], [221] and [401]) of shock compression using molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. The results showed a high pressure (>160 GPa for Cu and >40 GPa for Al) of the FCC-to-BCC transition.… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yao-Hsin Chou1, Cheng-Yen Hua1, Ru-Wei Tseng1, Shu-Yu Kuo2,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.075705
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Heuristic Algorithms for Optimizing Network Technologies: Innovations and Applications)
Abstract The rapid growth of mobile and Internet of Things (IoT) applications in dense urban environments places stringent demands on future Beyond 5G (B5G) or Beyond 6G (B6G) networks, which must ensure high Quality of Service (QoS) while maintaining cost-efficiency and sustainable deployment. Traditional strategies struggle with complex 3D propagation, building penetration loss, and the balance between coverage and infrastructure cost. To address this challenge, this study presents the first application of a Global-best Guided Quantum-inspired Tabu Search with Quantum-Not Gate (GQTS-QNG) framework for 3D base-station deployment optimization. The problem is formulated as a multi-objective model… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Zhanglei Wang1,2, Shuo Yan1,2, Jingyu Gao1,2, Haoyu Wu1,2, Baili Wang1,2, Xiuying Zhao1,2,*, Shikai Hu1,2,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.075667
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Machine Learning Methods in Materials Science)
Abstract The glass transition temperature (Tg) of styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is a key parameter determining its low-temperature flexibility and processing performance. Accurate prediction of Tg is crucial for material design and application optimisation. Addressing the limitations of traditional experimental measurements and theoretical models in terms of efficiency, cost, and accuracy, this study proposes a machine learning prediction framework that integrates multi-model ensemble and Bayesian optimization by constructing a multi-component feature dataset and algorithm optimization strategy. Based on the constructed high-quality dataset containing 96 SBR samples, nine machine learning models were employed to predict the Tg of SBR and… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Heesoo Kim1, Minwook Kim1, Hyorim Han2, Soongbong Lee2, Tai-jin Song1,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.074802
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: AI-Driven Big Data Analytics for Sustainable Mixed Traffic and Mobility Systems)
Abstract Autonomous vehicles operate without direct human intervention, which introduces safety risks that differ from those of conventional vehicles. Although many studies have examined safety issues related to autonomous driving, high-risk situations have often been defined using single indicators, making it difficult to capture the complex and evolving nature of accident risk. To address this limitation, this study proposes a structured framework for defining and analyzing high-risk situations throughout the traffic accident process. High-risk situations are described using three complementary indicators: accident likelihood, accident severity, and accident duration. These indicators explain how risk emerges, increases, and… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Mohammad Nauman*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.077259
Abstract Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly utilized for semantic understanding and reasoning, yet their use in sensitive settings is limited by privacy concerns. This paper presents In-Mig, a mobile-agent architecture that integrates LLM reasoning within agents that can migrate across organizational venues. Unlike centralized approaches, In-Mig performs reasoning in situ, ensuring that raw data remains within institutional boundaries while allowing for cross-venue synthesis. The architecture features a policy-scoped memory model, utility-driven route planning, and cryptographic trust enforcement. A prototype using JADE for mobility and quantized Mistral-7B demonstrates practical feasibility. Evaluation across various scenarios shows that In-Mig achieves More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Muhammad Ishtiaq1, Yeon-Ju Lee2, Annabathini Geetha Bhavani3, Sung-Gyu Kang1,*, Nagireddy Gari Subba Reddy2,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075957
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: M5S: Multiphysics Modelling of Multiscale and Multifunctional Materials and Structures)
Abstract Lithium manganese silicate (Li-Mn-Si-O) cathodes are key components of lithium-ion batteries, and their physical and mechanical properties are strongly influenced by their underlying crystal structures. In this study, a range of machine learning (ML) algorithms were developed and compared to predict the crystal systems of Li-Mn-Si-O cathode materials using density functional theory (DFT) data obtained from the Materials Project database. The dataset comprised 211 compositions characterized by key descriptors, including formation energy, energy above the hull, bandgap, atomic site number, density, and unit cell volume. These features were utilized to classify the materials into monoclinic… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Xi Cai, Xiaoqiang Wang, Huiying Zhao, Guang Han*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075756
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Development and Application of Deep Learning and Image Processing)
Abstract Low-light image enhancement (LLIE) remains challenging due to underexposure, color distortion, and amplified noise introduced during illumination correction. Existing deep learning–based methods typically apply uniform enhancement across the entire image, which overlooks scene semantics and often leads to texture degradation or unnatural color reproduction. To overcome these limitations, we propose a Semantic-Guided Visual Mamba Network (SGVMNet) that unifies semantic reasoning, state-space modeling, and mixture-of-experts routing for adaptive illumination correction. SGVMNet comprises three key components: (1) a semantic modulation module (SMM) that extracts scene-aware semantic priors from pretrained multimodal models—Large Language and Vision Assistant (LLaVA) and… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Guotai Huang, Xiyu Gao, Peng Liu, Liming Zhou*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.074941
Abstract To address the insufficient prediction accuracy of multi-state parameters in electro-hydraulic servo material fatigue testing machines under complex loading and nonlinear coupling conditions, this paper proposes a multivariate sequence-to-sequence prediction model integrating a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) encoder, a Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) decoder, and a multi-head attention mechanism. This approach enhances prediction accuracy and robustness across different control modes and load spectra by leveraging multi-channel inputs and cross-variable feature interactions, thereby capturing both short-term high-frequency dynamics and long-term slow drift characteristics. Experiments using long-term data from real test benches demonstrate that the model achieves… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yingli Liu1,2, Weiyong Tang1,2, Xiao Yang1,2, Jiancheng Yin3,*, Haihe Zhou1,2
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.074681
Abstract Quantitative analysis of aluminum-silicon (Al-Si) alloy microstructure is crucial for evaluating and controlling alloy performance. Conventional analysis methods rely on manual segmentation, which is inefficient and subjective, while fully supervised deep learning approaches require extensive and expensive pixel-level annotated data. Furthermore, existing semi-supervised methods still face challenges in handling the adhesion of adjacent primary silicon particles and effectively utilizing consistency in unlabeled data. To address these issues, this paper proposes a novel semi-supervised framework for Al-Si alloy microstructure image segmentation. First, we introduce a Rotational Uncertainty Correction Strategy (RUCS). This strategy employs multi-angle rotational perturbations… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Samia Allaoua Chelloug1,*, Ahmed A. Abd El-Latif2,3,*, Samah AlShathri1, Mohamed Hammad2,4
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.074485
Abstract Scene recognition is a critical component of computer vision, powering applications from autonomous vehicles to surveillance systems. However, its development is often constrained by a heavy reliance on large, expensively annotated datasets. This research presents a novel, efficient approach that leverages multi-model transfer learning from pre-trained deep neural networks—specifically DenseNet201 and Visual Geometry Group (VGG)—to overcome this limitation. Our method significantly reduces dependency on vast labeled data while achieving high accuracy. Evaluated on the Aerial Image Dataset (AID) dataset, the model attained a validation accuracy of 93.6% with a loss of 0.35, demonstrating robust performance More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Wang Cheng1, Zhuodong Liu2, Xiangyu Li3,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074250
Abstract Smart pest control is crucial for building farm resilience and ensuring sustainable agriculture in the face of climate change and environmental challenges. To achieve effective intelligent monitoring systems, agricultural pest and disease detection must overcome three fundamental challenges: feature degradation in dense vegetation environments, limited detection capability for sub-
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Seunggyu Byeon1, Jung-hun Lee2, Jong-Deok Kim3,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074033
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Recent Fuzzy Techniques in Image Processing and its Applications)
Abstract This paper introduces a fuzzy C-means-based pooling layer for convolutional neural networks that explicitly models local uncertainty and ambiguity. Conventional pooling operations, such as max and average, apply rigid aggregation and often discard fine-grained boundary information. In contrast, our method computes soft memberships within each receptive field and aggregates cluster-wise responses through membership-weighted pooling, thereby preserving informative structure while reducing dimensionality. Being differentiable, the proposed layer operates as standard two-dimensional pooling. We evaluate our approach across various CNN backbones and open datasets, including CIFAR-10/100, STL-10, LFW, and ImageNette, and further probe small training set restrictions More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Anfeng Yang, Fei Kang, Wenjuan Bu*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073979
Abstract Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated significant capabilities in semantic understanding and code generation. However, cybersecurity tasks often require prompting the adaptation of open-source models to this domain. Despite their effectiveness, large-parameter LLMs incur substantial memory usage and runtime costs during task inference and downstream fine-tuning for cybersecurity applications. In this study, we fine-tuned six LLMs with parameters under 4 billion using LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation) on specific cybersecurity instruction datasets, employing evaluation metrics similar to Hackmentor. Results indicate that post-fine-tuning, smaller models achieved victory or parity rates up to 85% against larger models like Qwen-1.5-14B… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Boram Kim, Guebin Choi*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073500
Abstract Traditional anomaly detection methods often assume that data points are independent or exhibit regularly structured relationships, as in Euclidean data such as time series or image grids. However, real-world data frequently involve irregular, interconnected structures, requiring a shift toward non-Euclidean approaches. This study introduces a novel anomaly detection framework designed to handle non-Euclidean data by modeling transactions as graph signals. By leveraging graph convolution filters, we extract meaningful connection strengths that capture relational dependencies often overlooked in traditional methods. Utilizing the Graph Convolutional Networks (GCN) framework, we integrate graph-based embeddings with conventional anomaly detection models, More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Tianze Yu, Jianxun Zhang*, Hongji Chen
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.073119
Abstract Camouflaged Object Detection (COD) aims to identify objects that share highly similar patterns—such as texture, intensity, and color—with their surrounding environment. Due to their intrinsic resemblance to the background, camouflaged objects often exhibit vague boundaries and varying scales, making it challenging to accurately locate targets and delineate their indistinct edges. To address this, we propose a novel camouflaged object detection network called Edge-Guided and Multi-scale Fusion Network (EGMFNet), which leverages edge-guided multi-scale integration for enhanced performance. The model incorporates two innovative components: a Multi-scale Fusion Module (MSFM) and an Edge-Guided Attention Module (EGA). These designs… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Nataliya Kazantseva1,2,*, Nikolai Saharov1, Denis Davydov1,2, Nikolai Popov2, Maxim Il’inikh1
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.073078
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Perspective Materials for Science and Industrial: Modeling and Simulation)
Abstract Because of the developed surface of the Triply Periodic Minimum Surface (TPMS) structures, polylactide (PLA) products with a TPMS structure are thought to be promising bio soluble implants with the potential for targeted drug delivery. For implants, mechanical properties are key performance characteristics, so understanding the deformation and failure mechanisms is essential for selecting the appropriate implant structure. The deformation and fracture processes in PLA samples with different interior architectures have been studied through computer simulation and experimental research. Two TPMS topologies, the Schwarz Diamond and Gyroid architectures, were used for the sample construction by… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Sin-Ye Jhong1, Hui-Che Hsu1,2, Hsin-Hua Huang2, Chih-Hsien Hsia3,4,*, Yulius Harjoseputro2,5, Yung-Yao Chen2,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.072633
Abstract Automated grading of dandruff severity is a clinically significant but challenging task due to the inherent ordinal nature of severity levels and the high prevalence of label noise from subjective expert annotations. Standard classification methods fail to address these dual challenges, limiting their real-world performance. In this paper, a novel, three-phase training framework is proposed that learns a robust ordinal classifier directly from noisy labels. The approach synergistically combines a rank-based ordinal regression backbone with a cooperative, semi-supervised learning strategy to dynamically partition the data into clean and noisy subsets. A hybrid training objective is… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Jianzhong Chen, Yunsheng Xu, Zirui Guo, Tianmin Liu, Ying Pan*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.071777
Abstract The rapid development of information technology and accelerated digitalization have led to an explosive growth of data across various fields. As a key technology for knowledge representation and sharing, knowledge graphs play a crucial role by constructing structured networks of relationships among entities. However, data sparsity and numerous unexplored implicit relations result in the widespread incompleteness of knowledge graphs. In static knowledge graph completion, most existing methods rely on linear operations or simple interaction mechanisms for triple encoding, making it difficult to fully capture the deep semantic associations between entities and relations. Moreover, many methods… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Sangeeta Mittal1, Chetna Gupta1, Varun Gupta2,3,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.071599
Abstract This survey presents a comprehensive examination of sensor fusion research spanning four decades, tracing the methodological evolution, application domains, and alignment with classical hierarchical models. Building on this long-term trajectory, the foundational approaches such as probabilistic inference, early neural networks, rule-based methods, and feature-level fusion established the principles of uncertainty handling and multi-sensor integration in the 1990s. The fusion methods of 2000s marked the consolidation of these ideas through advanced Kalman and particle filtering, Bayesian–Dempster–Shafer hybrids, distributed consensus algorithms, and machine learning ensembles for more robust and domain-specific implementations. From 2011 to 2020, the widespread… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Lixing Tan1,2, Liusiyu Chen1, Yang Wang1, Zhenyu Song1,*, Zenan Lu1,3,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075959
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advanced Networking Technologies for Intelligent Transportation and Connected Vehicles)
Abstract Anomaly detection is a vibrant research direction in controller area networks, which provides the fundamental real-time data transmission underpinning in-vehicle data interaction for the internet of vehicles. However, existing unsupervised learning methods suffer from insufficient temporal and spatial constraints on shallow features, resulting in fragmented feature representations that compromise model stability and accuracy. To improve the extraction of valuable features, this paper investigates the influence of clustering constraints on shallow feature convergence paths at the model level and further proposes an end-to-end intrusion detection system based on efficient deep embedded subspace clustering (EDESC-IDS). Following the… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Ksenia Kharitonova1, David Pérez-Fernández2, Zoraida Callejas1,3, David Griol1,3,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075777
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Security and Robustness of Large Language Models (LLMs))
Abstract Building reliable intent-based, task-oriented dialog systems typically requires substantial manual effort: designers must derive intents, entities, responses, and control logic from raw conversational data, then iterate until the assistant behaves consistently. This paper investigates how far large language models (LLMs) can automate this development. In this paper, we use two reference corpora, Let’s Go (English, public transport) and MEDIA (French, hotel booking), to prompt four LLM families (GPT-4o, Claude, Gemini, Mistral Small) and generate the core specifications required by the
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Zhengyu Wu1, Kejun Kang2, Yixiu Liu3,*, Chenpu Li3
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.075593
Abstract Binary segmentation tasks in computer vision exhibit diverse appearance distributions and complex boundary characteristics. To address the limited generalization and adaptability of existing models across heterogeneous tasks, we propose Abel-Net, an Aggregated Bilateral Edge Localization Network designed as a universal framework for multi-task binary segmentation. Abel-Net integrates global and local contextual cues to enhance feature learning and edge precision. Specifically, a multi-scale feature pyramid fusion strategy is implemented via an Aggregated Skip Connection (ASC) module to strengthen feature adaptability, while the Edge Dual Localization (EDL) mechanism performs coarse-to-fine refinement through edge-aware supervision. Additionally, Edge Attention More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Shih-Ming Cho1, Sung-Wen Wang1, Min-Chie Chiu2,*, Shao-Chun Chen1
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074911
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Development and Application of Deep Learning based Object Detection)
Abstract To address crop depredation by intelligent species (e.t, macaques) and the habituation from traditional methods, this study proposes an intelligent, closed-loop, adaptive laser deterrence system. A core contribution is an efficient multi-stage Semi-Supervised Learning (SSL) and incremental fine-tuning (IFT) framework, which reduced manual annotation by ~60% and training time by ~68%. This framework was benchmarked against YOLOv8n, v10n, and v11n. Our analysis revealed that YOLOv12n’s high Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) (47.1% retention) pseudo-labels made it the only model to gain performance (+0.010 mAP) from SSL, allowing it to overtake competitors. Subsequently, in the IFT stress test,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Talha Farooq Khan1, Fahad Ali2, Majid Hussain1, Lal Khan3,*, Hsien-Tsung Chang4,5,6,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074557
Abstract The outstanding growth in the applications of large language models (LLMs) demonstrates the significance of adaptive and efficient prompt engineering tactics. The existing methods may not be variable, vigorous and streamlined in different domains. The offered study introduces an immediate optimization outline, named PROMPTx-PE, that is going to yield a greater level of precision and strength when it comes to the assignments that are premised on LLM. The proposed system features a timely selection scheme which is informed by reinforcement learning, a contextual layer and a dynamic weighting module which is regulated by Lyapunov-based stability More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Zhendong Du*, Hanliu Wang, Kenji Hashimoto
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074520
Abstract Planning in lexical-prior-free environments presents a fundamental challenge for evaluating whether large language models (LLMs) possess genuine structural reasoning capabilities beyond lexical memorization. When predicates and action names are replaced with semantically irrelevant random symbols while preserving logical structures, existing direct generation approaches exhibit severe performance degradation. This paper proposes a symbol-agnostic closed-loop planning pipeline that enables models to construct executable plans through systematic validation and iterative refinement. The system implements a complete generate-verify-repair cycle through six core processing components: semantic comprehension extracts structural constraints, language planner generates text plans, symbol translator performs structure-preserving mapping,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Naresh Kumar1, Anuj Kumar1,*, Abhishek K. Mishra2,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074430
Abstract Density functional theory (DFT) calculations were employed to investigate the adsorption behavior of NH3, AsH3, PH3, CO2, and CH4 molecules on both pristine and mono-vacancy phosphorene sheets. The pristine phosphorene surface shows weak physisorption with all the gas molecules, inducing only minor changes in its structural and electronic properties. However, the introduction of mono-vacancies significantly enhances the interaction strength with NH3, PH3, CO2, and CH4. These variations are attributed to substantial charge redistribution and orbital hybridization in the presence of defects. The defective phosphorene sheet also exhibits enhanced adsorption energies, along with favorable sensitivity and recovery characteristics, highlighting its potential More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Argho Dey1, Yunfei Yin1,2,*, Zheng Yuan1, Zhiwen Zeng1, Xianjian Bao3, Md Minhazul Islam1
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074122
Abstract Autonomous vehicles rely heavily on accurate and efficient scene segmentation for safe navigation and efficient operations. Traditional Bird’s Eye View (BEV) methods on semantic scene segmentation, which leverage multimodal sensor fusion, often struggle with noisy data and demand high-performance GPUs, leading to sensor misalignment and performance degradation. This paper introduces an Enhanced Channel Attention BEV (ECABEV), a novel approach designed to address the challenges under insufficient GPU memory conditions. ECABEV integrates camera and radar data through a de-noise enhanced channel attention mechanism, which utilizes global average and max pooling to effectively filter out noise while… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Fawad Salam Khan1,*, Noman Hasany2, Muzammil Ahmad Khan3, Shayan Abbas4, Sajjad Ahmed5, Muhammad Zorain6, Wai Yie Leong7,*, Susama Bagchi8, Sanjoy Kumar Debnath8
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.072893
Abstract The initial noise present in the depth images obtained with RGB-D sensors is a combination of hardware limitations in addition to the environmental factors, due to the limited capabilities of sensors, which also produce poor computer vision results. The common image denoising techniques tend to remove significant image details and also remove noise, provided they are based on space and frequency filtering. The updated framework presented in this paper is a novel denoising model that makes use of Boruta-driven feature selection using a Long Short-Term Memory Autoencoder (LSTMAE). The Boruta algorithm identifies the most useful… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Cosmin Dumitru, Emanuel Pantelimon, Alexandru Guzu, Georgian Nicolae*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072749
Abstract Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), especially quadcopters, have become indispensable in numerous industrial and scientific applications due to their flexibility, low cost, and capability to operate in dynamic environments. This paper presents a complete design and implementation of a compact autonomous quadcopter capable of trajectory tracking, object detection, precision landing, and real-time telemetry via long-range communication protocols. The system integrates an onboard flight controller running real-time sensor fusion algorithms, a vision-based detection system on a companion single-board computer, and a telemetry unit using Long Range (LoRa) communication. Extensive flight tests were conducted to validate the system’s More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Nouf Abdullah Almujally1, Tanvir Fatima Naik Bukht2, Shuaa S. Alharbi3, Asaad Algarni4, Ahmad Jalal2,5, Jeongmin Park6,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072243
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Object Detection and Recognition)
Abstract Recognising human-object interactions (HOI) is a challenging task for traditional machine learning models, including convolutional neural networks (CNNs). Existing models show limited transferability across complex datasets such as D3D-HOI and SYSU 3D HOI. The conventional architecture of CNNs restricts their ability to handle HOI scenarios with high complexity. HOI recognition requires improved feature extraction methods to overcome the current limitations in accuracy and scalability. This work proposes a Novel quantum gate-enabled hybrid CNN (QEH-CNN) for effective HOI recognition. The model enhances CNN performance by integrating quantum computing components. The framework begins with bilateral image filtering,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Tran Minh Bao1, Kumar Shashvat2, Nguyen Gia Nhu3,*, Dac-Nhuong Le4
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.075161
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Artificial Intelligence Methods and Techniques to Cybersecurity)
Abstract The sudden growth of harmful web pages, including spam and phishing URLs, poses a greater threat to global cybersecurity than ever before. These URLs are commonly utilised to trick people into divulging confidential details or to stealthily deploy malware. To address this issue, we aimed to assess the efficiency of popular machine learning and neural network models in identifying such harmful links. To serve our research needs, we employed two different datasets: the PhiUSIIL dataset, which is specifically designed to address phishing URL detection, and another dataset developed to uncover spam links by examining the… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Hui Yu1, Jun Liu1,*, Mingwei Lin2,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074191
Abstract Small object detection has been a focus of attention since the emergence of deep learning-based object detection. Although classical object detection frameworks have made significant contributions to the development of object detection, there are still many issues to be resolved in detecting small objects due to the inherent complexity and diversity of real-world visual scenes. In particular, the YOLO (You Only Look Once) series of detection models, renowned for their real-time performance, have undergone numerous adaptations aimed at improving the detection of small targets. In this survey, we summarize the state-of-the-art YOLO-based small object detection More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Zheng Zhao1, Doo Heon Song2, Kwang Baek Kim1,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2026.073969
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Recent Fuzzy Techniques in Image Processing and its Applications)
Abstract Deep learning attention mechanisms have achieved remarkable progress in computer vision, but still face limitations when handling images with ambiguous boundaries and uncertain feature representations. Conventional attention modules such as SE-Net, CBAM, ECA-Net, and CA adopt a deterministic paradigm, assigning fixed scalar weights to features without modeling ambiguity or confidence. To overcome these limitations, this paper proposes the Fuzzy Attention Network Layer (FANL), which integrates intuitionistic fuzzy set theory with convolutional neural networks to explicitly represent feature uncertainty through membership (
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Chih-Chieh Chang*, Khairul Izyan Bin Anuar, Yu-Hwa Liu
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073177
Abstract Small datasets are often challenging due to their limited sample size. This research introduces a novel solution to these problems: average linkage virtual sample generation (ALVSG). ALVSG leverages the underlying data structure to create virtual samples, which can be used to augment the original dataset. The ALVSG process consists of two steps. First, an average-linkage clustering technique is applied to the dataset to create a dendrogram. The dendrogram represents the hierarchical structure of the dataset, with each merging operation regarded as a linkage. Next, the linkages are combined into an average-based dataset, which serves as… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Md. Al-Hasan1, Mst. Rubina Aktar2, Fahmid Al Farid3,4,*, Md. Shamim Anower5, Abu Saleh Musa Miah1,6, Md. Hezerul Abdul Karim4,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.071280
Abstract The rapid growth in available network bandwidth has directly contributed to an exponential increase in mobile data traffic, creating significant challenges for network energy consumption. Also, with the extraordinary growth of mobile communications, the data traffic has dramatically expanded, which has led to massive grid power consumption and incurred high operating expenditure (OPEX). However, the majority of current network designs struggle to efficiently manage a massive amount of data using little power, which degrades energy efficiency performance. Thereby, it is necessary to have an efficient mechanism to reduce power consumption when processing large amounts of… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Oumaima Saidani1, Nazia Azim2, Ateeq Ur Rehman3,*, Akbayan Bekarystankyzy4, Hala AbdelHameed Mostafa5, Mohamed R. Abonazel6, Ehab Ebrahim Mohamed Ebrahim7, Sarah Abu Ghazalah8
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072772
Abstract The convergence of Software Defined Networking (SDN) in Internet of Vehicles (IoV) enables a flexible, programmable, and globally visible network control architecture across Road Side Units (RSUs), cloud servers, and automobiles. While this integration enhances scalability and safety, it also raises sophisticated cyberthreats, particularly Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. Traditional rule-based anomaly detection methods often struggle to detect modern low-and-slow DDoS patterns, thereby leading to higher false positives. To this end, this study proposes an explainable hybrid framework to detect DDoS attacks in SDN-enabled IoV (SDN-IoV). The hybrid framework utilizes a Residual Network (ResNet)… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yiming Yu1, Yunfei Guo2, Junchen Liu3, Yiping Sun4, Junliang Du5,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074959
Abstract Graph neural networks (GNNs) have shown notable success in identifying security vulnerabilities within Ethereum smart contracts by capturing structural relationships encoded in control- and data-flow graphs. Despite their effectiveness, most GNN-based vulnerability detectors operate as black boxes, making their decisions difficult to interpret and thus less suitable for critical security auditing. The information bottleneck (IB) principle provides a theoretical framework for isolating task-relevant graph components. However, existing IB-based implementations often encounter unstable optimization and limited understanding of code semantics. To address these issues, we introduce ContractGIB, an interpretable graph information bottleneck framework for function-level vulnerability More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Omar Almomani1,*, Mahran Al-Zyoud1, Ahmad Adel Abu-Shareha2, Ammar Almomani3,4,*, Said A. Salloum5, Khaled Mohammad Alomari6
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.075465
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Heuristic Algorithms for Optimizing Network Technologies: Innovations and Applications)
Abstract In Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs), survivability is a crucial issue that is greatly impacted by energy efficiency. Solutions that satisfy application objectives while extending network life are needed to address severe energy constraints in WSNs. This paper presents an Adaptive Enhanced Grey Wolf Optimizer (AEGWO) for energy-efficient cluster head (CH) selection that mitigates the exploration–exploitation imbalance, preserves population diversity, and avoids premature convergence inherent in baseline GWO. The AEGWO combines adaptive control of the parameter of the search pressure to accelerate convergence without stagnation, a hybrid velocity-momentum update based on the dynamics of PSO, and… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Changxu Zhao1, Jianping Liu1,*, Xiaofeng Wang1, Wei Sun2, Libo Liu3, Haiyu Ren1, Pan Liu1, Qiantong Wang1
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074409
Abstract Foundation models are reshaping artificial intelligence, yet their deployment in specialised domains such as agricultural question answering (AQA) still faces challenges including data scarcity and barriers to domain-specific knowledge. To systematically review recent progress in this area, this paper adopts a task–paradigm perspective and examines applications across three major AQA task families. For text-based QA, we analyse the strengths and limitations of retrieval-based, generative, and hybrid approaches built on large language models, revealing a clear trend toward hybrid paradigms that balance precision and flexibility. For visual diagnosis, we discuss techniques such as cross-modal alignment and More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yuji Sang1, Lijun Liu1,*, Long Lv1,*, Husheng Wu2, Hemin Yin1
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073837
Abstract Aiming at the challenges of low throughput, excessive consensus latency and high communication complexity in the Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) algorithm in blockchain networks, its application in identity verification for distributed networking of a drone cluster is limited. Therefore, a lightweight blockchain-based identity authentication model for UAV swarms is designed, and a Credit-score and Grouping-mechanism Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (CG-PBFT) algorithm is proposed. CG-PBFT introduces a reputation score evaluation mechanism, classifies the reputation levels of nodes in the network, and optimizes the consensus process based on grouping consensus and BLS aggregate signature technology. Experimental More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Chiwan Ahn1, Daehee Kim2,*, Seongkeun Park3,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073330
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Object Detection: Methods and Applications)
Abstract This paper proposes a deep learning-based 3D LiDAR perception framework designed for applications such as autonomous robots and vehicles. To address the high dependency on large-scale annotated data—an inherent limitation of deep learning models—this study introduces a hybrid perception architecture that incorporates expert-driven LiDAR processing techniques into the deep neural network. Traditional 3D LiDAR processing methods typically remove ground planes and apply distance- or density-based clustering for object detection. In this work, such expert knowledge is encoded as feature-level inputs and fused with the deep network, thereby mitigating the data dependency issue of conventional learning-based… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Hafiz Burhan Ul Haq1, Waseem Akram2, Haroon ur Rashid Kayani3, Khalid Mahmood4,*, Chihhsiong Shih5, Rupak Kharel6,7, Amina Salhi8
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073188
Abstract The Internet of Things (IoT) is a new model that evolved with the rapid progress of advanced technology and gained tremendous popularity due to its applications. Anomaly detection has widely attracted researchers’ attention in the last few years, and its effects on diverse applications. This review article covers the various methods and tools developed to perform the task efficiently and automatically in a smart city. In this work, we present a comprehensive literature review (2011 onwards) of three major types of anomalies: network anomalies, sensor anomalies, and video-based anomalies, along with their methods and software… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Le Thi Hong Van1,*, Le Duc Thuan1, Pham Van Huong1, Nguyen Hieu Minh2
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.075027
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence for Intrusion Detection Systems)
Abstract Optimizing convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for IoT attack detection remains a critical yet challenging task due to the need to balance multiple performance metrics beyond mere accuracy. This study proposes a unified and flexible optimization framework that leverages metaheuristic algorithms to automatically optimize CNN configurations for IoT attack detection. Unlike conventional single-objective approaches, the proposed method formulates a global multi-objective fitness function that integrates accuracy, precision, recall, and model size (speed/model complexity penalty) with adjustable weights. This design enables both single-objective and weighted-sum multi-objective optimization, allowing adaptive selection of optimal CNN configurations for diverse deployment… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Qingwen Yang1, Zhi Li2, Jiawei Tang1, Yanyi Liu1, Tiezheng Guo1, Yingyou Wen1,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074384
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Intelligent Computation and Large Machine Learning Models for Edge Intelligence in industrial Internet of Things)
Abstract Deploying Large Language Model (LLM)-based agents in the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) presents significant challenges, including high latency from cloud-based APIs, data privacy concerns, and the infeasibility of deploying monolithic models on resource-constrained edge devices. While smaller models (SLMs) are suitable for edge deployment, they often lack the reasoning power for complex, multi-step tasks. To address these issues, this paper introduces LEAF, a Lightweight Edge Agent Framework designed for efficiently executing complex tasks at the edge. LEAF employs a novel architecture where multiple expert SLMs—specialized for planning, execution, and interaction—work in concert, decomposing complex… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Md. Ahsan Habib1, Md. Anwar Hussen Wadud2, M. F. Mridha3,*, Md. Jakir Hossen4,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.070235
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Visual and Large Language Models for Generalized Applications)
Abstract The problem of fake news detection (FND) is becoming increasingly important in the field of natural language processing (NLP) because of the rapid dissemination of misleading information on the web. Large language models (LLMs) such as GPT-4. Zero excels in natural language understanding tasks but can still struggle to distinguish between fact and fiction, particularly when applied in the wild. However, a key challenge of existing FND methods is that they only consider unimodal data (e.g., images), while more detailed multimodal data (e.g., user behaviour, temporal dynamics) is neglected, and the latter is crucial for… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Saifullah Tumrani1,2,*, Abdul Jabbar Siddiqui2,3,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.075152
Abstract Vehicle re-identification (ReID) is a challenging task in intelligent transportation, and urban surveillance systems due to its complications in camera viewpoints, vehicle scales, and environmental conditions. Recent transformer-based approaches have shown impressive performance by utilizing global dependencies, these models struggle with aspect ratio distortions and may overlook fine-grained local attributes crucial for distinguishing visually similar vehicles. We introduce a framework based on Swin Transformers that addresses these challenges by implementing three components. First, to improve feature robustness and maintain vehicle proportions, our Aspect Ratio-Aware Swin Transformer (AR-Swin) preserve the native ratio via letterbox, uses a… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Faisal Albalwy1,*, Muhannad Almohaimeed2
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.075098
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Artificial Intelligence Methods and Techniques to Cybersecurity)
Abstract Intrusion detection in Internet of Things (IoT) environments presents challenges due to heterogeneous devices, diverse attack vectors, and highly imbalanced datasets. Existing research on the ToN-IoT dataset has largely emphasized binary classification and single-model pipelines, which often show strong performance but limited generalizability, probabilistic reliability, and operational interpretability. This study proposes a stacked ensemble deep learning framework that integrates random forest, extreme gradient boosting, and a deep neural network as base learners, with CatBoost as the meta-learner. On the ToN-IoT Linux process dataset, the model achieved near-perfect discrimination (macro area under the curve = 0.998),… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Alaa Tolah*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074997
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Artificial Intelligence Algorithms and Applications, 2nd Edition)
Abstract The rapidly evolving cybersecurity threat landscape exposes a critical flaw in traditional educational programs where static curricula cannot adapt swiftly to novel attack vectors. This creates a significant gap between theoretical knowledge and the practical defensive capabilities needed in the field. To address this, we propose TeachSecure-CTI, a novel framework for adaptive cybersecurity curriculum generation that integrates real-time Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) with AI-driven personalization. Our framework employs a layered architecture featuring a CTI ingestion and clustering module, natural language processing for semantic concept extraction, and a reinforcement learning agent for adaptive content sequencing. By… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Nien-Tsu Hu1,*, Hsiang-Tung Kao1, Chin-Sheng Chen1, Shih-Hao Chang2
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074993
Abstract Trajectory tracking for nonlinear robotic systems remains a fundamental yet challenging problem in control engineering, particularly when both precision and efficiency must be ensured. Conventional control methods are often effective for stabilization but may not directly optimize long-term performance. To address this limitation, this study develops an integrated framework that combines optimal control principles with reinforcement learning for a single-link robotic manipulator. The proposed scheme adopts an actor–critic structure, where the critic network approximates the value function associated with the Hamilton–Jacobi–Bellman equation, and the actor network generates near-optimal control signals in real time. This dual… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Chengqi Liu1, Yongtao Li2, Weiping Zou3,*, Deyu Lin4,5,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074975
Abstract With the large-scale deployment of the Internet of Things (IoT) devices, their weak security mechanisms make them prime targets for malware attacks. Attackers often use Domain Generation Algorithm (DGA) to generate random domain names, hiding the real IP of Command and Control (C&C) servers to build botnets. Due to the randomness and dynamics of DGA, traditional methods struggle to detect them accurately, increasing the difficulty of network defense. This paper proposes a lightweight DGA detection model based on knowledge distillation for resource-constrained IoT environments. Specifically, a teacher model combining CharacterBERT, a bidirectional long short-term memory More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Lishu Qin*, Yu Gao, Xinyuan Lu
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074739
Abstract With the rapid development of intelligent navigation technology, efficient and safe path planning for mobile robots has become a core requirement. To address the challenges of complex dynamic environments, this paper proposes an intelligent path planning framework based on grid map modeling. First, an improved Safe and Smooth A* (SSA*) algorithm is employed for global path planning. By incorporating obstacle expansion and corner-point optimization, the proposed SSA* enhances the safety and smoothness of the planned path. Then, a Partitioned Dynamic Window Approach (PDWA) is integrated for local planning, which is triggered when dynamic or sudden… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Mekhled Alharbi1,*, Khalid Haseeb2, Mamoona Humayun3,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073832
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Recent Advances in Blockchain Technology and Applications)
Abstract The Internet of Things (IoT) and cloud computing have significantly contributed to the development of smart cities, enabling real-time monitoring, intelligent decision-making, and efficient resource management. These systems, particularly in IoT networks, rely on numerous interconnected devices that handle time-sensitive data for critical applications. In related approaches, trusted communication and reliable device interaction have been overlooked, thereby lowering security when sharing sensitive IoT data. Moreover, it incurs additional energy consumption and overhead while addressing potential threats in the dynamic environment. In this research, an Artificial Intelligence (AI) recommended fault-tolerant framework is proposed that leverages blockchain More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Shahidatul Sadiah1,#, Toru Nakanishi2,#,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073774
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in IoT Security: Challenges, Solutions, and Future Applications)
Abstract V2X communication enables vehicles to share real-time traffic and road-condition data, but binding messages to persistent identifiers enables location tracking. Furthermore, since forged reports from malicious vehicles can distort trust decisions and threaten road safety, privacy-preserving trust management is essential. Lu et al. previously presented BARS, an anonymous reputation mechanism founded on blockchain technology to establish a privacy-preserving trust architecture for V2X communication. In this system, reputation certificates without a vehicle identifier ensure anonymity, while two authorities jointly manage certificate issuance and reputation updates. However, the centralized certificate updates introduce scalability limitations, and the authorities… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Tomás Bernal-Beltrán1, Ronghao Pan1, José Antonio García-Díaz1, María del Pilar Salas-Zárate2, Mario Andrés Paredes-Valverde2, Rafael Valencia-García1,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073629
Abstract The malicious dissemination of hate speech via compromised accounts, automated bot networks and malware-driven social media campaigns has become a growing cybersecurity concern. Automatically detecting such content in Spanish is challenging due to linguistic complexity and the scarcity of annotated resources. In this paper, we compare two predominant AI-based approaches for the forensic detection of malicious hate speech: (1) fine-tuning encoder-only models that have been trained in Spanish and (2) In-Context Learning techniques (Zero- and Few-Shot Learning) with large-scale language models. Our approach goes beyond binary classification, proposing a comprehensive, multidimensional evaluation that labels each… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Han-Yu Lin, Tung-Tso Tsai*, Yi-Jia Ye
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073553
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in IoT Security: Challenges, Solutions, and Future Applications)
Abstract Cloud data sharing is an important issue in modern times. To maintain the privacy and confidentiality of data stored in the cloud, encryption is an inevitable process before uploading the data. However, the centralized management and transmission latency of the cloud makes it difficult to support real-time processing and distributed access structures. As a result, fog computing and the Internet of Things (IoT) have emerged as crucial applications. Fog-assisted proxy re-encryption is a commonly adopted technique for sharing cloud ciphertexts. It allows a semi-trusted proxy to transform a data owner’s ciphertext into another re-encrypted ciphertext… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Jingru Lv1, Jianpeng Hu1,*, Jin Zhao2, Yonghao Luo1
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073212
Abstract Chinese abbreviations improve communicative efficiency by extracting key components from longer expressions. They are widely used in both daily communication and professional domains. However, existing abbreviation generation methods still face two major challenges. First, sequence-labeling-based approaches often neglect contextual meaning by making binary decisions at the character level, leading to abbreviations that fail to capture semantic completeness. Second, generation-based methods rely heavily on a single decoding process, which frequently produces correct abbreviations but ranks them lower due to inadequate semantic evaluation. To address these limitations, we propose a novel two-stage framework with Generation–Iterative Optimization for More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Zhongfan Sun, Kan Guo, Yongli Hu*, Yong Zhang
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072903
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Large Models and Domain-specific Applications)
Abstract Knowledge-based Visual Question Answering (VQA) requires the integration of visual information with external knowledge reasoning. Existing approaches typically retrieve information from external corpora and rely on pretrained language models for reasoning. However, their performance is often hindered by the limited capabilities of retrievers and the constrained size of knowledge bases. Moreover, relying on image captions to bridge the modal gap between visual and language modalities can lead to the omission of critical visual details. To address these limitations, we propose the Reflective Chain-of-Thought (ReCoT) method, a simple yet effective framework inspired by metacognition theory. ReCoT effectively activates… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Mehran Tarif1, Mohammadhossein Homaei2,*, Abbas Mirzaei3, Babak Nouri-Moghaddam3
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.071676
Abstract The Routing Protocol for Low-power and Lossy Networks (RPL) is widely used in Internet of Things (IoT) systems, where devices usually have very limited resources. However, RPL still faces several problems, such as high energy usage, unstable links, and inefficient routing decisions, which reduce the overall network performance and lifetime. In this work, we introduce TABURPL, an improved routing method that applies Tabu Search (TS) to optimize the parent selection process. The method uses a combined cost function that considers Residual Energy, Transmission Energy, Distance to the Sink, Hop Count, Expected Transmission Count (ETX), and More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Langyue Zhao1,2, Yubin Yuan3,*, Yiquan Wu2,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.070563
Abstract Regular detection of pavement cracks is essential for infrastructure maintenance. However, existing methods often ignore the challenges such as the continuous evolution of crack features between video frames and the difficulty of defect quantification. To this end, this paper proposes an integrated framework for pavement crack detection, segmentation, tracking and counting based on Transformer. Firstly, we design the VitSeg-Det network, which is an integrated detection and segmentation network that can accurately locate and segment tiny cracks in complex scenes. Second, the TransTra-Count system is developed to automatically count the number of defects by combining defect More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Simin Tang1,2,3,4, Zhiyong Zhang1,2,3,4,*, Junyan Pan1,2,3,4, Gaoyuan Quan1,2,3,4, Weiguo Wang5, Junchang Jing6
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073798
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Artificial Intelligence Methods and Techniques to Cybersecurity)
Abstract At inference time, deep neural networks are susceptible to backdoor attacks, which can produce attacker-controlled outputs when inputs contain carefully crafted triggers. Existing defense methods often focus on specific attack types or incur high costs, such as data cleaning or model fine-tuning. In contrast, we argue that it is possible to achieve effective and generalizable defense without removing triggers or incurring high model-cleaning costs. From the attacker’s perspective and based on characteristics of vulnerable neuron activation anomalies, we propose an Adaptive Feature Injection (AFI) method for black-box backdoor detection. AFI employs a pre-trained image encoder… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Zhongbin Luo1,2, Zhaoyang Guan3, Wenxing You2, Yunteng Wang2, Yanqiu Bi4,5,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.075704
Abstract Gait recognition is a key biometric for long-distance identification, yet its performance is severely degraded by real-world challenges such as varying clothing, carrying conditions, and changing viewpoints. While combining silhouette and skeleton data is a promising direction, effectively fusing these heterogeneous modalities and adaptively weighting their contributions in response to diverse conditions remains a central problem. This paper introduces GaitMAFF, a novel Multi-modal Adaptive Feature Fusion Network, to address this challenge. Our approach first transforms discrete skeleton joints into a dense Skeleton Map representation to align with silhouettes, then employs an attention-based module to dynamically More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Weimin Shi1,*, Kuntao Lv1, Chang Xuan1, Ji Wu2
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.075203
Abstract The application of deep learning in fabric defect detection has become increasingly widespread. To address false positives and false negatives in fabric roll seam detection, and to improve automation efficiency and product quality, we propose the Multi-scale Context DeepLabV3+ (MSC-DeepLabV3+), a semantic segmentation network designed for fabric roll seam detection, based on DeepLabV3+. The model improvements include enhancing the backbone performance through optimization of the UIB-MobileNetV2 network; designing the Dynamic Atrous and Sliding-window Fusion (DASF) module to improve adaptability to multi-scale seam structures with dynamic dilation rates and a sliding-window mechanism; and utilizing the Progressive… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Thi-Xuyen Bui1,2, Yu-Sheng Lu1, Yu-Sheng Liao1, Te-Hua Fang1,3,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074862
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Computational Approaches for Tribological Materials and Surface Engineering)
Abstract The mechanical performance of exceedingly soft materials such as Ag is significantly influenced by various working conditions. Therefore, this study systematically investigates the effects of crack geometry, substrate crystal orientation, and indenter shape on crack propagation. The mechanical response of Ag is analyzed using the quasi-continuum (QC) method. A pre-crack with a predefined depth and angle was introduced to initiate fracture behavior. The results show that when the pre-crack height is 50 Å, the crack propagates rapidly as the imprint depth increases from 0 to 7 Å, grows steadily up to 15 Å, and then… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Feihong Xu1, Jianbo Wu1,*, Qing An1,*, Fei Zhu1,2, Zhaoyang Han3, Saru Kumari4
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073441
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in IoT Security: Challenges, Solutions, and Future Applications)
Abstract The large-scale deployment of Internet of Things (IoT) technology across various aspects of daily life has significantly propelled the intelligent development of society. Among them, the integration of IoT and named data networks (NDNs) reduces network complexity and provides practical directions for content-oriented network design. However, ensuring data integrity in NDN-IoT applications remains a challenging issue. Very recently, Wang et al. (Entropy, 27(5), 471(2025)) designed a certificateless aggregate signature (CLAS) scheme for NDN-IoT environments. Wang et al. stated that their construction was provably secure under various types of security attacks. Using theoretical analysis methods, in… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Ping Fang, Mengjun Tong*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073272
Abstract Defect detection in printed circuit boards (PCB) remains challenging due to the difficulty of identifying small-scale defects, the inefficiency of conventional approaches, and the interference from complex backgrounds. To address these issues, this paper proposes SIM-Net, an enhanced detection framework derived from YOLOv11. The model integrates SPDConv to preserve fine-grained features for small object detection, introduces a novel convolutional partial attention module (C2PAM) to suppress redundant background information and highlight salient regions, and employs a multi-scale fusion network (MFN) with a multi-grain contextual module (MGCT) to strengthen contextual representation and accelerate inference. Experimental evaluations demonstrate More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Zhichao Yu1, Jiahui Yu1, Simon James Fong1,*, Yaoyang Wu1,2
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074899
Abstract Accurately recognizing driver distraction is critical for preventing traffic accidents, yet current detection models face two persistent challenges. First, distractions are often fine-grained, involving subtle cues such as brief eye closures or partial yawns, which are easily missed by conventional detectors. Second, in real-world scenarios, drivers frequently exhibit overlapping behaviors, such as simultaneously holding a cup, closing their eyes, and yawning, leading to multiple detection boxes and degraded model performance. Existing approaches fail to robustly address these complexities, resulting in limited reliability in safety-critical applications. To overcome these pain points, we propose YOLO-Drive, a novel… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Liqiu Suo1, Lin Xia1, Yoona Chung1, Eunchan Kim1,2,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.076329
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Big Data Technologies and Applications for a Data-Driven World)
Abstract Accurate purchase prediction in e-commerce critically depends on the quality of behavioral features. This paper proposes a layered and interpretable feature engineering framework that organizes user signals into three layers: Basic, Conversion & Stability (efficiency and volatility across actions), and Advanced Interactions & Activity (cross-behavior synergies and intensity). Using real Taobao (Alibaba’s primary e-commerce platform) logs (57,976 records for 10,203 users; 25 November–03 December 2017), we conducted a hierarchical, layer-wise evaluation that holds data splits and hyperparameters fixed while varying only the feature set to quantify each layer’s marginal contribution. Across logistic regression (LR), decision… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Bassam Al-Shargabi1,*, Mohammed Abbas Fadhil Al-Husainy2, Abdelrahman Abuarqoub1, Omar Albahbouh Aldabbas3
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074550
Abstract The advent of 5G technology has significantly enhanced the transmission of images over networks, expanding data accessibility and exposure across various applications in digital technology and social media. Consequently, the protection of sensitive data has become increasingly critical. Regardless of the complexity of the encryption algorithm used, a robust and highly secure encryption key is essential, with randomness and key space being crucial factors. This paper proposes a new Robust Deoxyribonucleic Acid (RDNA) nucleotide-based encryption method. The RDNA encryption method leverages the unique properties of DNA nucleotides, including their inherent randomness and extensive key space,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Shu-Yin Chiang*, Shin-En Huang
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074528
Abstract This paper presents an intelligent patrol and security robot integrating 2D LiDAR and RGB-D vision sensors to achieve semantic simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM), real-time object recognition, and dynamic obstacle avoidance. The system employs the YOLOv7 deep-learning framework for semantic detection and SLAM for localization and mapping, fusing geometric and visual data to build a high-fidelity 2D semantic map. This map enables the robot to identify and project object information for improved situational awareness. Experimental results show that object recognition reached 95.4% mAP@0.5. Semantic completeness increased from 68.7% (single view) to 94.1% (multi-view) with an More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Zuyi Huang1, Yue Wang1, Jia Liu2, Haodong Yi1, Lejun Ai1, Min Chen1,3,*, Salman A. AlQahtani4
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074034
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advancing Network Intelligence: Communication, Sensing and Computation)
Abstract The personalized fine-tuning of large language models (LLMs) on edge devices is severely constrained by limited computation resources. Although split federated learning alleviates on-device burdens, its effectiveness diminishes in few-shot reasoning scenarios due to the low data efficiency of conventional supervised fine-tuning, which leads to excessive communication overhead. To address this, we propose Language-Empowered Split Fine-Tuning (LESFT), a framework that integrates split architectures with a contrastive-inspired fine-tuning paradigm. LESFT simultaneously learns from multiple logically equivalent but linguistically diverse reasoning chains, providing richer supervisory signals and improving data efficiency. This process-oriented training allows more effective reasoning More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Shao-Qiang Ye*, Azlan Mohd Zain, Yusliza Yusoff
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073411
Abstract Engineering optimization problems are often characterized by high dimensionality, constraints, and complex, multimodal landscapes. Traditional deterministic methods frequently struggle under such conditions, prompting increased interest in swarm intelligence algorithms. Among these, the Cuckoo Search (CS) algorithm stands out for its promising global search capabilities. However, it often suffers from premature convergence when tackling complex problems. To address this limitation, this paper proposes a Grouped Dynamic Adaptive CS (GDACS) algorithm. The enhancements incorporated into GDACS can be summarized into two key aspects. Firstly, a chaotic map is employed to generate initial solutions, leveraging the inherent randomness… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Jian Huang1, Mingwei Li1, Yulong Tian1, Yi Yao2, Hao Han1,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073201
Abstract With the popularization of new technologies, telephone fraud has become the main means of stealing money and personal identity information. Taking inspiration from the website authentication mechanism, we propose an end-to-end data modem scheme that transmits the caller’s digital certificates through a voice channel for the recipient to verify the caller’s identity. Encoding useful information through voice channels is very difficult without the assistance of telecommunications providers. For example, speech activity detection may quickly classify encoded signals as non-speech signals and reject input waveforms. To address this issue, we propose a novel modulation method based… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Jinhuo Liang, Jinan Shen*, Pengfei Wang, Fang Liang, Xuejian Deng
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073076
Abstract The method for malware detection based on Application Programming Interface (API) call sequences, as a primary research focus within dynamic detection technologies, currently lacks attention to subsequences of API calls, the variety of API call types, and the length of sequences. This oversight leads to overly complex call sequences. To address this issue, a dynamic malware detection approach based on multiple subsequences is proposed. Initially, APIs are remapped and encoded, with the introduction of percentile lengths to process sequences. Subsequently, a combination of One-Dimensional Convolutional Neural Network (1D-CNN) and Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (Bi-LSTM) networks, More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Muhammad Hamdan Azhar1,2,#, Yanfeng Wu1,#, Nouf Abdullah Almujally3, Shuaa S. Alharbi4, Asaad Algarni5, Ahmad Jalal2,6, Hui Liu1,7,8,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.071988
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Image Recognition: Innovations, Applications, and Future Directions)
Abstract Recognizing human interactions in RGB videos is a critical task in computer vision, with applications in video surveillance. Existing deep learning-based architectures have achieved strong results, but are computationally intensive, sensitive to video resolution changes and often fail in crowded scenes. We propose a novel hybrid system that is computationally efficient, robust to degraded video quality and able to filter out irrelevant individuals, making it suitable for real-life use. The system leverages multi-modal handcrafted features for interaction representation and a deep learning classifier for capturing complex dependencies. Using Mask R-CNN and YOLO11-Pose, we extract grayscale… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Jeng-Shyang Pan1,2, Yan-Na Wei3, Ling-Da Chi4, Shu-Chuan Chu1,*, Ru-Yu Wang5, Junzo Watada6
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074447
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Nature-Inspired and Metaheuristic Optimization Algorithms: Theory, Applications, and Emerging Trends)
Abstract Multilevel image segmentation is a critical task in image analysis, which imposes high requirements on the global search capability and convergence efficiency of segmentation algorithms. In this paper, an improved Artificial Protozoa Optimization algorithm, termed the two-stage Taguchi-assisted Gaussian–Lévy Artificial Protozoa Optimization (TGAPO) algorithm, is proposed and applied to multilevel image segmentation. The proposed algorithm adopts a two-stage evolutionary mechanism. In the first stage, Gaussian perturbation is introduced to enhance local search capability; in the second stage, Lévy flight is incorporated to expand the global search range; and finally, the Taguchi strategy is employed to… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Tianxia Zou1,*, Yilin Sun2, Fuhao Fan1, Zhen Zheng1, Yanjin Xu2, Baoshuai Han2
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074121
Abstract Ultra-high-strength aluminum alloy profile is an ideal choice for aerospace structural materials due to its excellent specific strength and corrosion resistance. However, issues such as uneven metal flow, stress concentration, and forming defects are prone to occur during their extrusion. This study focuses on an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu ultra-high-strength aluminum alloy profile with a double-U, multi-cavity thin-walled structure. Firstly, hot compression experiments were conducted at temperatures of 350°C, 400°C, and 450°C, with strain rates of 0.01 and 1.0 s−1, to investigate the plastic deformation behavior of the material. Subsequently, a 3D coupled thermo-mechanical extrusion simulation model was established… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Qasem Abu Al-Haija1,*, Shahad Al Tamimi2
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073540
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in IoT Security: Challenges, Solutions, and Future Applications)
Abstract Adversarial Reinforcement Learning (ARL) models for intelligent devices and Network Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS) improve system resilience against sophisticated cyber-attacks. As a core component of ARL, Adversarial Training (AT) enables NIDS agents to discover and prevent new attack paths by exposing them to competing examples, thereby increasing detection accuracy, reducing False Positives (FPs), and enhancing network security. To develop robust decision-making capabilities for real-world network disruptions and hostile activity, NIDS agents are trained in adversarial scenarios to monitor the current state and notify management of any abnormal or malicious activity. The accuracy and timeliness of… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Aman Aman Ullah1,2,#, Yanfeng Wu1,#, Shaheryar Najam3, Nouf Abdullah Almujally4, Ahmad Jalal5,6,*, Hui Liu1,7,8,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072508
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Object Detection and Recognition)
Abstract Human object detection and recognition is essential for elderly monitoring and assisted living however, models relying solely on pose or scene context often struggle in cluttered or visually ambiguous settings. To address this, we present SCENET-3D, a transformer-driven multimodal framework that unifies human-centric skeleton features with scene-object semantics for intelligent robotic vision through a three-stage pipeline. In the first stage, scene analysis, rich geometric and texture descriptors are extracted from RGB frames, including surface-normal histograms, angles between neighboring normals, Zernike moments, directional standard deviation, and Gabor-filter responses. In the second stage, scene-object analysis, non-human objects… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Ye Tian1,*, Zhuokun Fan1, Yifeng Zhang2
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073935
Abstract Amid the increasing demand for data sharing, the need for flexible, secure, and auditable access control mechanisms has garnered significant attention in the academic community. However, blockchain-based ciphertext-policy attribute-based encryption (CP-ABE) schemes still face cumbersome ciphertext re-encryption and insufficient oversight when handling dynamic attribute changes and cross-chain collaboration. To address these issues, we propose a dynamic permission attribute-encryption scheme for multi-chain collaboration. This scheme incorporates a multi-authority architecture for distributed attribute management and integrates an attribute revocation and granting mechanism that eliminates the need for ciphertext re-encryption, effectively reducing both computational and communication overhead. It More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Umar Hayat1,2,*, Ikram Ullah2, Muhammad Bilal2
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073097
Abstract Elliptic curve (EC) based cryptosystems gained more attention due to enhanced security than the existing public key cryptosystems. A substitution box (S-box) plays a vital role in securing modern symmetric key cryptosystems. However, the recently developed EC based algorithms usually trade off between computational efficiency and security, necessitating the design of a new algorithm with the desired cryptographic strength. To address these shortcomings, this paper proposes a new scheme based on Mordell elliptic curve (MEC) over the complex field for generating distinct, dynamic, and highly uncorrelated S-boxes. Furthermore, we count the exact number of the… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Isam Bahaa Aldallal1, Abdullahi Abdu Ibrahim1,*, Saadaldeen Rashid Ahmed2,3
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.075212
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence for Intrusion Detection Systems)
Abstract The rapid growth of IoT networks necessitates efficient Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) capable of addressing dynamic security threats under constrained resource environments. This paper proposes a hybrid IDS for IoT networks, integrating Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Genetic Algorithm (GA) for feature selection and parameter optimization. The GA reduces the feature set from 41 to 7, achieving a 30% reduction in overhead while maintaining an attack detection rate of 98.79%. Evaluated on the NSL-KDD dataset, the system demonstrates an accuracy of 97.36%, a recall of 98.42%, and an F1-score of 96.67%, with a low false More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Bo Zhu#, Enzhi Dong#, Zhonghua Cheng*, Kexin Jiang, Chiming Guo, Shuai Yue
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074009
Abstract Accurate prediction of remaining useful life serves as a reliable basis for maintenance strategies, effectively reducing both the frequency of failures and associated costs. As a core component of PHM, RUL prediction plays a crucial role in preventing equipment failures and optimizing maintenance decision-making. However, deep learning models often falter when processing raw, noisy temporal signals, fail to quantify prediction uncertainty, and face challenges in effectively capturing the nonlinear dynamics of equipment degradation. To address these issues, this study proposes a novel deep learning framework. First, a new bidirectional long short-term memory network integrated with More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Maha Abdelhaq1, Ahmad Sami Al-Shamayleh2, Adnan Akhunzada3,*, Nikola Ivković4, Toobah Hasan5
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073577
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Malware Analysis, Forensics, and Detection Using Artificial Intelligence)
Abstract The rapid expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT) and Edge Artificial Intelligence (AI) has redefined automation and connectivity across modern networks. However, the heterogeneity and limited resources of IoT devices expose them to increasingly sophisticated and persistent malware attacks. These adaptive and stealthy threats can evade conventional detection, establish remote control, propagate across devices, exfiltrate sensitive data, and compromise network integrity. This study presents a Software-Defined Internet of Things (SD-IoT) control-plane-based, AI-driven framework that integrates Gated Recurrent Units (GRU) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks for efficient detection of evolving multi-vector, malware-driven botnet attacks.… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yu Du1, Runwei Guan2, Ho-Pun Lam1, Jeremy Smith3, Yutao Yue4,5, Ka Lok Man1, Yan Li6,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072544
Abstract As a cornerstone for applications such as autonomous driving, 3D urban perception is a burgeoning field of study. Enhancing the performance and robustness of these perception systems is crucial for ensuring the safety of next-generation autonomous vehicles. In this work, we introduce a novel neural scene representation called Street Detection Gaussians (SDGs), which redefines urban 3D perception through an integrated architecture unifying reconstruction and detection. At its core lies the dynamic Gaussian representation, where time-conditioned parameterization enables simultaneous modeling of static environments and dynamic objects through physically constrained Gaussian evolution. The framework’s radar-enhanced perception module… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Zhen Wu1,2, Hao Liu3, Linlin Zhang4, Zehui Zhang5,*, Jie Wu1, Haibin He1, Bin Zhou6
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.075156
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Integrating Split Learning with Tiny Models for Advanced Edge Computing Applications in the Internet of Vehicles)
Abstract Recently, Internet of Things (IoT) has been increasingly integrated into the automotive sector, enabling the development of diverse applications such as the Internet of Vehicles (IoV) and intelligent connected vehicles. Leveraging IoV technologies, operational data from core vehicle components can be collected and analyzed to construct fault diagnosis models, thereby enhancing vehicle safety. However, automakers often struggle to acquire sufficient fault data to support effective model training. To address this challenge, a robust and efficient federated learning method (REFL) is constructed for machinery fault diagnosis in collaborative IoV, which can organize multiple companies to collaboratively More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Yu-Xuan Zhou1, Kai-Qing Zhou1,*, Wei-Lin Chen1, Zhou-Hua Liao1, Di-Wen Kang1,2
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.075099
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Bio-Inspired Optimization Algorithms: Theory, Algorithms, and Applications)
Abstract The Pigeon-Inspired Optimization (PIO) algorithm constitutes a metaheuristic method derived from the homing behaviour of pigeons. Initially formulated for three-dimensional path planning in unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), the algorithm has attracted considerable academic and industrial interest owing to its effective balance between exploration and exploitation, coupled with advantages in real-time performance and robustness. Nevertheless, as applications have diversified, limitations in convergence precision and a tendency toward premature convergence have become increasingly evident, highlighting a need for improvement. This review systematically outlines the developmental trajectory of the PIO algorithm, with a particular focus on its core… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Gang Xu1,2, Lefeng Wang1, Yuwei Huang2, Yong Lu3, Xin Liu4, Weijie Tan5, Zongpeng Li6, Xiu-Bo Chen2,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074256
Abstract The Intrusion Detection System (IDS) is a security mechanism developed to observe network traffic and recognize suspicious or malicious activities. Clustering algorithms are often incorporated into IDS; however, conventional clustering-based methods face notable drawbacks, including poor scalability in handling high-dimensional datasets and a strong dependence of outcomes on initial conditions. To overcome the performance limitations of existing methods, this study proposes a novel quantum-inspired clustering algorithm that relies on a similarity coefficient-based quantum genetic algorithm (SC-QGA) and an improved quantum artificial bee colony algorithm hybrid K-means (IQABC-K). First, the SC-QGA algorithm is constructed based on… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Lu Rong1,#, Manyu Xu2,3,#, Wenbo Zhu2,*, Zhihao Yang2,3, Chao Dong1,4,5, Yunzhi Zhang2,3, Kai Wang1,2, Bing Zheng1,4,5
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073442
Abstract Deep learning has become integral to robotics, particularly in tasks such as robotic grasping, where objects often exhibit diverse shapes, textures, and physical properties. In robotic grasping tasks, due to the diverse characteristics of the targets, frequent adjustments to the network architecture and parameters are required to avoid a decrease in model accuracy, which presents a significant challenge for non-experts. Neural Architecture Search (NAS) provides a compelling method through the automated generation of network architectures, enabling the discovery of models that achieve high accuracy through efficient search algorithms. Compared to manually designed networks, NAS methods… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Noor Mueen Mohammed Ali Hayder1,2, Seyed Amin Hosseini Seno2,*, Hamid Noori2, Davood Zabihzadeh3, Mehdi Ebady Manaa4,5
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073236
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence for Intrusion Detection Systems)
Abstract Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks are one of the severe threats to network infrastructure, sometimes bypassing traditional diagnosis algorithms because of their evolving complexity. Present Machine Learning (ML) techniques for DDoS attack diagnosis normally apply network traffic statistical features such as packet sizes and inter-arrival times. However, such techniques sometimes fail to capture complicated relations among various traffic flows. In this paper, we present a new multi-scale ensemble strategy given the Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) for improving DDoS detection. Our technique divides traffic into macro- and micro-level elements, letting various GNN models to get… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Ahmad Junaid1, Abid Iqbal2,*, Abuzar Khan1, Ghassan Husnain1,*, Abdul-Rahim Ahmad3, Mohammed Al-Naeem4
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073189
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: AI for Industry 4.0 and 5.0: Intelligent Robotics, Cyber-Physical Systems, and Resilient Automation)
Abstract Most predictive maintenance studies have emphasized accuracy but provide very little focus on Interpretability or deployment readiness. This study improves on prior methods by developing a small yet robust system that can predict when turbofan engines will fail. It uses the NASA CMAPSS dataset, which has over 200,000 engine cycles from 260 engines. The process begins with systematic preprocessing, which includes imputation, outlier removal, scaling, and labelling of the remaining useful life. Dimensionality is reduced using a hybrid selection method that combines variance filtering, recursive elimination, and gradient-boosted importance scores, yielding a stable set of… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Zeyu Wang1, Jian-Hong Wang1,*, Kuo-Chun Hsu2,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072881
Abstract In daily life, keyword spotting plays an important role in human-computer interaction. However, noise often interferes with the extraction of time-frequency information, and achieving both computational efficiency and recognition accuracy on resource-constrained devices such as mobile terminals remains a major challenge. To address this, we propose a novel time-frequency dual-branch parallel residual network, which integrates a Dual-Branch Broadcast Residual module and a Time-Frequency Coordinate Attention module. The time-domain and frequency-domain branches are designed in parallel to independently extract temporal and spectral features, effectively avoiding the potential information loss caused by serial stacking, while enhancing information… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Xiaorui Zhang1,2,*, Yingying Wang2, Wei Sun3, Shiyu Zhou2, Haoming Zhang4, Pengpai Wang1
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072626
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Image Recognition: Innovations, Applications, and Future Directions)
Abstract Discriminative region localization and efficient feature encoding are crucial for fine-grained object recognition. However, existing data augmentation methods struggle to accurately locate discriminative regions in complex backgrounds, small target objects, and limited training data, leading to poor recognition. Fine-grained images exhibit “small inter-class differences,” and while second-order feature encoding enhances discrimination, it often requires dual Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), increasing training time and complexity. This study proposes a model integrating discriminative region localization and efficient second-order feature encoding. By ranking feature map channels via a fully connected layer, it selects high-importance channels to generate an More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Ming Chen1,*, Guoqiang Ma2, Ping Qi1, Fucheng Wang1, Lin Shen3, Xiaoya Pi1
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072623
Abstract In the image fusion field, fusing infrared images (IRIs) and visible images (VIs) excelled is a key area. The differences between IRIs and VIs make it challenging to fuse both types into a high-quality image. Accordingly, efficiently combining the advantages of both images while overcoming their shortcomings is necessary. To handle this challenge, we developed an end-to-end IRI and VI fusion method based on frequency decomposition and enhancement. By applying concepts from frequency domain analysis, we used the layering mechanism to better capture the salient thermal targets from the IRIs and the rich textural information… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Fei Yu1,2,3,*, Zhenya Diao1,2, Hongrun Wu1,2,*, Yingpin Chen1,3, Xuewen Xia1,2, Yuanxiang Li2,3,4
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072593
Abstract Feature selection serves as a critical preprocessing step in machine learning, focusing on identifying and preserving the most relevant features to improve the efficiency and performance of classification algorithms. Particle Swarm Optimization has demonstrated significant potential in addressing feature selection challenges. However, there are inherent limitations in Particle Swarm Optimization, such as the delicate balance between exploration and exploitation, susceptibility to local optima, and suboptimal convergence rates, hinder its performance. To tackle these issues, this study introduces a novel Leveraged Opposition-Based Learning method within Fitness Landscape Particle Swarm Optimization, tailored for wrapper-based feature selection. The… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Shereen S. Jumaa1, Mohsin H. Challoob2, Amjad J. Humaidi2,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074752
Abstract Military image encryption plays a vital role in ensuring the secure transmission of sensitive visual information from unauthorized access. This paper proposes a new Tri-independent keying method for encrypting military images. The proposed encryption method is based on multilevel security stages of pixel-level scrambling, bit-level manipulation, and block-level shuffling operations. For having a vast key space, the input password is hashed by the Secure Hash Algorithm 256-bit (SHA-256) for generating independently deterministic keys used in the multilevel stages. A piecewise pixel-level scrambling function is introduced to perform a dual flipping process controlled with an adaptive… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Wenhe Chen1, Yue Wang1, Shuonan Shen1, Leer Hua1, Caixia Zheng2, Qi Pu1,*, Xundiao Ma3,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074682
Abstract In fire rescue scenarios, traditional manual operations are highly dangerous, as dense smoke, low visibility, extreme heat, and toxic gases not only hinder rescue efficiency but also endanger firefighters’ safety. Although intelligent rescue robots can enter hazardous environments in place of humans, smoke poses major challenges for human detection algorithms. These challenges include the attenuation of visible and infrared signals, complex thermal fields, and interference from background objects, all of which make it difficult to accurately identify trapped individuals. To address this problem, we propose VIF-YOLO, a visible–infrared fusion model for real-time human detection in… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Junnian Wang1, Xiaoxia Wang1, Zexin Luo1, Qixiang Ouyang1, Chao Zhou1, Huanyu Wang2,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074473
Abstract Internet of Things (IoTs) devices are bringing about a revolutionary change our society by enabling connectivity regardless of time and location. However, The extensive deployment of these devices also makes them attractive victims for the malicious actions of adversaries. Within the spectrum of existing threats, Side-Channel Attacks (SCAs) have established themselves as an effective way to compromise cryptographic implementations. These attacks exploit unintended, unintended physical leakage that occurs during the cryptographic execution of devices, bypassing the theoretical strength of the crypto design. In recent times, the advancement of deep learning has provided SCAs with a… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yunhao Yu1, Fuhua Luo1, Zhenyong Zhang2,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074277
Abstract This paper investigates the detection and mitigation of coordinated cyberattacks on Load Frequency Control (LFC) systems integrated with Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS). As renewable energy sources gain greater penetration, power grids are becoming increasingly vulnerable to cyber threats, potentially leading to frequency instability and widespread disruptions. We model two significant attack vectors: load-altering attacks (LAAs) and false data injection attacks (FDIAs) that corrupt frequency measurements. These are analyzed for their impact on grid frequency stability in both linear and nonlinear LFC models, incorporating generation rate constraints and nonlinear loads. A coordinated attack strategy is… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Ye-Chan Park1, Mohd Asyraf Zulkifley2, Bong-Soo Sohn3, Jaesung Lee4,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074141
Abstract Legal case classification involves the categorization of legal documents into predefined categories, which facilitates legal information retrieval and case management. However, real-world legal datasets often suffer from class imbalances due to the uneven distribution of case types across legal domains. This leads to biased model performance, in the form of high accuracy for overrepresented categories and underperformance for minority classes. To address this issue, in this study, we propose a data augmentation method that masks unimportant terms within a document selectively while preserving key terms from the perspective of the legal domain. This approach enhances More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Hyunki Lim*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074138
Abstract High-dimensional data causes difficulties in machine learning due to high time consumption and large memory requirements. In particular, in a multi-label environment, higher complexity is required as much as the number of labels. Moreover, an optimization problem that fully considers all dependencies between features and labels is difficult to solve. In this study, we propose a novel regression-based multi-label feature selection method that integrates mutual information to better exploit the underlying data structure. By incorporating mutual information into the regression formulation, the model captures not only linear relationships but also complex non-linear dependencies. The proposed… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Jinzheng Yu1, Yang Xu2, Haozhen Li2, Junqi Li3, Ligu Zhu1, Hao Shen1,*, Lei Shi1,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073771
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Big Data and Artificial Intelligence in Control and Information System)
Abstract Online Public Opinion Reports consolidate news and social media for timely crisis management by governments and enterprises. While large language models (LLMs) enable automated report generation, this specific domain lacks formal task definitions and corresponding benchmarks. To bridge this gap, we define the Automated Online Public Opinion Report Generation (OPOR-Gen) task and construct OPOR-Bench, an event-centric dataset with 463 crisis events across 108 countries (comprising 8.8 K news articles and 185 K tweets). To evaluate report quality, we propose OPOR-Eval, a novel agent-based framework that simulates human expert evaluation. Validation experiments show OPOR-Eval achieves a More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Su Zhang1, Song Deng1,*, Qingsheng Liu2
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072777
Abstract Accurate and reliable power system data are fundamental for critical operations such as grid monitoring, fault diagnosis, and load forecasting, underpinned by increasing intelligentization and digitalization. However, data loss and anomalies frequently compromise data integrity in practical settings, significantly impacting system operational efficiency and security. Most existing data recovery methods require complete datasets for training, leading to substantial data and computational demands and limited generalization. To address these limitations, this study proposes a missing data imputation model based on an improved Generative Adversarial Network (BAC-GAN). Within the BAC-GAN framework, the generator utilizes Bidirectional Long Short-Term… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Enzo Hoummady*, Fehmi Jaafar
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074897
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Intelligence and Security Enhancement for Internet of Things)
Abstract With the proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, securing these interconnected systems against cyberattacks has become a critical challenge. Traditional security paradigms often fail to cope with the scale and diversity of IoT network traffic. This paper presents a comparative benchmark of classic machine learning (ML) and state-of-the-art deep learning (DL) algorithms for IoT intrusion detection. Our methodology employs a two-phased approach: a preliminary pilot study using a custom-generated dataset to establish baselines, followed by a comprehensive evaluation on the large-scale CICIoTDataset2023. We benchmarked algorithms including Random Forest, XGBoost, CNN, and Stacked LSTM. The… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Tongcheng Geng1,#, Zhiyuan Xu2,#, Yubin Qu3,*, W. Eric Wong4
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074081
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Large Language Models in Password Authentication Security: Challenges, Solutions and Future Directions)
Abstract Large language models (LLMs) have revolutionized AI applications across diverse domains. However, their widespread deployment has introduced critical security vulnerabilities, particularly prompt injection attacks that manipulate model behavior through malicious instructions. Following Kitchenham’s guidelines, this systematic review synthesizes 128 peer-reviewed studies from 2022 to 2025 to provide a unified understanding of this rapidly evolving threat landscape. Our findings reveal a swift progression from simple direct injections to sophisticated multimodal attacks, achieving over 90% success rates against unprotected systems. In response, defense mechanisms show varying effectiveness: input preprocessing achieves 60%–80% detection rates and advanced architectural defenses More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Noura Mohammed Alaskar1, Muzammil Hussain2, Saif Jasim Almheiri1, Atta-ur-Rahman3, Adnan Khan4,5,6, Khan M. Adnan7,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074041
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence for Intrusion Detection Systems)
Abstract The increasing number of interconnected devices and the incorporation of smart technology into contemporary healthcare systems have significantly raised the attack surface of cyber threats. The early detection of threats is both necessary and complex, yet these interconnected healthcare settings generate enormous amounts of heterogeneous data. Traditional Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), which are generally centralized and machine learning-based, often fail to address the rapidly changing nature of cyberattacks and are challenged by ethical concerns related to patient data privacy. Moreover, traditional AI-driven IDS usually face challenges in handling large-scale, heterogeneous healthcare data while ensuring data… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Zeyuan Chen, Yafei Xie, Jinkun Li, Song Wang, Yingqiang Ding*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073846
Abstract Stereo matching is a pivotal task in computer vision, enabling precise depth estimation from stereo image pairs, yet it encounters challenges in regions with reflections, repetitive textures, or fine structures. In this paper, we propose a Semantic-Guided Parallax Attention Stereo Matching Network (SGPASMnet) that can be trained in unsupervised manner, building upon the Parallax Attention Stereo Matching Network (PASMnet). Our approach leverages unsupervised learning to address the scarcity of ground truth disparity in stereo matching datasets, facilitating robust training across diverse scene-specific datasets and enhancing generalization. SGPASMnet incorporates two novel components: a Cross-Scale Feature Interaction… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Abdu Salam1, Fahd M. Aldosari2, Donia Y. Badawood3, Farhan Amin4,*, Isabel de la Torre5,*, Gerardo Mendez Mezquita6, Henry Fabian Gongora6
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073342
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advancements in Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence for Pattern Detection and Predictive Analytics in Healthcare)
Abstract Lung cancer remains a major global health challenge, with early diagnosis crucial for improved patient survival. Traditional diagnostic techniques, including manual histopathology and radiological assessments, are prone to errors and variability. Deep learning methods, particularly Vision Transformers (ViT), have shown promise for improving diagnostic accuracy by effectively extracting global features. However, ViT-based approaches face challenges related to computational complexity and limited generalizability. This research proposes the DualSet ViT-PSO-SVM framework, integrating a ViT with dual attention mechanisms, Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO), and Support Vector Machines (SVM), aiming for efficient and robust lung cancer classification across multiple… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Jianing Wu1, Yufeng Chen1,*, Li Yin1, Huajun He2, Panshuan Jin2
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072937
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Intelligent Perception, Decision-making and Security Control for Unmanned Systems in Complex Environments)
Abstract To conduct marine surveys, multiple unmanned surface vessels (Multi-USV) with different capabilities perform collaborative mapping in multiple designated areas. This paper proposes a task allocation algorithm based on integer linear programming (ILP) with flow balance constraints, ensuring the fair and efficient distribution of sub-areas among USVs and maintaining strong connectivity of assigned regions. In the established grid map, a search-based path planning algorithm is performed on the sub-areas according to the allocation scheme. It uses the greedy algorithm and the A* algorithm to achieve complete coverage of the barrier-free area and obtain an efficient trajectory More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Kirubavathi Ganapathiyappan1, Chahana Ravikumar1, Raghul Alagunachimuthu Ranganayaki1, Ayman Altameem2, Ateeq Ur Rehman3,*, Ahmad Almogren4,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072840
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence for Intrusion Detection Systems)
Abstract Android smartphones have become an integral part of our daily lives, becoming targets for ransomware attacks. Such attacks encrypt user information and ask for payment to recover it. Conventional detection mechanisms, such as signature-based and heuristic techniques, often fail to detect new and polymorphic ransomware samples. To address this challenge, we employed various ensemble classifiers, such as Random Forest, Gradient Boosting, Bagging, and AutoML models. We aimed to showcase how AutoML can automate processes such as model selection, feature engineering, and hyperparameter optimization, to minimize manual effort while ensuring or enhancing performance compared to traditional… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yingkai Ge, Jiasheng Zhang, Jiale Zhang, Zhenguo Ma, Yu Liu, Lihua Wang*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072799
Abstract With the continuous development of artificial intelligence and computer vision technology, numerous deep learning-based lane line detection methods have emerged. DeepLabv3+, as a classic semantic segmentation model, has found widespread application in the field of lane line detection. However, the accuracy of lane line segmentation is often compromised by factors such as changes in lighting conditions, occlusions, and wear and tear on the lane lines. Additionally, DeepLabv3+ suffers from high memory consumption and challenges in deployment on embedded platforms. To address these issues, this paper proposes a lane line detection method for complex road scenes… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Xiaoyu Li1,2, Jie Zhang3, Wen Shi1,2,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074005
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Large Models and Domain-specific Applications)
Abstract The emergence of large language models (LLMs) has brought about revolutionary social value. However, concerns have arisen regarding the generation of deceptive content by LLMs and their potential for misuse. Consequently, a crucial research question arises: How can we differentiate between AI-generated and human-authored text? Existing detectors face some challenges, such as operating as black boxes, relying on supervised training, and being vulnerable to manipulation and misinformation. To tackle these challenges, we propose an innovative unsupervised white-box detection method that utilizes a “dual-driven verification mechanism” to achieve high-performance detection, even in the presence of obfuscated… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Danyang Zheng*, Jinchen Xv, Xin Zhou, Zheng Shan
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073860
Abstract The increasing popularity of quantum computing has resulted in a considerable rise in demand for cloud quantum computing usage in recent years. Nevertheless, the rapid surge in demand for cloud-based quantum computing resources has led to a scarcity. In order to meet the needs of an increasing number of researchers, it is imperative to facilitate efficient and flexible access to computing resources in a cloud environment. In this paper, we propose a novel quantum computing paradigm, Virtual QPU (VQPU), which addresses this issue and enhances quantum cloud throughput with guaranteed circuit fidelity. The proposal introduces More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Haiyan Long1, Gang Chen2,*, Hai Chen3,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073243
Abstract The performance of deep recommendation models degrades significantly under data poisoning attacks. While adversarial training methods such as Vulnerability-Aware Training (VAT) enhance robustness by injecting perturbations into embeddings, they remain limited by coarse-grained noise and a static defense strategy, leaving models susceptible to adaptive attacks. This study proposes a novel framework, Self-Purification Data Sanitization (SPD), which integrates vulnerability-aware adversarial training with dynamic label correction. Specifically, SPD first identifies high-risk users through a fragility scoring mechanism, then applies self-purification by replacing suspicious interactions with model-predicted high-confidence labels during training. This closed-loop process continuously sanitizes the training More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Nouman Ahmad1,*, Changsheng Zhang1, Uroosa Sehar2,3,4
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073029
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Utilizing and Securing Large Language Models for Cybersecurity and Beyond)
Abstract Although Named Entity Recognition (NER) in cybersecurity has historically concentrated on threat intelligence, vital security data can be found in a variety of sources, such as open-source intelligence and unprocessed tool outputs. When dealing with technical language, the coexistence of structured and unstructured data poses serious issues for traditional BERT-based techniques. We introduce a three-phase approach for improved NER in multi-source cybersecurity data that makes use of large language models (LLMs). To ensure thorough entity coverage, our method starts with an identification module that uses dynamic prompting techniques. To lessen hallucinations, the extraction module uses… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Longcang Wang, Yongbing Gao*, Xinguang Wang, Xin Liu
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072889
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Sentiment Analysis for Social Media Data: Lexicon-Based and Large Language Model Approaches)
Abstract Aiming at the problem of insufficient recognition of implicit variants by existing Chinese sensitive text detection methods, this paper proposes the IPKE-MoE framework, which consists of three parts, namely, a sensitive word variant extraction framework, a sensitive word variant knowledge enhancement layer and a mixture-of-experts (MoE) classification layer. First, sensitive word variants are precisely extracted through dynamic iterative prompt templates and the context-aware capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs). Next, the extracted variants are used to construct a knowledge enhancement layer for sensitive word variants based on RoCBert models. Specifically, after locating variants via n-gram… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Sooyong Jeong1,#, Cheolhee Park2,#, Dowon Hong3,*, Changho Seo4
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072561
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: AI-Driven Intrusion Detection and Threat Analysis in Cybersecurity)
Abstract With the growing complexity and decentralization of network systems, the attack surface has expanded, which has led to greater concerns over network threats. In this context, artificial intelligence (AI)-based network intrusion detection systems (NIDS) have been extensively studied, and recent efforts have shifted toward integrating distributed learning to enable intelligent and scalable detection mechanisms. However, most existing works focus on individual distributed learning frameworks, and there is a lack of systematic evaluations that compare different algorithms under consistent conditions. In this paper, we present a comprehensive evaluation of representative distributed learning frameworks—Federated Learning (FL), Split… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Leyu Dai1,2,3, Jindong Wang1,2,3, Ming Zhou1,2,3, Song Guo1,2,3, Hengwei Zhang1,2,3,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072449
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Object Detection: Methods and Applications)
Abstract In recent years, with the rapid advancement of artificial intelligence, object detection algorithms have made significant strides in accuracy and computational efficiency. Notably, research and applications of Anchor-Free models have opened new avenues for real-time target detection in optical remote sensing images (ORSIs). However, in the realm of adversarial attacks, developing adversarial techniques tailored to Anchor-Free models remains challenging. Adversarial examples generated based on Anchor-Based models often exhibit poor transferability to these new model architectures. Furthermore, the growing diversity of Anchor-Free models poses additional hurdles to achieving robust transferability of adversarial attacks. This study presents… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Sara Tehsin1, Inzamam Mashood Nasir1,*, Wiem Abdelbaki2, Fadwa Alrowais3, Khalid A. Alattas4, Sultan Almutairi5, Radwa Marzouk6
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.074416
Abstract Objective: Deep learning is employed increasingly in Gastroenterology (GI) endoscopy computer-aided diagnostics for polyp segmentation and multi-class disease detection. In the real world, implementation requires high accuracy, therapeutically relevant explanations, strong calibration, domain generalization, and efficiency. Current Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and transformer models compromise border precision and global context, generate attention maps that fail to align with expert reasoning, deteriorate during cross-center changes, and exhibit inadequate calibration, hence diminishing clinical trust. Methods: HMA-DER is a hierarchical multi-attention architecture that uses dilation-enhanced residual blocks and an explainability-aware Cognitive Alignment Score (CAS) regularizer to directly align… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Sghaier Guizani1,*, Tehseen Mazhar2,3,*, Habib Hamam4,5,6,7
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073883
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Next-Generation Cybersecurity: AI, Post-Quantum Cryptography, and Chaotic Innovations)
Abstract The advent of quantum computing poses a significant challenge to traditional cryptographic protocols, particularly those used in Secure Multiparty Computation (MPC), a fundamental cryptographic primitive for privacy-preserving computation. Classical MPC relies on cryptographic techniques such as homomorphic encryption, secret sharing, and oblivious transfer, which may become vulnerable in the post-quantum era due to the computational power of quantum adversaries. This study presents a review of 140 peer-reviewed articles published between 2000 and 2025 that used different databases like MDPI, IEEE Explore, Springer, and Elsevier, examining the applications, types, and security issues with the solution of… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Jiaxi Wang1, Wenbo Sun2, Ziyuan Zhou1, Shihua Wu1, Jiang Xu1, Shan Ji3,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073237
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Recent Advances in Blockchain Technology and Applications)
Abstract Lightweight nodes are crucial for blockchain scalability, but verifying the availability of complete block data puts significant strain on bandwidth and latency. Existing data availability sampling (DAS) schemes either require trusted setups or suffer from high communication overhead and low verification efficiency. This paper presents ISTIRDA, a DAS scheme that lets light clients certify availability by sampling small random codeword symbols. Built on ISTIR, an improved Reed–Solomon interactive oracle proof of proximity, ISTIRDA combines adaptive folding with dynamic code rate adjustment to preserve soundness while lowering communication. This paper formalizes opening consistency and prove security… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Huihui Zhu1, Fei Tang2,*, Chunhua Jin3, Ping Wang1
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.073550
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Privacy-Enhancing Technologies for Secure Data Cooperation and Circulation)
Abstract The ubiquitous adoption of mobile devices as essential platforms for sensitive data transmission has heightened the demand for secure client-server communication. Although various authentication and key agreement protocols have been developed, current approaches are constrained by homogeneous cryptosystem frameworks, namely public key infrastructure (PKI), identity-based cryptography (IBC), or certificateless cryptography (CLC), each presenting limitations in client-server architectures. Specifically, PKI incurs certificate management overhead, IBC introduces key escrow risks, and CLC encounters cross-system interoperability challenges. To overcome these shortcomings, this study introduces a heterogeneous signcryption-based authentication and key agreement protocol that synergistically integrates IBC for client More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Roshni Khedgaonkar1, Pravinkumar Sonsare2, Kavita Singh1, Ayman Altameem3, Hameed R. Farhan4, Salil Bharany5, Ateeq Ur Rehman6,*, Ahmad Almogren7,*
CMC-Computers, Materials & Continua, DOI:10.32604/cmc.2025.072651
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Healthcare Applications)
Abstract Recent studies indicate that millions of individuals suffer from renal diseases, with renal carcinoma, a type of kidney cancer, emerging as both a chronic illness and a significant cause of mortality. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Computed Tomography (CT) have become essential tools for diagnosing and assessing kidney disorders. However, accurate analysis of these medical images is critical for detecting and evaluating tumor severity. This study introduces an integrated hybrid framework that combines three complementary deep learning models for kidney tumor segmentation from MRI images. The proposed framework fuses a customized U-Net and Mask R-CNN… More >