 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
The Potential of Circular RNAs as Biomarkers in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Related to Congenital Heart Disease
1 Doctorate Program of Medical and Health Science, Faculty of Medicine, Public Health and Nursing, Universitas Gadjah Mada, Yogyakarta, 55281, Indonesia
2 Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Riau, Pekanbaru, 28133, Indonesia
3 Department of Histology and Cell Biology, Faculty of Medicine, Public Health and Nursing, Universitas Gadjah Mada, Yogyakarta, 55281, Indonesia
4 Department of Cardiology and Vascular Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Public Health and Nursing, Universitas Gadjah Mada Dr. Sardjito Hospital, Yogyakarta, 55281, Indonesia
* Corresponding Author: Anggoro Budi Hartopo. Email:
Congenital Heart Disease 2024, 19(4), 375-388. https://doi.org/10.32604/chd.2024.054742
Received 06 June 2024; Accepted 29 September 2024; Issue published 31 October 2024
Abstract
A particular type of endogenous noncoding RNAs known as circular RNAs (circRNAs) has now become possible biomarkers for several diseases because of their stability and tissue-specific expression patterns. CircRNAs might play a role in various of biological processes. The identification of particular circRNAs dysregulated in pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) raises the possibility of these molecules serving as biomarkers for the disease’s early diagnosis and treatment. This review mainly summarizes the role and potential of circRNA as a future biomarker in PAH related to congenital heart disease. This study presented several potential circRNA targets as diagnostic biomarkers for PAH, discussed their biological functions, and addressed the challenges that need to be considered for their application in clinical settings.Graphic Abstract
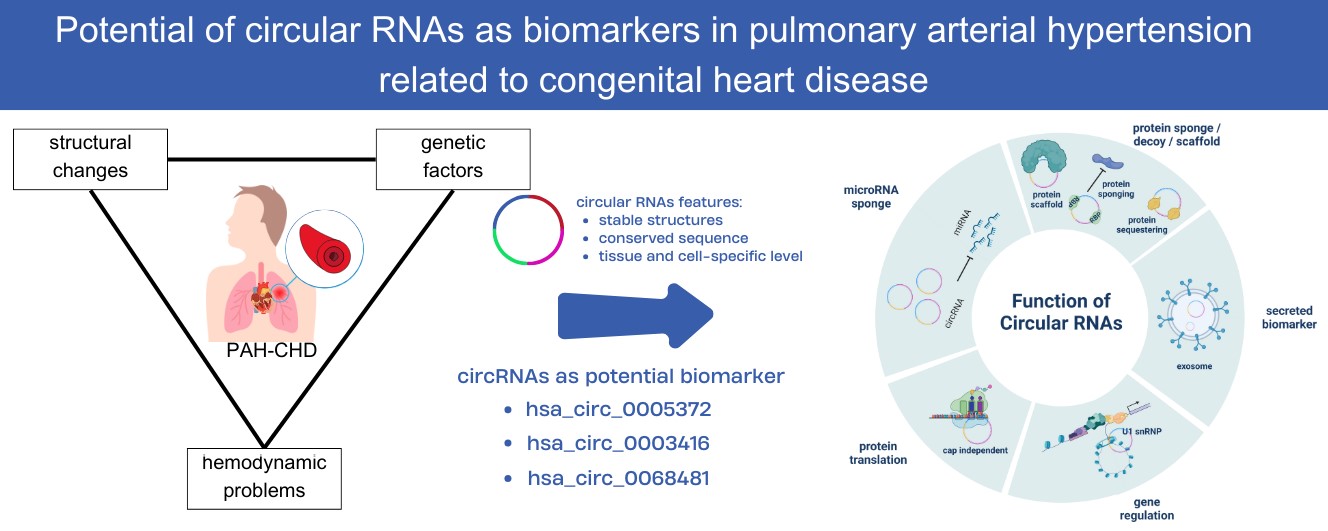
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools