 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Reliability of Echocardiographic Pulmonary Vascular Resistance to Screen for the New Definition of Precapillary Pulmonary Hypertension in Uncorrected Secundum Atrial Septal Defect
1 Department of Cardiology and Vascular Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Sebelas Maret, Surakarta, 57126, Indonesia
2 Department of Cardiology and Vascular Medicine, Universitas Sebelas Maret Hospital, Sukoharjo, 57161, Indonesia
3 Department of Cardiology and Vascular Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Public Health, and Nursing, Universitas Gadjah Mada, Yogyakarta, 55281, Indonesia
4 Department of Cardiology and Vascular Medicine, Dr. Sardjito Hospital, Yogyakarta, 55284, Indonesia
* Corresponding Author: Risalina Myrtha. Email:
Congenital Heart Disease 2024, 19(3), 315-324. https://doi.org/10.32604/chd.2024.051587
Received 09 March 2024; Accepted 31 May 2024; Issue published 26 July 2024
Abstract
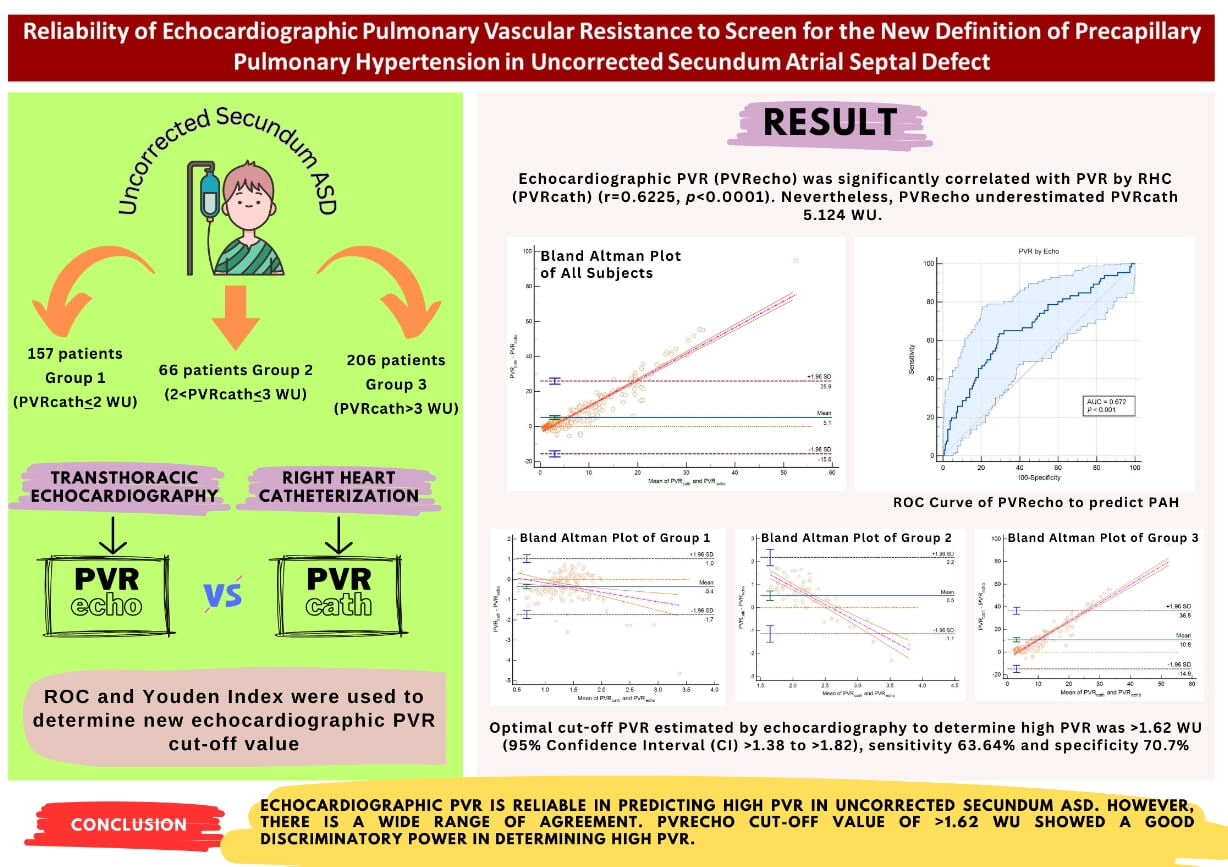
Background and Objective: The most feared complication of uncorrected secundum Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) is pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). Pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) is crucial in detecting precapillary pulmonary hypertension (PH) to guide the need for PAH-specific therapy. There is a change in the cut-off value of PVR according to the recently updated PH guideline. How echocardiographic PVR (PVR) correlates to PVR by right heart catheterization (RHC) (PVR) according to the new guidelines has not been known. The aim of this study is to determine the reliability of PVR in detecting PAH in Uncorrected Ostium Secundum ASD based on the current updated guideline and to help screen the high PVR group. Methods: 429 ostium secundum ASD in the COngenital HeARt Disease in Adult and Pulmonary Hypertension (COHARD-PH) registry was divided into three groups according to the PVR. PVR was calculated using Abbas’ Formula and compared the its gold standard, the PVR. The correlation between the two methods was analyzed. The Bland-Altman plot was used to analyze the agreement between the two methods. Receiver operating characteristics (ROC) analysis was used to determine the PVR cut-off value for high PVR. Results: The majority of the population (63.5%) had high PVR. Female gender dominated the study population (84%). PVR was significantly correlated with PVR (r = 0.6225, p < 0.0001). Bland-Altman plot among all groups and in subgroups analysis showed a wide range of agreement. PVR underestimated PVR 5.124 WU. In subgroup analysis, PVR overestimated PVR 0.35 WU in those with PVR < 2 WU. In the second and third groups, PVR underestimated PVR 0.52 and 10.77 WU, respectively. Conclusion: PVR is reliable in predicting high PVR in uncorrected secundum ASD. However, there is a wide range of agreement. PVR cut-off value of >1.62 WU showed good discriminatory power in determining high PVR.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools