 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Comparison of 2D and 4D Flow MRI Measurements for Hemodynamic Evaluation of the Fontan Palliation
1 Department of Radiology, IRCCS Istituto Giannina Gaslini, Genova, Italy
2 U.O.C. Bioingegneria, Gabriele Monasterio CNR-Tuscany Foundation, Pisa, Italy
3 Institute of Clinical Physiology CNR, Pisa, Italy
4 Cardiology Unit, IRCCS Istituto Giannina Gaslini, Genova, Italy
5 Pediatric Cardiology and GUCH Unit Massa, Gabriele Monasterio CNR-Tuscany Foundation, Massa, Italy
6 Gabriele Monasterio CNR-Tuscany Foundation, Pisa, Italy
7 Department of Cardiology, Azienda Ospedaliero-Universitaria Meyer, Florence, Italy
8 Institute of Clinical Physiology CNR, Massa, Italy
* Corresponding Authors: Francesca Raimondi. Email: ; Lamia Ait Ali. Email:
# Elisa Listo and Nicola Martini contributed equally to the study
Congenital Heart Disease 2023, 18(6), 627-638. https://doi.org/10.32604/chd.2023.030312
Received 30 March 2023; Accepted 10 August 2023; Issue published 19 January 2024
Abstract
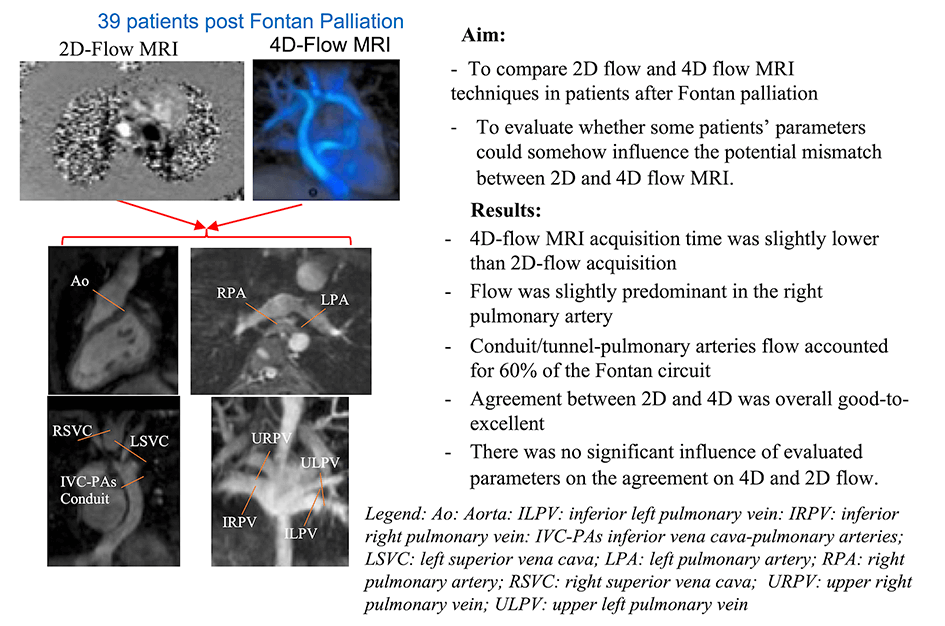
Background: The assessment of Fontan circuit’s flow is traditionally evaluated by multiple through-plane phase-contrast MRI acquisitions (2D flow), while recently, a single volumetric 4D-flow MRI acquisition is emerging as a comprehensive tool for the hemodynamic evaluation in congenital heart diseases. Purpose: To compare 2D and 4D-flow MRI measurements in patients after Fontan palliation and to evaluate parameters affecting potential disagreement. Methods: 39 patients after Fontan palliation (23 males, age 22 ± 11 years) who underwent cardiac MRI with 2D and 4D-flow MRI acquisition were included in the study. In all patients, blood flow quantification in the Fontan circuit and aorta by 2D flow and by 4D flow MRI acquisition blinding to the 2D results was performed. The agreement between 2D and 4D-flow MRI was calculated as the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC). The mean absolute differences between 4D and 2D flows were analyzed using linear regression models. Results: 4D-flow MRI acquisition time was slightly lower than 2D (7.6 ± 1.8 min vs. 9.4 ± 3.3 min, p = 0.03). Flow was slightly predominant in the right pulmonary artery (58% of total pulmonary flow). Conduit/tunnel-pulmonary arteries flow accounted for 60% of the Fontan circuit. Agreement between 2D and 4D was overall good-to-excellent from ICC: 0.817 95% CI: 0.637–0.907 to 0.932 95% CI: 0.866–0.965. There was no significant influence of evaluated parameters on the agreement on 4D and 2D flow. Conclusions: 4D-flow MRI represents a valid tool in Fontan’s flow quantification. Further larger studies are needed to confirm our results and to evaluate the impact of advanced 4D-flow MRI parameters on the prognostic stratification in patients after Fontan palliation.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material FileCite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools