 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Assessment of Intracardiac and Extracardiac Deformities in Patients with Various Types of Pulmonary Atresia by Dual-Source Computed Tomography
1 Department of Radiology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
2 Department of Radiology, Chengdu Women’s and Children’s Central Hospital, School of Medicine, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China
3 Department of Radiology, Peking University Cancer Hospital and Institute, Beijing, China
* Corresponding Author: Zhigang Yang. Email:
# These authors contributed equally to this work and should be considered the co-first authors
Congenital Heart Disease 2023, 18(1), 113-125. https://doi.org/10.32604/chd.2023.023542
Received 25 May 2022; Accepted 29 November 2022; Issue published 09 January 2023
Abstract
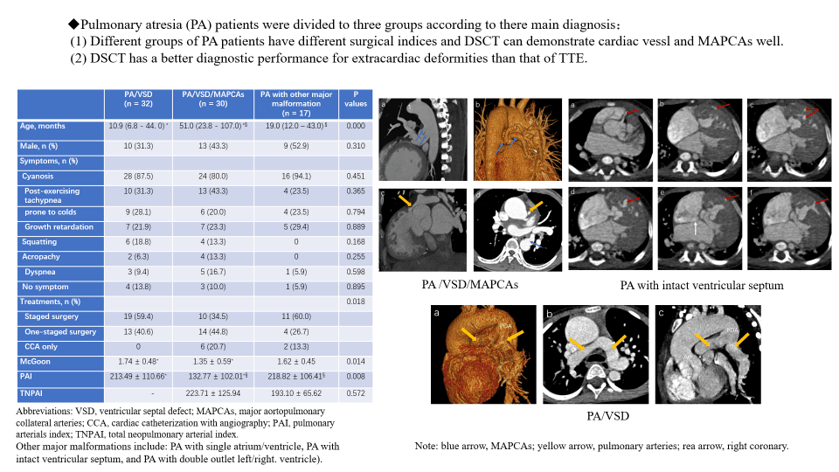
Background: Pulmonary atresia (PA) is a group of heterogeneous complex congenital heart disease. Only one study modality might not get a correct diagnosis. This study aims to investigate the diagnostic power of dual-source computed tomography (DSCT) for all intracardiac and extracardiac deformities in patients with PA compared with transthoracic echocardiography (TTE). Materials and Methods: This retrospective study enrolled 79 patients and divided them into three groups according to their main diagnosis. All associated malformations and clinical information, including treatments, were recorded and compared among the three groups. The diagnostic power of DSCT and TTE on all associated malformations were compared. The surgical index (McGoon ratio, pulmonary arterials index (PAI), and total neopulmonary arterial index) and radiation dose were calculated on the basis of DSCT. Results: Of the patients, 32, 30, and 17 were divided into the groups of PA with ventricular septal defect (VSD), PA with VSD and major aortopulmonary collateral arteries, and PA with other major malformations, respectively. Consequently, 182, 162, and 13 intracardiac, extracardiac, and other major malformations were diagnosed, respectively. Moreover, DSCT showed a better diagnostic performance in extracardiac deformities (154 vs. 117, p < 0.001), whereas TTE could diagnose intracardiac deformities better (159 vs. 139, p = 0.001). The McGoon ratio, PAI, and treatment methods were significantly different among the three groups (p = 0.014, p = 0.008, and p = 0.018, respectively). Conclusion: More than one imaging modality should be used to make a correct diagnosis when clinically suspecting PA. DSCT is superior to TTE in diagnosing extracardiac deformities and could be used to roughly calculate surgical indices to optimize treatment strategy.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools