 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Mortality and Long-Term Outcome of Neonates with Congenital Heart Disease and Acute Perinatal Stroke: A Population-Based Case-Control Study
1 First Department of Pediatrics, Semmelweis University, MTA Centre of Excellence, Budapest, Hungary
2 Department of Pediatrics, Saint John Hospital and North-Buda Unified Hospitals, Budapest, Hungary
3 Epiconsult BioMedical Consulting and Medical Communications Agency, Dover, USA
4 Department of Epidemiology, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, USA
5 Department of Rehabilitation, Saint John Hospital and North-Buda Unified Hospitals, Budapest, Hungary
6 Institute of Mathematics and Base Sciences, Hungarian University of Agriculture and Life Sciences, Gödöllő, Hungary
7 Gottsegen National Cardiovascular Center, Budapest, Hungary
8 Children’s Hospital Los Angeles, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, USA
* Corresponding Author: Eszter Vojcek. Email:
Congenital Heart Disease 2022, 17(4), 447-461. https://doi.org/10.32604/chd.2022.022274
Received 07 March 2022; Accepted 25 May 2022; Issue published 04 July 2022
Abstract
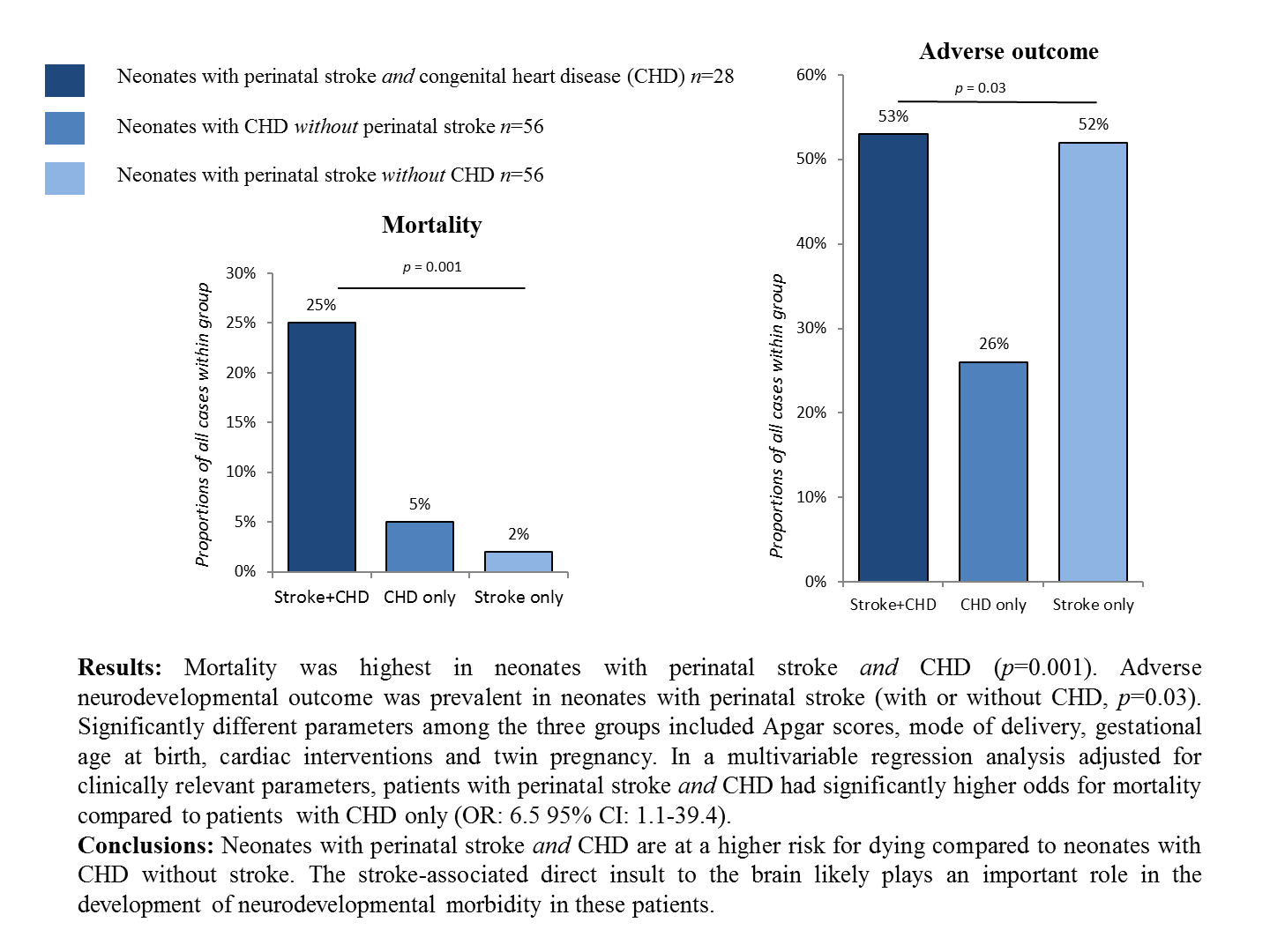
Objective: Neonates with congenital heart disease (CHD) and perinatal stroke have high mortality and survivors are at risk for poor long-term neurodevelopmental outcome. The aim of this study was to assess the risk factors and outcome of neonates with both CHD and MRI-confirmed perinatal stroke (Study Group) and compare those to the risk factors and outcome of infants matched for CHD without stroke (Control-1) and of infants matched for MRI-confirmed stroke without CHD (Control-2). Methods: We conducted a population-based case-control study enrolling 28 term neonates with CHD and MRI-confirmed acute perinatal stroke born between 2007–2017 in the Central-Hungarian Region. Each of the control groups included 56 infants. The Bayley Scales of Infant Development-II, the Brunet-Lézine test and the Binet Intelligence scales-V were used for neurodevelopmental follow-up at a median age of 61 months. Results: Mortality was highest in the Study Group (25% compared to 5% and 2%, respectively, p = 0.001). Adverse neurodevelopmental outcome was prevalent in the Study (53%) and Control-2 Groups (52%, p = 0.03). Significantly different parameters among the three groups included Apgar scores, mode of delivery, gestational age at birth, cardiac interventions and twin pregnancy. In a multivariable regression analysis adjusted for clinically relevant parameters, patients in the Study Group had significantly higher odds for mortality compared to patients in the Control-1 Group (OR: 6.5 95% CI: 1.1–39.4). Conclusions: Neonates with perinatal stroke and CHD are at a higher risk for dying compared to neonates with CHD without stroke. In addition, the stroke-associated direct insult to the brain likely plays an important role in the development of neurodevelopmental morbidity in these patients.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools