 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Modulatory role of plant-derived metabolites on host-microbiota interactions: personalized therapeutics outlook
Department of Biochemistry, Maharshi Dayanand University Rohtak, Rohtak, Haryana, India
* Corresponding Author: NAR SINGH CHAUHAN. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Gut Microbiota in Human Health: Exploring the Complex Interplay)
BIOCELL 2024, 48(8), 1127-1143. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2024.051318
Received 02 March 2024; Accepted 10 May 2024; Issue published 02 August 2024
Abstract
A diverse array of microbes in and on the human body constitute the microbiota. These micro-residents continuously interact with the human host through the language of metabolites to dictate the host’s physiology in health and illnesses. Any biotic and abiotic component ensuring a balanced host-microbiota interaction are potential microbiome therapeutic agents to overcome human diseases. Plant metabolites are continually being used to treat various illnesses. These metabolites target the host’s metabolic machinery and host-gut microbiota interactions to overcome human diseases. Despite the paramount therapeutic significance of the factors affecting host-microbiota interactions, a comprehensive overview of the modulatory role of plant-derived metabolites in host-microbiota interactions is lacking. The current review puts an effort into comprehending the role of medicinal plants in gut microbiota modulation to mitigate various human illnesses. It would develop a holistic understanding of host-microbiota interactions and the role of effectors in health and diseases.Graphic Abstract
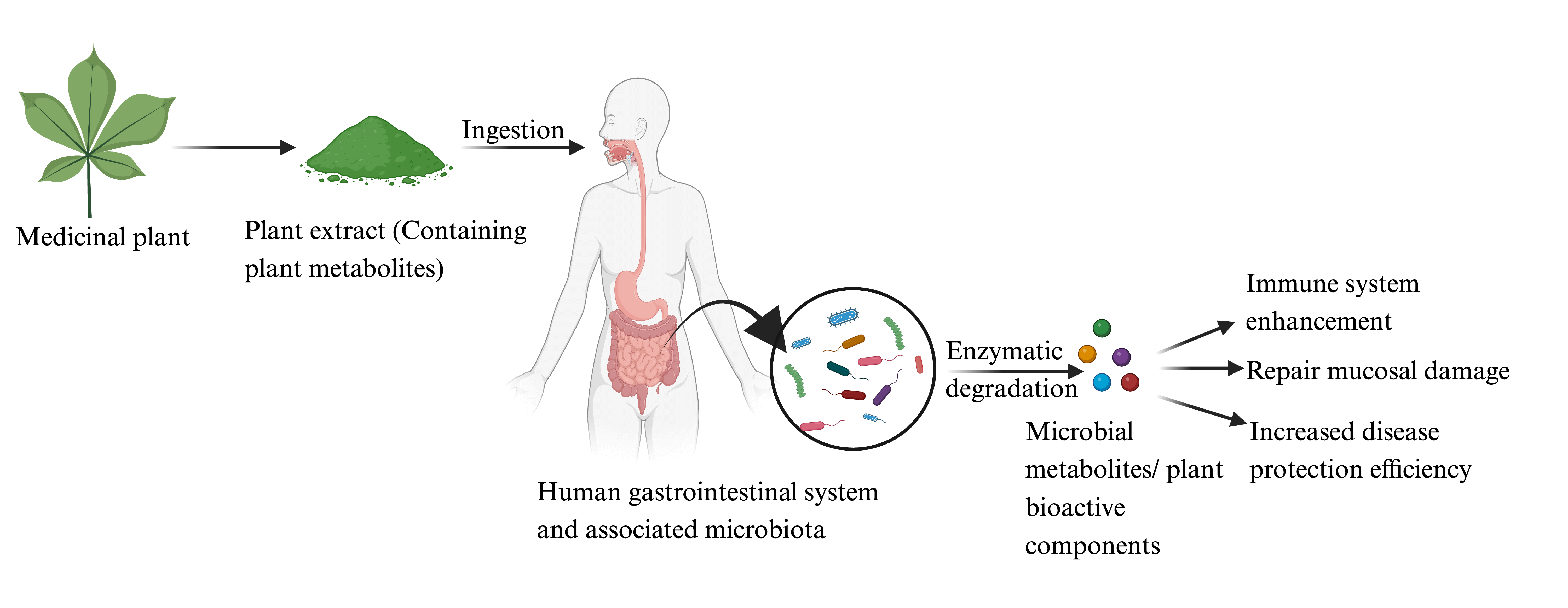
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools