 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Paclitaxel induces human KOSC3 oral cancer cell apoptosis through caspase pathways
1 School of Medicine, College of Medicine, I-Shou University, Kaohsiung, 82445, Taiwan
2 Department of Otolaryngology, An Nan Hospital, China Medical University, Tainan, 70965, Taiwan
3 Department of Cell Biology and Anatomy, College of Medicine, National Cheng Kung University, Tainan, 70101, Taiwan
4 Department of Medical Research, China Medical University Hospital, China Medical University, Taichung, 40402, Taiwan
* Corresponding Authors: CHIA-YIH WANG. Email: ; BU-MIIN HUANG. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Navigating the Interplay of Cancer, Autophagy, ER Stress, Cell Cycle and Apoptosis: Mechanisms, Therapies, and Future Directions)
BIOCELL 2024, 48(7), 1047-1054. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2024.050701
Received 14 February 2024; Accepted 25 March 2024; Issue published 03 July 2024
Abstract
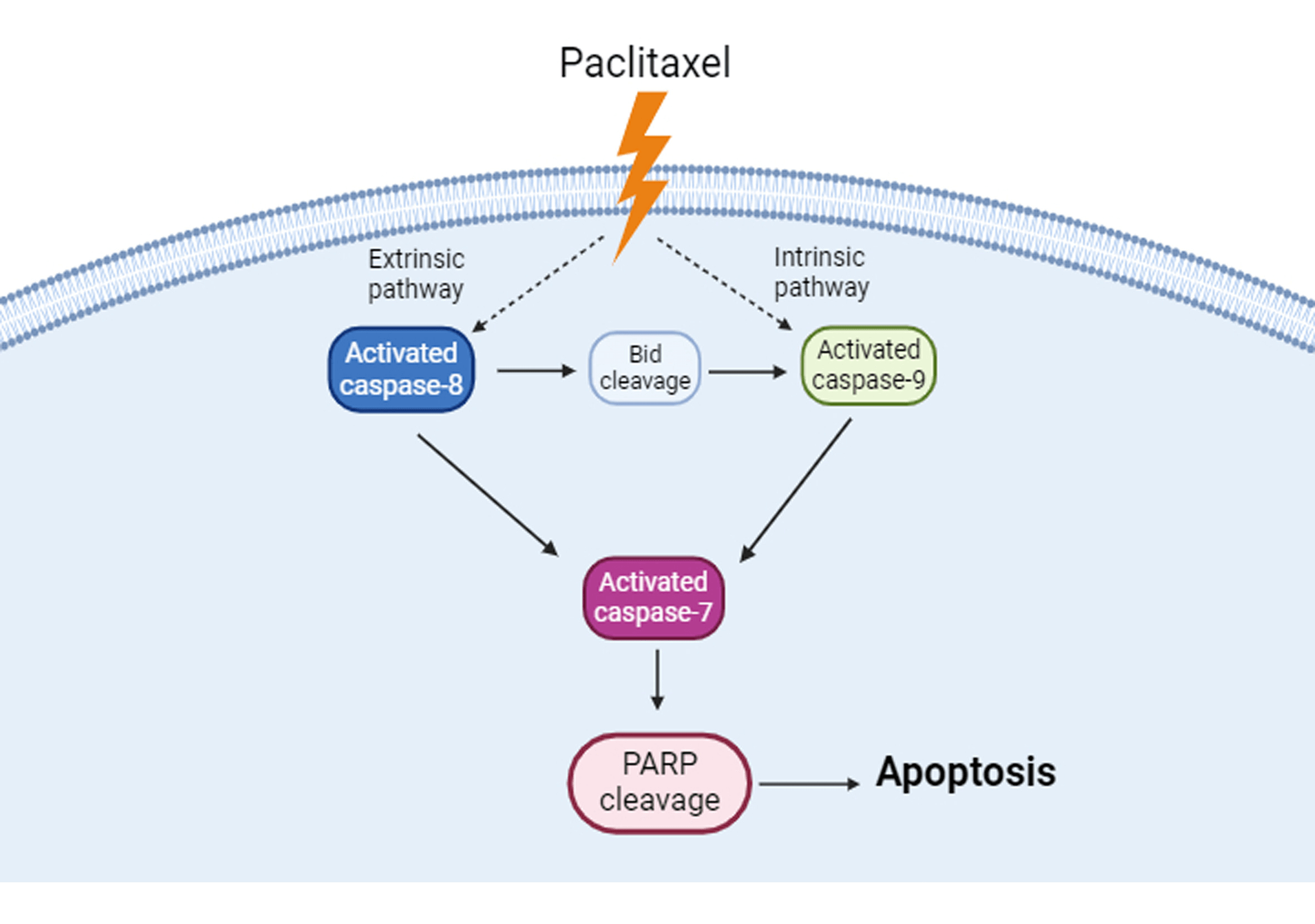
Background: Paclitaxel is a compound derived from Pacific yew bark that induces various cancer cell apoptosis. However, whether it also has anticancer activities in KOSC3 cells, an oral cancer cell line, is unclear. Methods: 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide, flow cytometry, and western blotting assays were carried out to assess cell viability, subG1 phase of the cell cycle, and apoptosis-related protein expression, respectively. Results: Our findings indicate that paclitaxel could inhibit cell viability and increase the expression of apoptotic markers, including plasma membrane blebbing and the cleavage of poly ADP-ribose polymerase in KOSC3 cells. Also, the treatment with paclitaxel remarkably elevated the percentage of the subG1 phase in KOSC3 cells. In addition, treatment with a pan-caspase inhibitor could recover paclitaxel-inhibited cell viability. Moreover, caspase-8, caspase-9, caspase-7, and BH3 interacting domain death agonist (Bid) were activated in paclitaxel-treated KOSC3 cells. Conclusions: Paclitaxel induced apoptosis through caspase cascade in KOSC3 cells.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools