 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
miR-557 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and migration via downregulating CBX4
1 Department of Orthopedics, Shanghai General Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, 200080, China
2 Department of General Surgery, Shanghai General Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, 200080, China
3 Department of Thoracic Surgery, Shanghai Chest Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, 200030, China
4 Department of Radiology, Zhongda Hospital, Southeast University School of Medicine, Nanjing, 210009, China
* Corresponding Author: ZHIAN FANG. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: New Perspectives on Inflammatory Cancer Transformation)
BIOCELL 2024, 48(7), 1071-1079. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2024.050519
Received 08 February 2024; Accepted 15 March 2024; Issue published 03 July 2024
Abstract
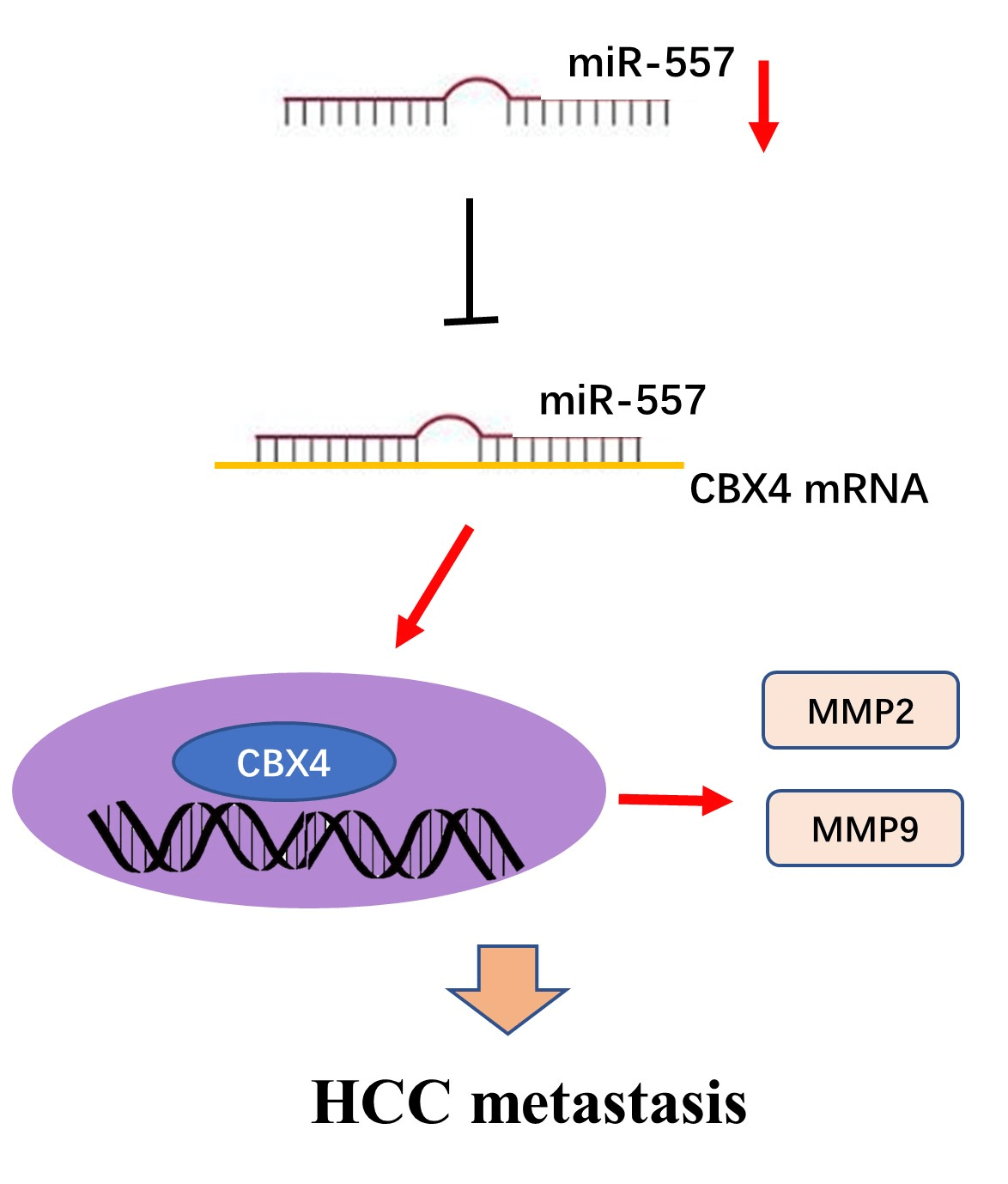
Introduction: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), a prevalent malignancy, poses significant challenges with high tumor heterogeneity and poor prognosis. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play a pivotal role in hepatocarcinogenesis. Although abnormalities in microRNA-557 (miR-557) expression have been implicated in various cancer types, its role in HCC remains unclear. Therefore, there is a need to explore the function of microRNA-557 in HCC. Methods: Candidate miRNAs were identified through screening in GSE108724 and GSE20077. Real-time PCR was employed to analyze the expression level of miR-557 in hepatoma cell lines and tissues. Cell viability and migration assays were applied to assess the impact of miR-557 on HCC cell lines. Furthermore, the miR-557 target was predicted through three algorithms (Targetscan, miRWalk, and miRanda), and this was confirmed through luciferase assay and Western blotting. Results: In this study, miR-557 was identified in two datasets and expressed at a low level in both hepatoma cell lines and tissues. Notably, high expression of miR-557 in HCC cells inhibited oncogenesis. Conversely, low expression of miR-557 enhanced tumor proliferation and migration. Polycomb chromobox 4 (CBX4) was identified as a direct target of miR-557. Silencing CBX4 influenced the functional impact of miR-557 on HCC cell migration. Conclusion: Taken together, our study contributed to elucidating the hepatoma molecular heterogeneity and provided novel insights into miR-557 role and its target CBX4 in HCC, suggesting its potential as a future effectively druggable target for HCC intervention.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools