 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Sciadopitysin exerts anticancer effects on HepG2 hepatocellular carcinoma cells by regulating reactive oxygen species-mediated signaling pathways
1 Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University, Daqing, China
2 Hemodialysis Center, Daqing Oilfield General Hospital, Daqing, China
3 Department of Food Science and Engineering, Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University, Daqing, China
4 Department of Molecular Biology, Chifeng University, Chifeng, China
5 National Coarse Cereals Engineering Research Center, Daqing, China
* Corresponding Authors: TIAN-ZHU LI. Email: ; CHENG-HAO JIN. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Navigating the Interplay of Cancer, Autophagy, ER Stress, Cell Cycle and Apoptosis: Mechanisms, Therapies, and Future Directions)
BIOCELL 2024, 48(7), 1055-1069. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2024.050515
Received 08 February 2024; Accepted 09 April 2024; Issue published 03 July 2024
Abstract
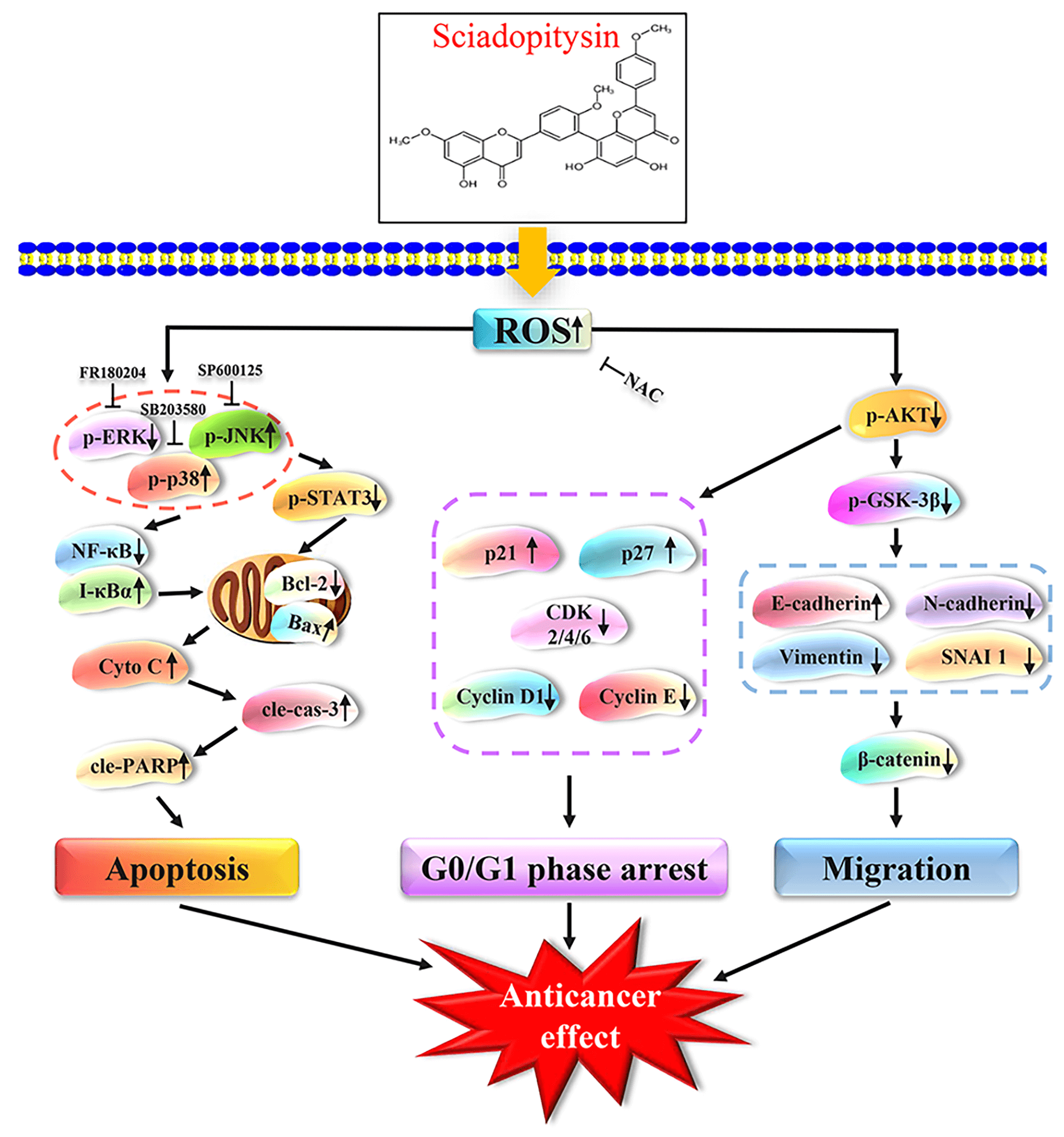
Objectives: Sciadopitysin (SP) is a flavonoid in Ginkgo biloba that exhibits various pharmacological activities. This study aimed to investigate its antitumor effects and the underlying molecular mechanism of SP in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells. Methods: Network pharmacology was used for target prediction analysis. Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay was used to test the cell viability. Flow cytometry was used to test the cell cycle distribution, apoptosis status, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels. Transwell and wound-healing assay was used to test the migration effect of SP on HepG2 cells. Western Blot assay was used to test the expression levels of proteins. Results: Network pharmacology analysis results showed that the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and other signaling pathways are involved in the SP anti-HCC biological process. CCK-8 assay results demonstrated that SP showed an obvious killing effect on three types of HCC cells and low cytotoxic effect on normal cells. Western Blot and flow cytometry results showed that SP regulated MAPK/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3)/nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) signaling pathway to induce mitochondrion-dependent apoptosis in HepG2 cells. Additionally, SP can arrest the G0/G1 phase cell cycle via the protein kinase B (AKT)/p21/p27/cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK)/Cyclin signaling pathway. Wound healing and transwell assays showed that SP inhibited cell motility and invasion through the AKT/glycogen synthase kinase3β (GSK-3β)/vimentin/β-catenin signaling pathway. Conclusion: These findings demonstrated that SP induced mitochondrion-dependent apoptosis, arrested cell cycle in the G0/G1 phase, and inhibited cell migration by regulating the ROS-mediated signaling pathway in HepG2 cells. Thus, SP could serve as a therapeutic agent for the treatment of human HCC.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools