 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Chemokine-like factor 1 (CKLF1) is expressed in myocardial ischemia injury in vivo and in vitro
1 School of Pharmacy, Department of Pharmacy, Hunan Engineering Technology Center of Standardization and Function of Chinese Herbal Decoction Pieces, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, 410208, China
2 Department of Pharmacology, State Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substances and Functions of Natural Medicines, Institute of Materia Medica & Neuroscience Center, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, 100050, China
3 Department of Diagnostics Research Lab of Translational Medicine, Hengyang Medical College, University of South China, Hengyang, 421001, China
4 Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital, Hengyang Medical College, University of South China, Hengyang, 421001, China
* Corresponding Authors: SHIFENG CHU. Email: ; NAIHONG CHEN. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Subcellular Organelles and Cellular Molecules: Localization, Detection, Prediction, and Diseases)
BIOCELL 2024, 48(6), 981-990. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2024.050011
Received 24 January 2024; Accepted 09 April 2024; Issue published 10 June 2024
Abstract
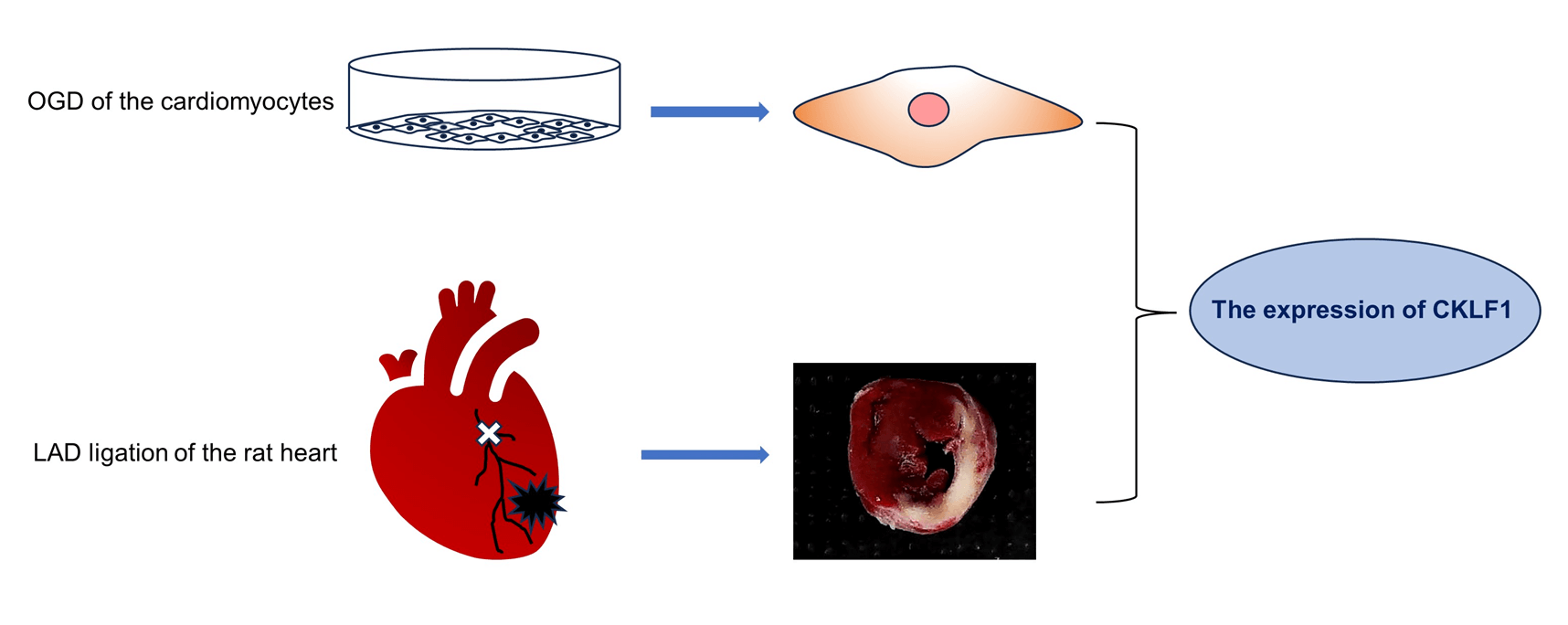
Introduction: Chemokine-like factor 1 (CKLF1) is a chemokine that is overexpressed in several diseases. Our previous findings revealed a significant increase in CKLF1 expression in the ischemic brain, suggesting its potential as a therapeutic target for ischemic stroke. Methods: In this study, we examined the expression dynamics of CKLF1 in both in vivo and in vitro models of ischemic cardiac injury. Myocardial infarction (MI) was induced in vivo by ligation of the left anterior descending artery (LAD) of the rat heart. The levels of CKLF1, Creatine Kinase MB Isoenzyme (CK-MB), and Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) in the serum were detected using Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The expression of CKLF1 in the infarcted area was detected by immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence, quantitative PCR (qPCR), and Western blotting (WB). H9C2 and AC16 cardiomyocytes cultured in vitro were subjected to oxygen and glucose deprivation (OGD). LDH was used to detect cell damage, and CKLF1 expression was detected by qPCR and WB. Results: CKLF1 mRNA and protein expression were significantly increased in h9c2 cells at 1.5 h and in AC16 cells at 4 h after OGD. The serum CK-MB in rats increased significantly on the first day after infarction, while the LDH concentration increased significantly on the third day after infarction. CKLF1 blood levels significantly increased on the first day following MI in rats. CKLF1 expression notably increased in the infarct area on days 1, 3, and 7 post-MI. In MI tissue, CKLF1 colocalizes with cardiomyocytes, macrophages, and neutrophils. Conclusion: CKLF1 was substantially expressed during myocardial ischemia injury both in vivo and in vitro and was colocalized with macrophages and neutrophils, indicating that CKLF1 is expected to be a biomarker and a drug target for the treatment of myocardial infarction.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools