 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
OPA3 overexpression modulates lipid droplet production and sensitizes colorectal cancer cells to bevacizumab treatment
Department of Colorectal and Anal Surgery, Ningbo First Hospital, Ningbo, 315010, China
* Corresponding Author: HONGBIAO WU. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Intestinal Epithelial Cells in Health and Disease)
BIOCELL 2024, 48(6), 971-980. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2024.049466
Received 08 January 2024; Accepted 07 March 2024; Issue published 10 June 2024
Abstract
Background: Colorectal cancer (CRC) represents a substantial risk to public health. Bevacizumab, the first US FDA-approved antiangiogenic drug (AAD) for human CRC treatment, faces resistance in patients. The role of lipid metabolism, particularly through OPA3-regulated lipid droplet production, in overcoming this resistance is under investigation. Methods: The protein expression pattern of OPA3 in CRC primary/normal tissues was evaluated by bioinformatics analysis. OPA3-overexpressed SW-480 and HCT-116 cell lines were established, and bevacizumab resistance and OPA3 effects on cell malignancy were examined. OPA3 protein/mRNA expression and lipid droplet-related genes were measured with Western blot and qRT-PCR. OPA3 subcellular localization was detected using immunofluorescence. Proliferation and apoptosis were assessed via colony formation and flow cytometry. Tube formation assays were conducted to assess the angiogenic potential of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Lipid analysis was used to measure the phosphatidylcholine (PC) and lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) levels in CRC cells. Results: Bioinformatics analysis revealed that OPA3 was downregulated in CRC. Overexpression of OPA3 inhibited CRC cell proliferation, stimulated apoptosis, and suppressed the angiogenic ability of HUVECs. OPA3 effectively reversed the resistance of CRC cells to bevacizumab and decreased lipid droplet production in CRC cells. Additionally, OPA3 reversed the bevacizumab-induced lipid droplet production in CRC cells, thereby increasing CRC cell sensitivity to bevacizumab treatment. Conclusion: This study suggests that OPA3 modulates lipid metabolism in CRC cells and reduces resistance to bevacizumab in CRC cells. Therefore, OPA3 may be a potential therapeutic target against the AAD resistance in CRC.Graphic Abstract
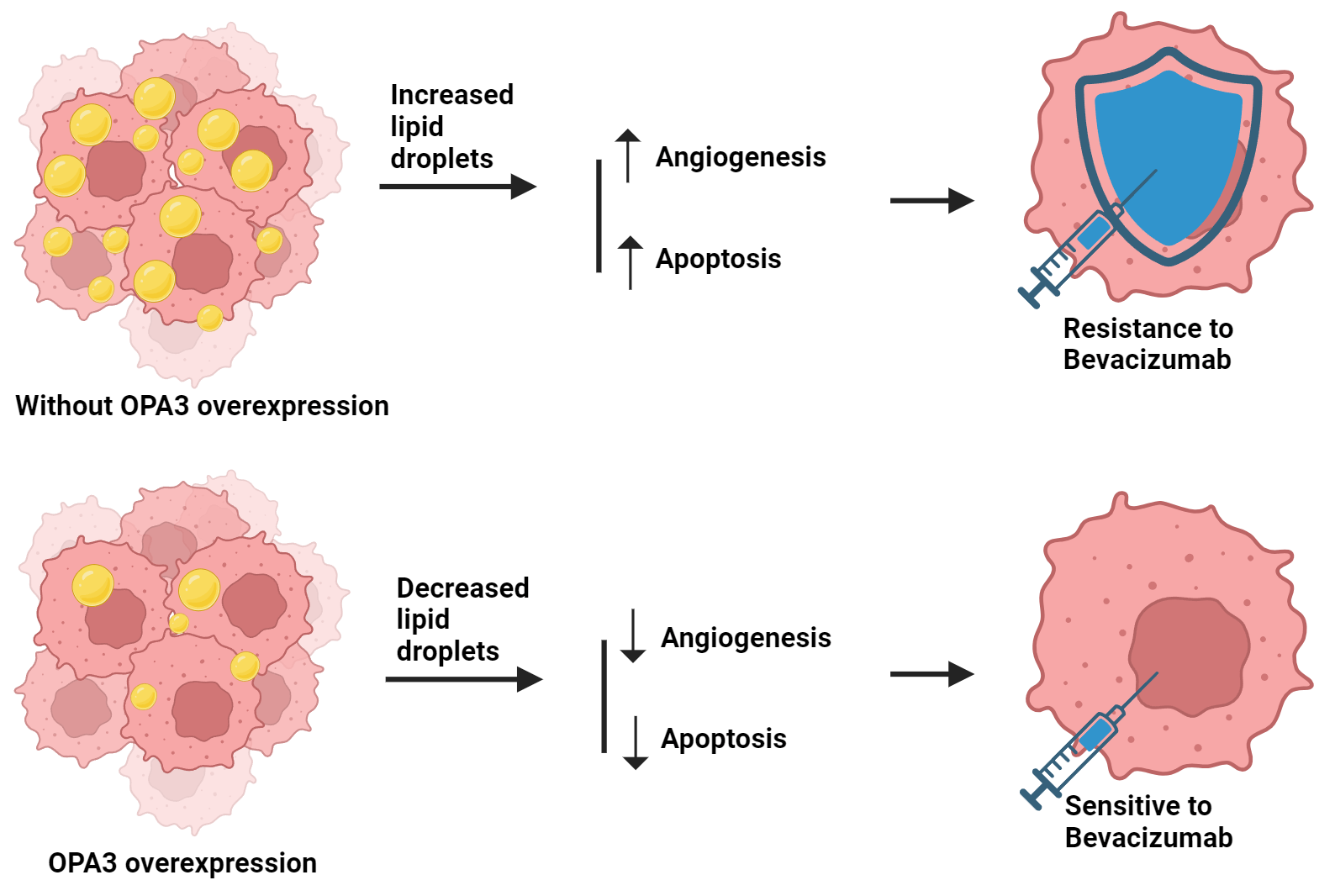
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools