 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CMTM6 deletion affects chemoresistance and macrophage M2 polarization in colorectal cancer cells
1 Department of Medical Oncology, The Third Medical Center of Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing, 100039, China
2 Department of Oncology, People’s Hospital of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, Yinchuan, 750000, China
* Corresponding Author: GE YOU. Email:
# Both of the two authors contributed equally and all authors agree to define them as co-first authors
BIOCELL 2024, 48(2), 229-237. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2023.045030
Received 15 August 2023; Accepted 02 November 2023; Issue published 23 February 2024
Abstract
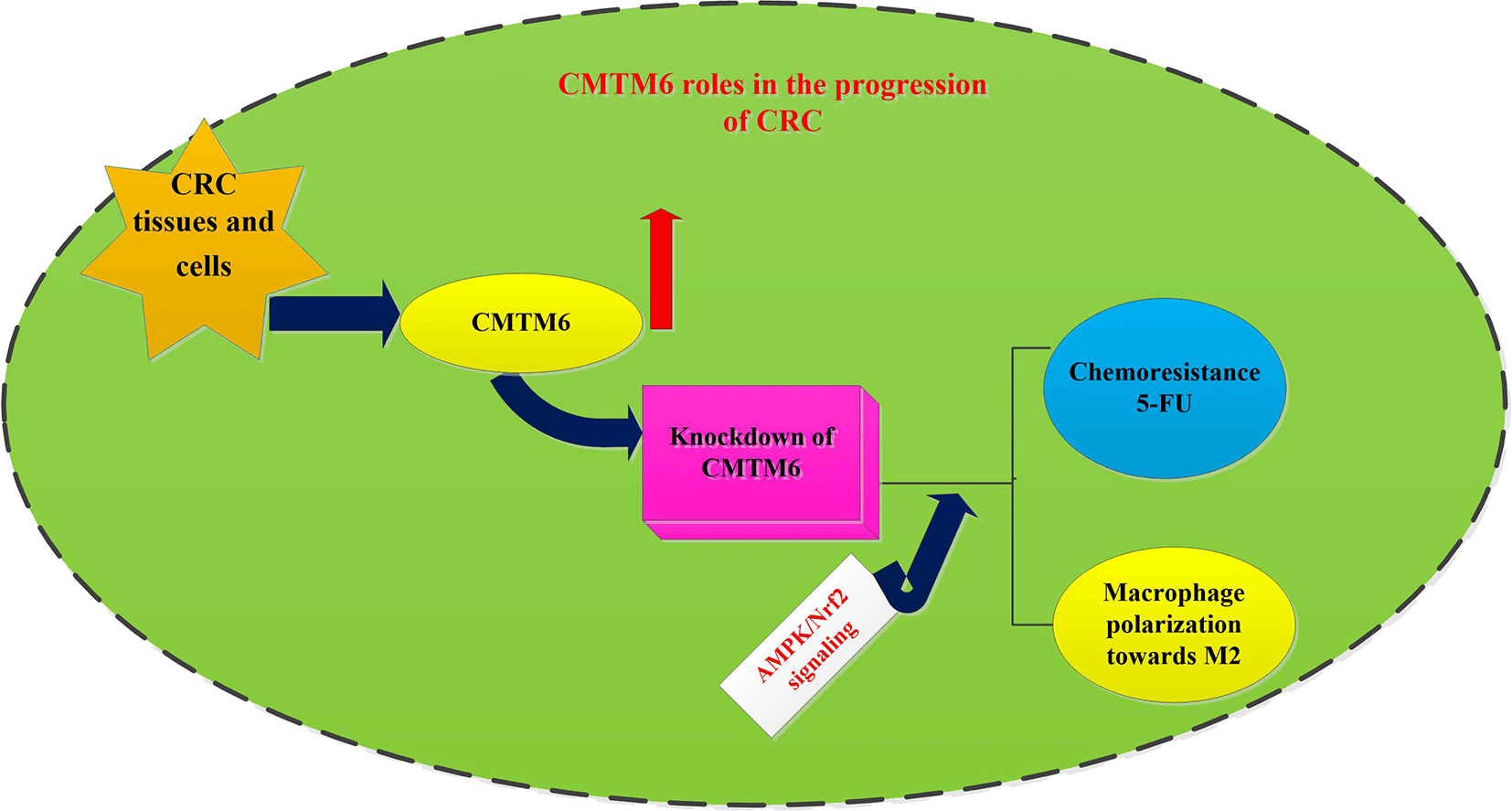
Background: Colorectal cancer (CRC) constitutes the leading cause of death worldwide. Chemoresistance and tumor immune evasion are critical contributors to therapeutic failure in cancer patients. CKLF-like MARVEL transmembrane domain-containing 6 (CMTM6) is aberrantly expressed in various cancers and can regulate tumor immunity. However, its role in chemoresistance and tumor immunity of CRC is not well understood. Methods: Online bioinformatics tools were used to analyze expression and prognosis of CMTM6 in CRC patients. CRC cells were transfected with si-CMTM6. Subsequently, the effects on CRC cell viability and chemoresistance were investigated by CCK-8 assay and flow cytometer. Furthermore, CRC cell-induced macrophage recruitments and polarization were also explored. Results: High expression of CMTM6 was detected in CRC tissues and cells, and its expression was associated with the prognosis of patients with CRC. Notably, CMTM6 knockdown suppressed cancer cell viability. Moreover, CMTM6 loss enhanced cancer cell sensitivity to 5-FU by reducing cell viability and enhancing apoptosis and activity of caspase-3. Importantly, CMTM6 loss inhibited CRC cells-evoked macrophage recruitments and polarization towards M2 phenotype by increasing the ratio of CD206+ cells and expression of M2 macrophage markers (arginase1, IL-10, CD206 and TGF-β). Intriguingly, targeting CMTM6 activated the AMPK singling and suppressed the subsequent activation of the NF-κB pathway. Blockage of the AMPK signaling reversed the suppressive efficacy of CMTM6 loss in 5-FU resistance and cancer cells-evoked macrophage M2-like polarization. Conclusion: CMTM6 may affect the progression of CRC by regulating chemoresistance and macrophage-related immune evasion, implying a promising target to overcome chemoresistance and immune escape in the treatment of CRC.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools