 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
A novel oxaliplatin-resistant gene signatures predicting survival of patients in colorectal cancer
1 Department of General Surgery, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China
2 Department of Oncology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China
* Corresponding Author: JIANPING ZHANG. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Frontiers in cancer: tumor microenvironment)
BIOCELL 2024, 48(2), 253-269. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2023.028336
Received 15 December 2022; Accepted 01 June 2023; Issue published 23 February 2024
Abstract
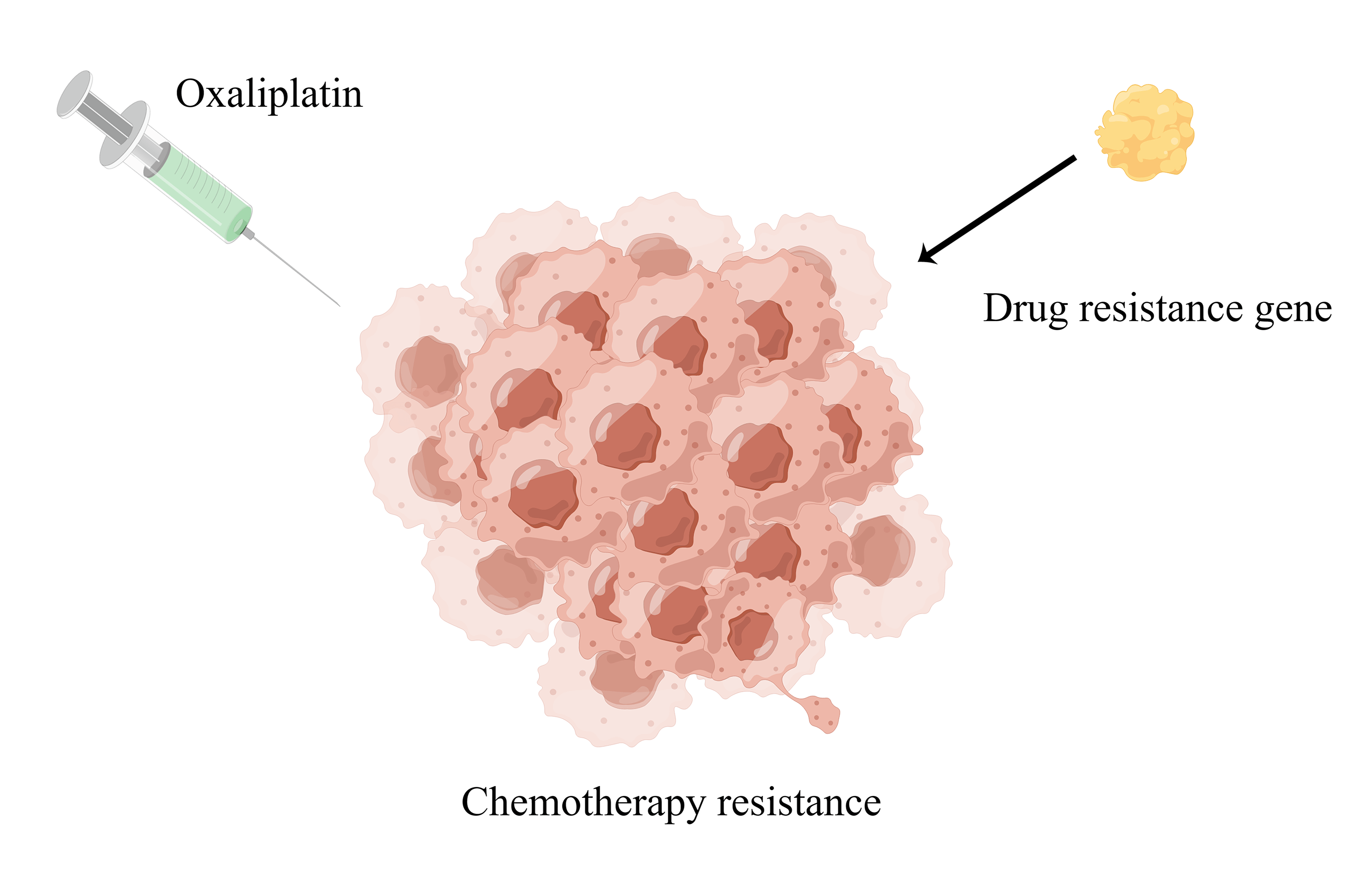
Objectives: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a serious threat to human health worldwide. Oxaliplatin is a platinum analog and is widely used to treat CRC. However, resistance to oxaliplatin restricts its effectiveness and application while its target recognition and mechanism of action also remain unclear. Therefore, we aimed to develop an oxaliplatin-resistant prognostic model to clarify these aspects. Methods: We first obtained oxaliplatin-resistant and parental cell lines, and identified oxaliplatin-resistant genes using RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) and differential gene analysis. We then acquired relevant data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) databases. Cox regression and Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) regression were used to identify satisfactory resistance genes, and a prognostic model was established. Finally, small-molecule drugs targeting the high-risk (HR) and low-risk (LR) groups were predicted. Results: We identified 14 oxaliplatin-resistance genes in CRC. We built a model with these and used it to classify patients with CRC. Overall survival was better in the LR group than in the HR group (p < 0.001). Multivariate and univariate prognostic analyses revealed that this newly developed model had an independent prognostic value (p < 0.001). The risk score was found to be associated with the tumor microenvironment (TME) and 11 types of immune cells as per the CIBERSORT algorithm results. Finally, we screened 47 small-molecule drugs with half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values that were related to the risk scores. Conclusion: Our novel prognostic model for oxaliplatin resistance can be used to stratify the risk of CRC.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools