 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Review on analytical technologies and applications in metabolomics
School of Pharmacy, Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine, Harbin, China
* Corresponding Author: XIN MENG. Email:
BIOCELL 2024, 48(1), 65-78. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2023.045986
Received 14 September 2023; Accepted 06 November 2023; Issue published 30 January 2024
Abstract
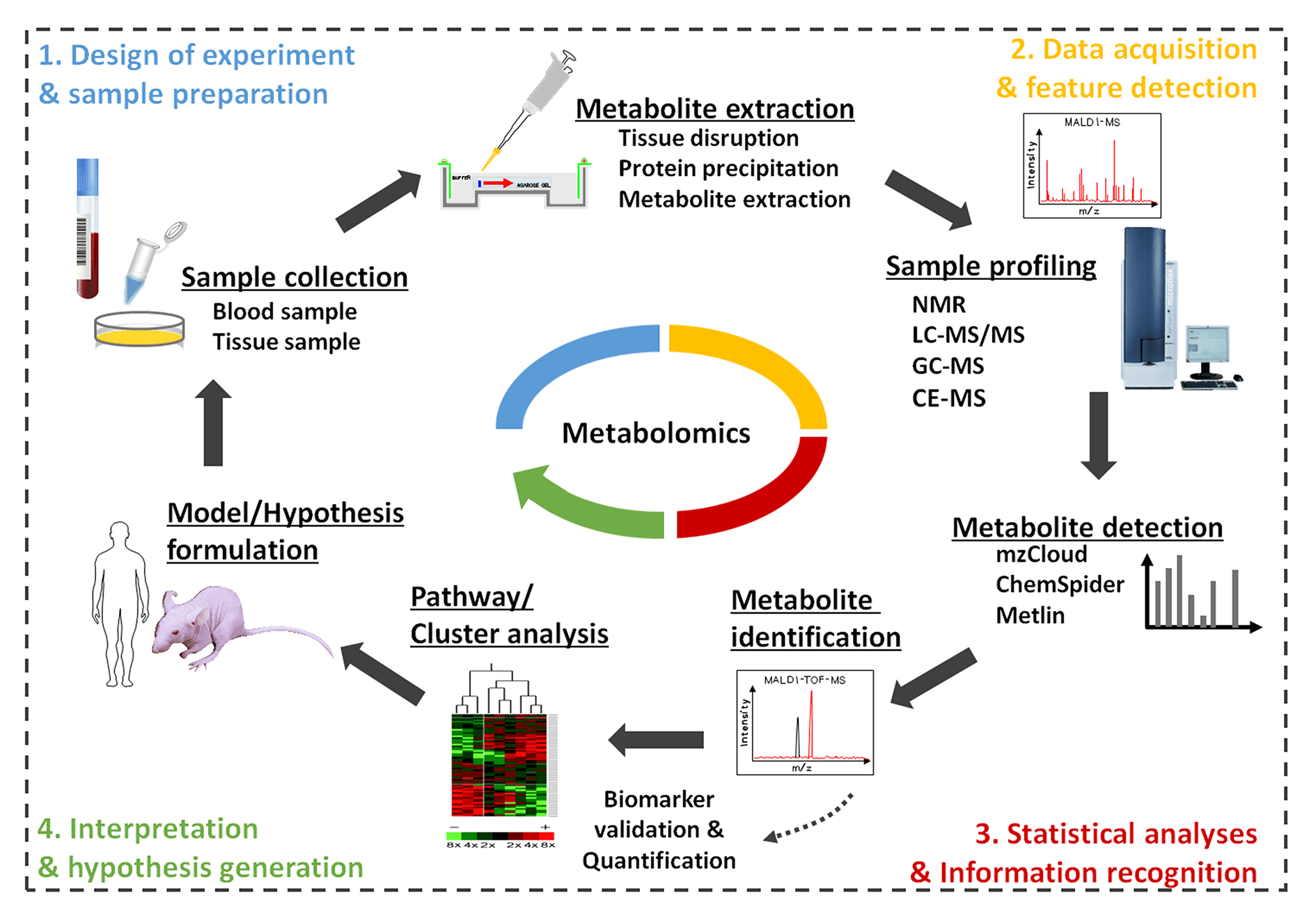
Over the past decade, the swift advancement of metabolomics can be credited to significant progress in technologies such as mass spectrometry, nuclear magnetic resonance, and multivariate statistics. Currently, metabolomics garners widespread application across diverse fields including drug research and development, early disease detection, toxicology, food and nutrition science, biology, prescription, and chinmedomics, among others. Metabolomics serves as an effective characterization technique, offering insights into physiological process alterations in vivo. These changes may result from various exogenous factors like environmental conditions, stress, medications, as well as endogenous elements including genetic and protein-based influences. The potential scientific outcomes gleaned from these insights have catalyzed the formulation of innovative methods, poised to further broaden the scope of this domain. Today, metabolomics has evolved into a valuable and widely accepted instrument in the life sciences. However, comprehensive reviews focusing on the sample preparation and analytical methodologies employed in metabolomics within the life sciences are surprisingly scant. This review aims to fill that gap, providing an overview of current trends and recent advancements in metabolomics. Particular emphasis is placed on sample preparation, sophisticated analytical techniques, and their applications in life science research.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools