 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
New insight into the role of exosomes in idiopathic membrane nephropathy
1 Department of Nephrology, Shaanxi Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Xian, 710000, China
2 School of Basic Medical Sciences and State Key Laboratory of Southwestern Chinese Medicine Resources, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu, 611137, China
3 Department of Pathophysiology, West China College of Basic Medical Sciences & Forensic Medicine, Sichuan University, Chengdu, 610041, China
* Corresponding Author: XIAOHONG CHENG. Email:
# These authors contributed equally to this work
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Biomarker Research: Unveiling the Pathways to Precision Medicine)
BIOCELL 2024, 48(1), 21-32. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2023.045631
Received 02 September 2023; Accepted 07 November 2023; Issue published 30 January 2024
Abstract
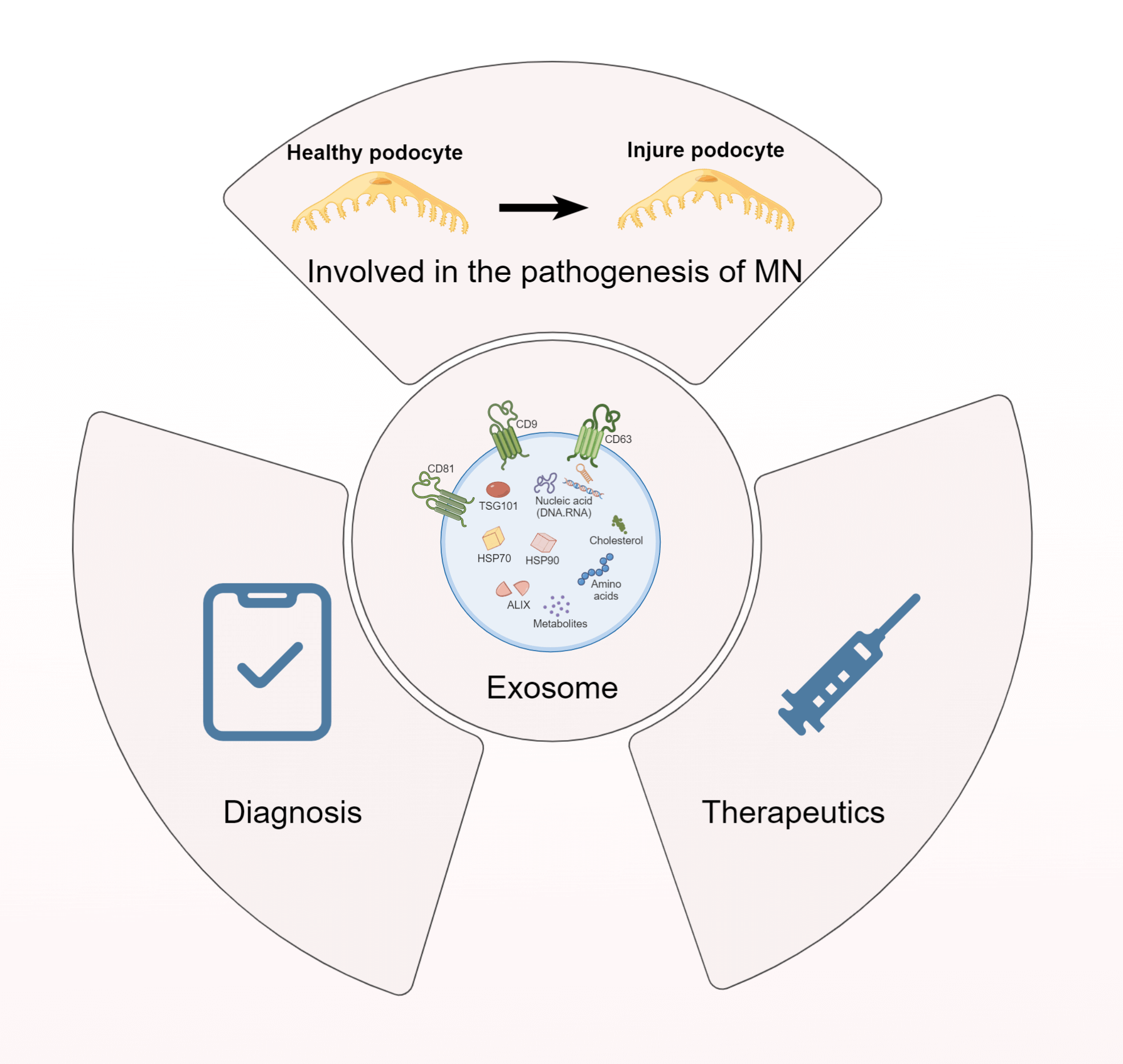
Exosomes, nanoscale extracellular vesicles (EVs) derived from the invagination of the endosomal membrane, are secreted by a majority of cell types. As carriers of DNA, mRNA, proteins, and microRNAs, exosomes are implicated in regulating biological activities under physiological and pathological conditions. Kidney-derived exosomes, which vary in origin and function, may either contribute to the pathogenesis of disease or represent a potential therapeutic resource. Membranous nephropathy (MN), an autoimmune kidney disease characterized by glomerular damage, is a predominant cause of nephrotic syndrome. Notably, MN, especially idiopathic membranous nephropathy (IMN), often results in end-stage renal disease (ESRD), affecting approximately 30% of patients and posing a considerable economic challenge to healthcare systems. Despite substantial research, therapeutic options remain ineffective at halting IMN progression, underscoring the urgent need for innovative strategies. Emerging evidence has implicated exosomes in IMN’s pathophysiology; Providing a fresh perspective for the discovery of novel biomarkers and therapeutic strategies. This review aims to scrutinize recent developments in exosome-related mechanisms in IMN and evaluate their potential as promising therapeutic targets and diagnostic biomarkers, with the hope of catalyzing further investigations into the utility of exosomes in MN, particularly IMN, ultimately contributing to improved patient outcomes in these challenging disease settings.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools