 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Molecular dynamics-driven exploration of peptides targeting SARS-CoV-2, with special attention on ACE2, S protein, Mpro, and PLpro: A review
1 Green Chemistry and Sustainable Technology Cluster, Bioengineering Section, Universiti Kuala Lumpur, Malaysian Institute of Chemical and Bioengineering Technology (UniKL MICET), Alor Gajah, 78000, Malaysia
2 Institute of General and Ecological Chemistry, Faculty of Chemistry, Lodz University of Technology, Lodz, 90-924, Poland
3 Department of Chemical Science, Faculty of Science, Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman, Kampar, 31900, Malaysia
4 Center for Agriculture and Food Research, Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman, Kampar, 31900, Malaysia
* Corresponding Author: TSUN-THAI CHAI. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Bioinformatics Study of Diseases)
BIOCELL 2023, 47(8), 1727-1742. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2023.029272
Received 10 February 2023; Accepted 12 April 2023; Issue published 28 August 2023
Abstract
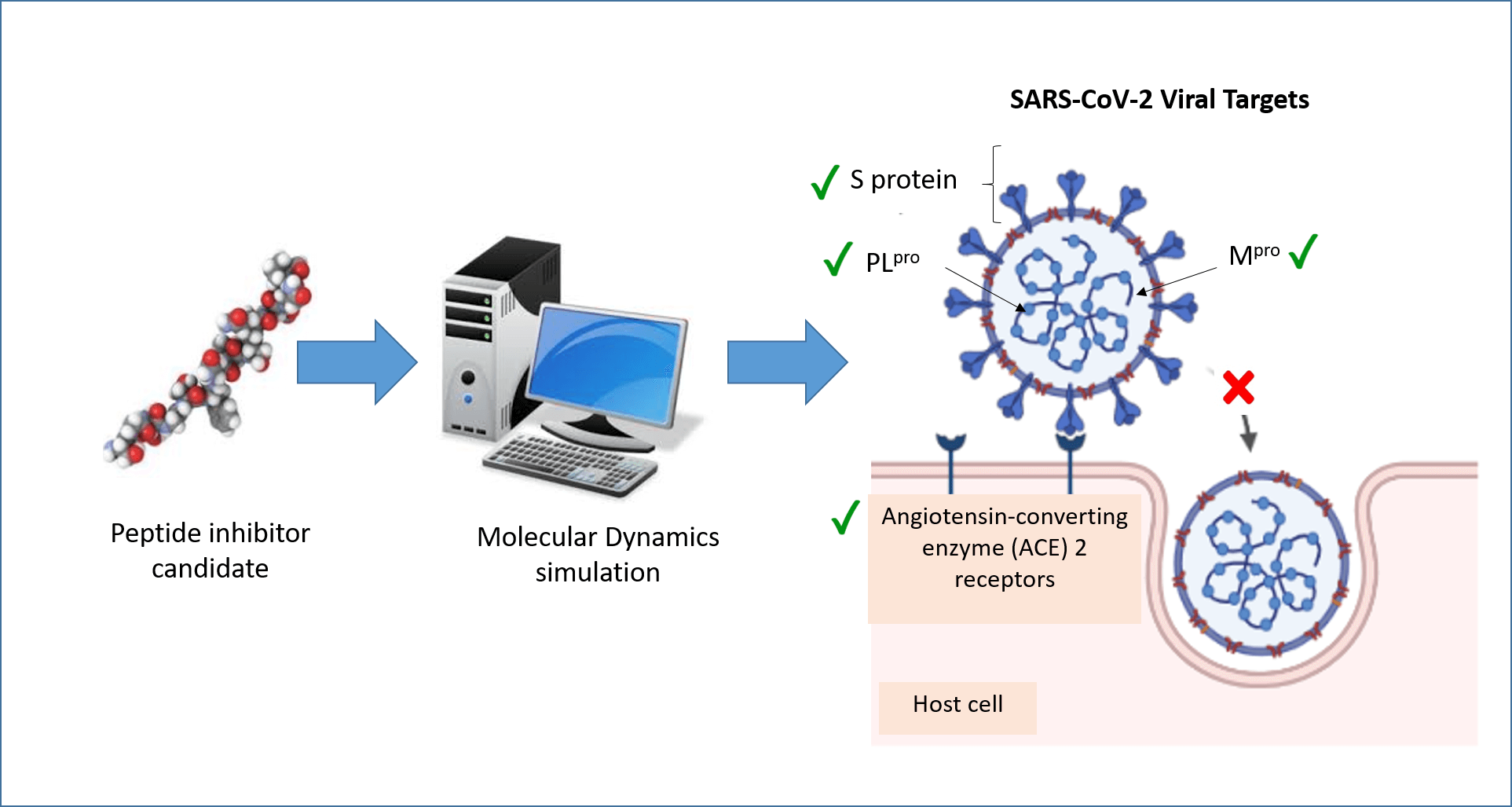
Molecular dynamics (MD) simulation is a computational technique that analyzes the movement of a system of particles over a given period. MD can provide detailed information about the fluctuations and conformational changes of biomolecules at the atomic level over time. In recent years, MD has been widely applied to the discovery of peptides and peptide-like molecules that may serve as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) inhibitors. This review summarizes recent advances in such explorations, focusing on four protein targets: angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), spike protein (S protein), main protease (Mpro), and papain-like protease (PLpro). These four proteins are important druggable targets of SARS-CoV-2 because of their roles in viral entry, maturation, and infectivity of the virus. A review of the literature revealed that ACE2, S protein, and Mpro have received more attention in MD research than PLpro. Inhibitors of the four targets identified by MD simulations included peptides derived from food and other bioresources, peptides designed using the targets as templates, and peptide-like molecules retrieved from databases. Many of the inhibitors have yet to be validated in experimental assays for potency. Nevertheless, the role of MD simulation as an efficient tool in the early stages of anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug discovery agents has been demonstrated.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools