 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
The role of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in tumor progression
1 Regenerative Processing Plant, LLC, Florida, USA
2 Institute of Anatomy, University of Bern, Bern, Switzerland
3 Department of Psychology, Faculty of Medical Sciences, University of Kragujevac, Kragujevac, Serbia
4 Department of Genetics, Faculty of Medical Sciences, University of Kragujevac, Kragujevac, Serbia
5 Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Faculty of Medical Sciences, University of Kragujevac, Kragujevac, Serbia
* Corresponding Author: VLADISLAV VOLAREVIC. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Extracellular Vesicles and Cancer)
BIOCELL 2023, 47(8), 1757-1769. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2023.028567
Received 25 December 2022; Accepted 08 May 2023; Issue published 28 August 2023
Abstract
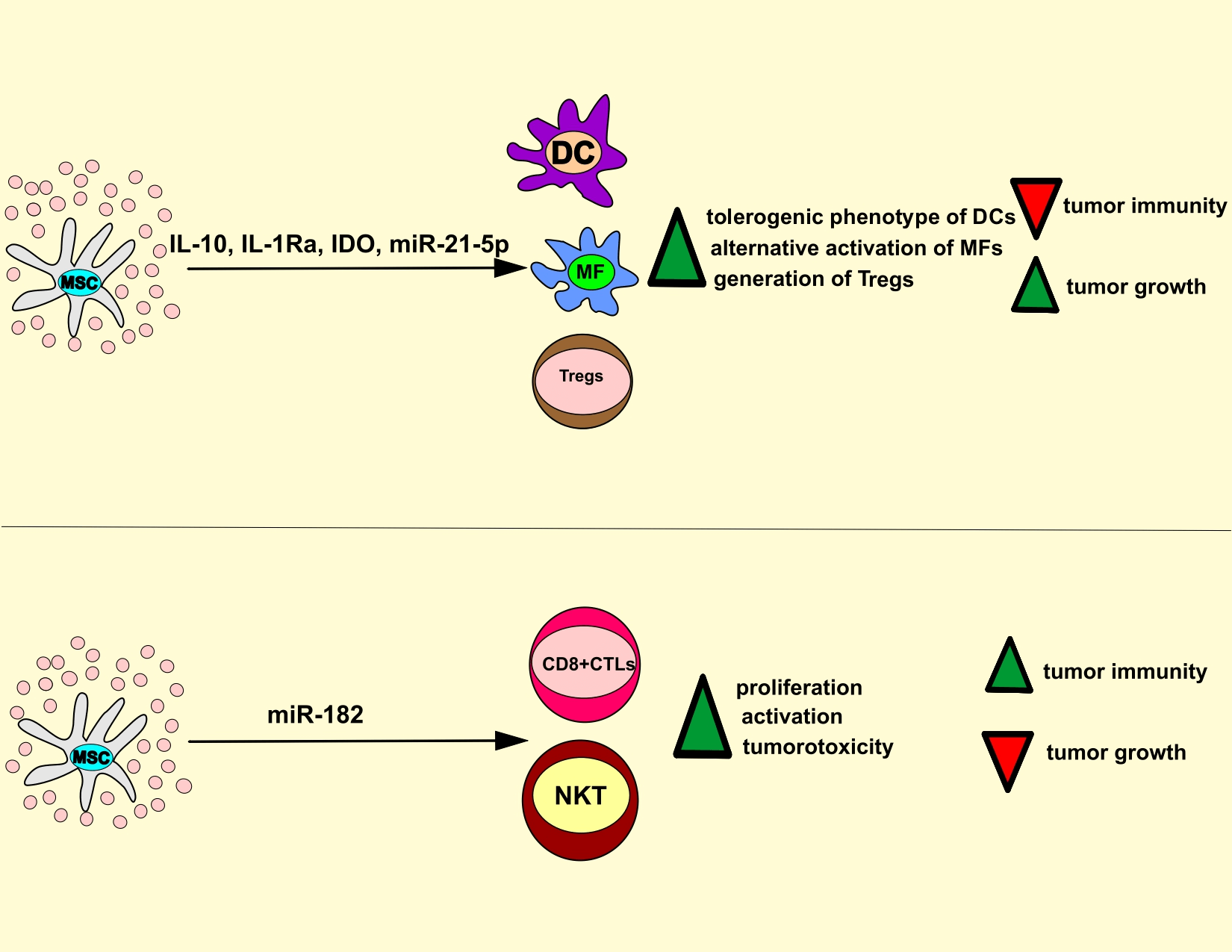
Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells (MSC-Exos) are nano-sized extracellular vesicles enriched with bioactive molecules, such as microRNAs, enzymes, cytokines, chemokines, immunomodulatory, trophic, and growth factors. These molecules regulate the survival, phenotype, and function of malignant and tumor-infiltrated immune cells. Due to their nano-size and bilayer lipid envelope, MSC-Exos can easily bypass biological barriers and may serve as drug carriers to deliver chemotherapeutics directly into the tumor cells. Here, we summarize current knowledge regarding molecular mechanisms responsible for MSC-Exos-dependent modulation of tumor progression and discuss insights regarding the therapeutic potential of MSC-Exos in the treatment of malignant diseases.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools