 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Photodynamic therapy with TBZPy regulates the PI3K/AKT and endoplasmic reticulum stress-related PERK/eIF2α pathways in HeLa cells
1 The Second Clinical Medical College of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou University Second Hospital, Lanzhou, 730000, China
2 Department of Dermatology, Lanzhou University Second Hospital, Lanzhou, 730000, China
3 Department of Dermatology and Venereology, Guangdong Women’s and Children’s Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, 510000, China
* Corresponding Authors: ZHIWEN ZHANG. Email: ; MUZHOU TENG. Email:
BIOCELL 2023, 47(8), 1783-1791. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2023.028056
Received 28 November 2022; Accepted 06 May 2023; Issue published 28 August 2023
Abstract
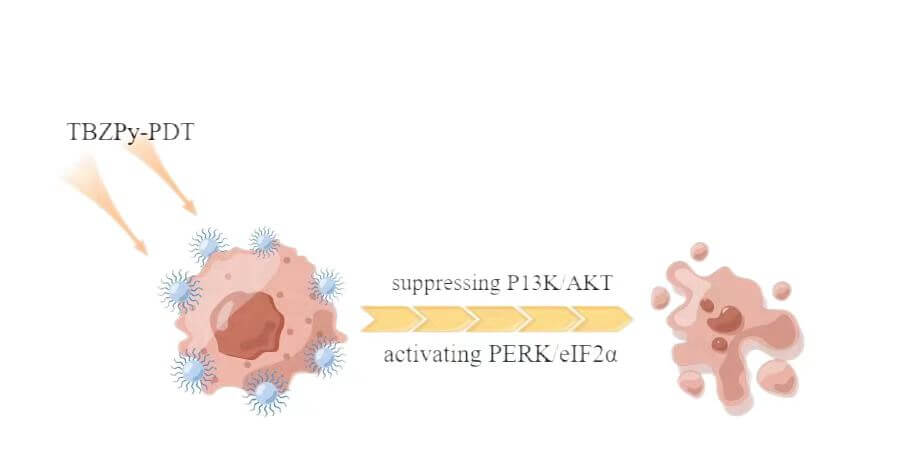
Background: ((1-triphenylaminebenzo[c][1,2,5] thiadiazole-4-yl) styryl)-1-methylpyridin methylpyridin-1-ium iodide salt (TBZPy) is a novel photosensitizer that displays excellent photodynamic properties. However, There are few reports on the mechanism of action of the TBZPy photodynamic. Previous studies revealed that photodynamic therapy (PDT) could induce endoplasmic reticulum stress by acting on the endoplasmic reticulum. Therefore, in this study, we investigated the effects of endoplasmic reticulum stress induced by TBZPy-PDT in treating High-risk human papillomavirus (HR-HPV) infection and their underlying mechanisms. Methods: The human cervical cancer cell line HeLa (containing whole genome of HR-HPV18) was treated with TBZPy-PDT. Cell migration, invasion, and colony-forming ability were evaluated using wound-healing, Transwell invasion, and colony-forming assays, respectively. Through western blot analysis, we determined the level of expression of the PI3K/AKT and PERK/eIF2α pathway proteins and the proteins associated with calcium trafficking and apoptosis. The calcium levels in the cytoplasm were detected via flow cytometry. Results: The result shows that TBZPy-PDT could inhibite the migration, invasion, and colony forming ability of infected HeLa cells by downregulating the PI3K/AKT pathway in vitro. And we found that TBZPy-PDT induced endoplasmic reticulum stress-specific apoptosis via the PERK/eIF2α pathway. Moreover, TBZPy-PDT increased the levels of calcium and calmodulin, while decreasing the levels of endoplasmic reticulum calcium-binding proteins. Conclusions: TBZPy-PDT is effective on treating human papillomavirus-infected cells. Targeting the PI3K/AKT and PERK/eIF2α pathways and the endoplasmic reticulum stress process may help improve the effects of TBZPy-PDT for treating high-risk human papillomavirus infection.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools