 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
The role of periodontal disease in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
1 Beijing Laboratory of Oral Health, School of Basic Medicine, School of Stomatology, Capital Medical University, Beijing, 100069, China
2 Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, School of Basic Medicine, Capital Medical University, Beijing, 100069, China
3 Immunology Research Center for Oral and Systemic Health, Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, 100050, China
4 Research Unit of Tooth Development and Regeneration, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing, 100700, China
5 Department of VIP Dental Service, School of Stomatology, Capital Medical University, Beijing, 100050, China
* Corresponding Authors: JIAN ZHOU. Email: ; LEI HU. Email:
# These authors contributed equally to this article
BIOCELL 2023, 47(7), 1431-1438. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2023.028217
Received 02 December 2022; Accepted 20 March 2023; Issue published 21 June 2023
Abstract
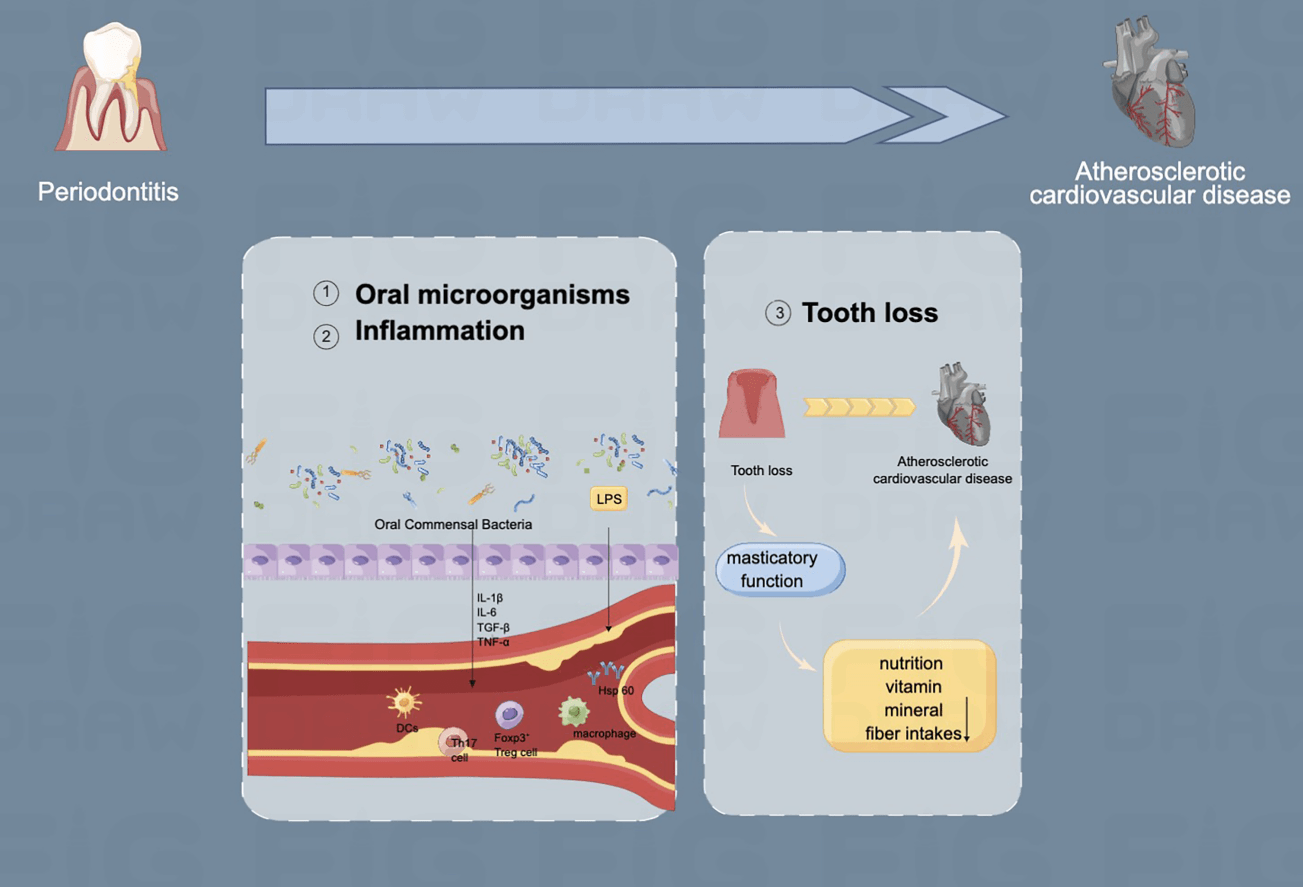
Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) includes a group of disorders of the heart and blood vessels and accounts for major morbidity and premature death worldwide. Periodontitis is a chronic inflammatory disease with the gradual destruction of supporting tissues around the teeth, including gingiva, periodontal ligament, alveolar bone, and cementum. Periodontitis has been found to potentially increase the risk of ASCVD. Generally, oral microorganisms and inflammation are the major factors for periodontitis to the incidence of ASCVD. Recently, evidence has shown that the loss of masticatory function is another important factor of periodontitis to the incidence of ASCVD. In this review, we illustrate the recent finding of the relationship between periodontitis and ASCVD, from a microscale perspective-oral microorganisms, inflammation, and tooth loss. With the high prevalence of periodontitis, it is important to add oral therapy as a regular ASCVD prevention strategy. Regular dental visits could be a helpful strategy for ASCVD patients or general medical practitioners.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools