 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Anti-fibrotic and anti-inflammatory effect of mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles in chronic kidney disease
1 Department of Medical Sciences, University of Torino, Torino, 10126, Italy
2 Molecular Biotechnology Center, University of Torino, Torino, 10126, Italy
* Corresponding Authors: GIULIA CHIABOTTO. Email: ; STEFANIA BRUNO. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Cell-Based Regenerative Therapies)
BIOCELL 2023, 47(7), 1499-1508. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2023.028121
Received 30 November 2022; Accepted 20 March 2023; Issue published 21 June 2023
Abstract
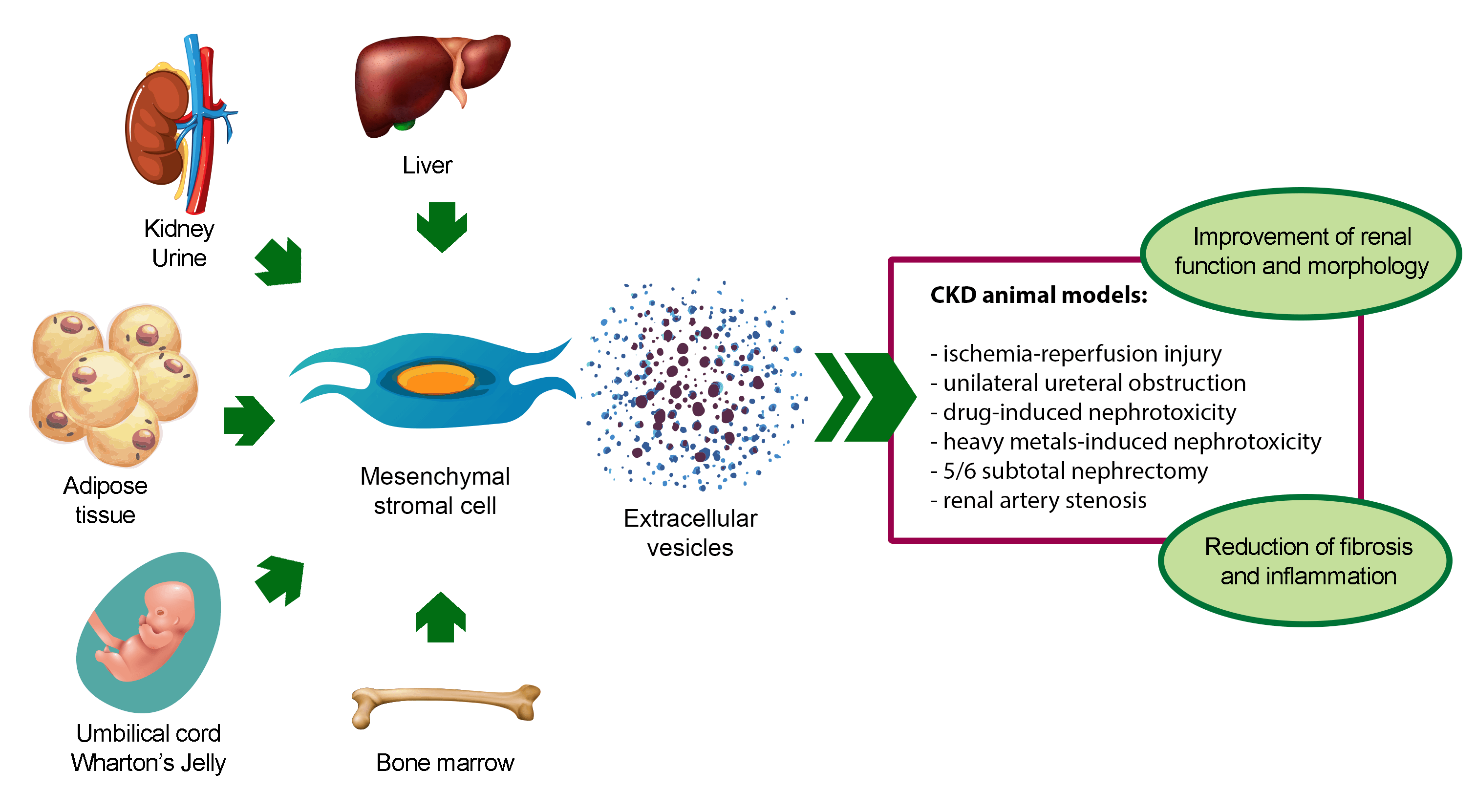
Renal fibrosis and inflammation are common pathological features of chronic kidney disease (CKD). Since currently available treatments can only delay the progression of CKD, the outcome of patients with CKD is still poor. One therapeutic option for the prevention of CKD-related complications could be the use of mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs), which have shown beneficial effects in tissue fibrosis and regeneration after damage. However, safety issues, such as cellular rejection and carcinogenicity, limit their clinical application. Among the bioactive factors secreted by MSCs, extracellular vesicles (EVs) have shown the same beneficial effect of MSCs, without any notable side effects. This heterogeneous population of membranous nano-sized particles can deliver genetic material and functional proteins to injured cells, prompting tissue regeneration. Here we describe the anti-fibrotic and anti-inflammatory properties of MSC-derived EVs in CKD preclinical models and summarize the potential molecular mechanisms involved in the regulation of renal fibrosis and inflammation.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools