 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Expression and function of long non-coding RNA DLX6-AS1 in endometrial cancer
1 Department of Gynecologic Oncology, The International Peace Maternity and Child Health Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200030, China
2 Shanghai Key Laboratory of Embryo Original Diseases, Shanghai, 200030, China
3 Shanghai Municipal Key Clinical Specialty, Shanghai, 200030, China
* Corresponding Author: YAN LIANG. Email:
# These authors contributed to the work equally
BIOCELL 2023, 47(4), 869-877. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2023.026037
Received 11 August 2022; Accepted 15 November 2022; Issue published 08 March 2023
Abstract
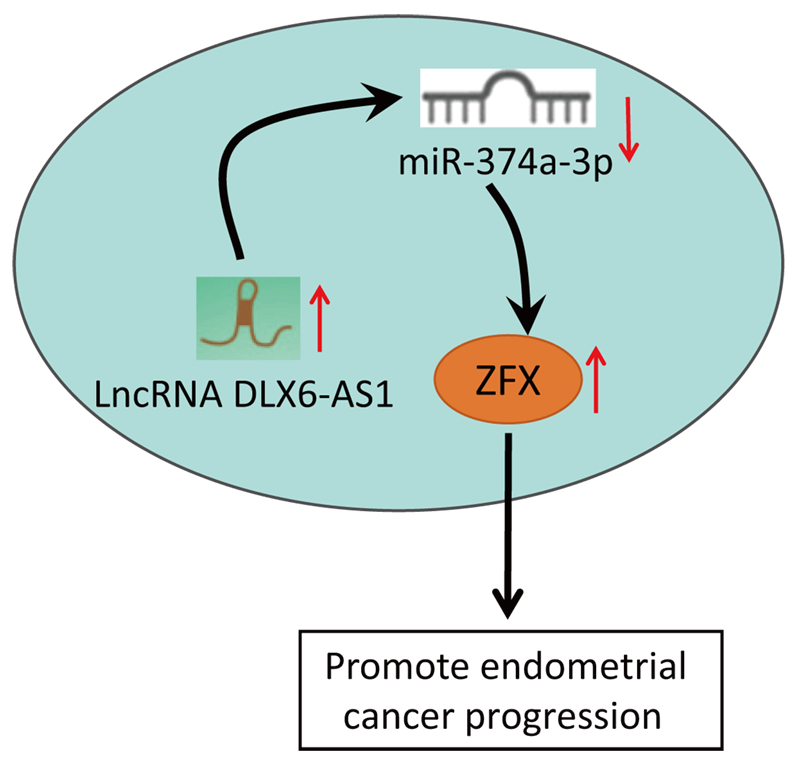
Background: LncRNA DLX6-AS1 has been uncovered to exert effects on various cancers. Nevertheless, the impacts of DLX6-AS1 on endometrial cancer (EC) development remained obscure. The study explored the influence of DLX6-AS1 on EC progression via the microRNA (miR)-374a-3p/zinc-finger protein (ZFX) axis.Methods: EC cell lines were collected and DLX6-AS1, miR-374a-3p, and ZFX levels in EC cell lines were detected. The EC cells were transfected with DLX6-AS1, miR-374a-3p, and ZFX constructs to examine the biological functions of EC cells. The xenograft model was established for detecting tumor growth. Rescue experiments were conducted to verify the interaction of DLX6-AS1, miR-374a-3p, and ZFX in EC cells.Results: DLX6-AS1 and ZFX levels were elevated, while miR-374a-3p exhibited a reduced level in EC cells. Silencing DLX6-AS1 and elevated miR-374a-3p expressions repressed the biological activities of EC cells. Reduced DLX6-AS1 repressed tumor development. MiR-374a-3p silencing reversed the impacts of DLX6-AS1 silencing, while ZFX overexpression abrogated the impacts of miR-374a-3p elevation on EC cell growth. Mechanically, DLX6-AS1 was found to bind to miR-374a-3p, and miR-374a-3p targeted ZFX.Conclusion: DLX6-AS1 depletion restricts the malignant phenotype of EC cells. The study might provide novel therapeutic biomarkers for EC treatment.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools