 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
AKT regulates IL-1β-induced proliferation and activation of hepatic stellate cells
1 Regeneration Medicine Research Center, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, 26426, Korea
2 Department of Biochemistry, Lee Gil Ya Cancer and Diabetes Institute, GAIST, Gachon University College of Medicine, Incheon, 21999, Korea
3 Cell Therapy and Tissue Engineering Center, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, 26426, Korea
4 Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, 26426, Korea
* Corresponding Authors: SOON KOO BAIK. Email: ; YOUNG WOO EOM. Email:
# These authors contributed equally to this work
BIOCELL 2023, 47(3), 669-676. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2023.025365
Received 07 July 2022; Accepted 06 September 2022; Issue published 03 January 2023
Abstract
Background: Activated hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) are closely involved in the initiation, perpetuation, and resolution of liver fibrosis. Pro-inflammatory cytokine levels are positively correlated with the transition from liver injury to fibrogenesis and contribute to HSC pathophysiology in liver fibrosis. Methods: In this study, we investigated the effect of the pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin (IL)-1β on the proliferation and signaling pathways involved in fibrogenesis in LX-2 cells, an HSC cell line, using western blotting and cell proliferation assays. Results: IL-1β increased the proliferation rate and α-smooth muscle actin (SMA) expression of LX-2 cells in a dose-dependent manner. Within 1 h after IL-1β treatment, c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), p38, and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling was activated in LX-2 cells. Subsequently, protein kinase B (AKT) phosphorylation and an increase in α- SMA expression were observed in LX-2 cells. Each inhibitor of JNK, p38, or NF-κB decreased cell proliferation, AKT phosphorylation, and α-SMA expression in IL-1β-treated LX-2 cells. Conclusion: These results indicate that JNK, p38, and NF-κB signals converge at AKT phosphorylation, leading to LX-2 activation by IL-1β. Therefore, the AKT signaling pathway can be used as a target for alleviating liver fibrosis by the inflammatory cytokine IL-1β.Keywords
Fibrosis is characterized by extensive deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM) components. It is a pathological feature of a chronic inflammatory response caused by various types of damage in several organs, including the skin, kidney, lung, heart, intestine, and liver (Tomasek et al., 2002; Friedman, 2004; Wynn, 2007). The primary cellular mediators of fibrosis are myofibroblasts transdifferentiated from fibroblasts, which originate from tissue-resident fibroblasts (Geerts, 2001; Mueller et al., 2007; Hung et al., 2013), pericytes (Hung et al., 2013), and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (Kramann et al., 2015). Other myofibroblasts are also proposed to be derived from epithelial, endothelial, and mesothelial cells, which undergo epithelial-mesenchymal transition, endothelial-mesenchymal transition, and mesothelial-mesenchymal transition, respectively (Kalluri and Neilson, 2003; Willis et al., 2006; Hinz et al., 2007; Zeisberg et al., 2007; Kis et al., 2011; Hinz et al., 2012).
Hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) are liver-resident fibroblasts located in the space of Disse, accounting for 5%–8% of the total resident cells in the healthy human liver (Geerts, 2001). They remain quiescent and are responsible for the intracellular lipid droplet storage containing vitamin A as retinyl palmitate (Friedman, 2008; Trivedi et al., 2021). In response to liver injury, they proliferate and transdifferentiate from a “quiescent” to an “activated” phenotype responsible for most of the ECM deposition in liver tissue, leading to liver fibrosis (Blaner et al., 2009; Friedman, 2000). HSCs communicate with immune cells, sinusoidal endothelial cells, and/or hepatocytes during liver pathophysiology via various growth factors, chemokines, and cytokines (Baghaei et al., 2022). Growth factors, including transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1, connective tissue growth factor, platelet-derived growth factor, and vascular endothelial growth factor, play essential roles in HSC activation. Among them, TGF-β1 induces HSC activation as a principal factor through signal transducers for receptors of the TGF-β superfamily-dependent or -independent pathways, resulting in upregulated expression of ECM components (Fabregat et al., 2016; Zhang, 2017; Baghaei et al., 2022). Inflammation is a major hallmark of liver fibrosis and is mediated by chemokines, which induce the chemotaxis of immune cells in the liver (Hellerbrand et al., 1998; Sahin et al., 2012; Lee et al., 2018b; Bartneck et al., 2021). Therefore, chemokines regulate HSC activation and liver fibrosis progression. Various cell types release inflammatory cytokines during liver injury, promoting HSC activation and liver fibrosis (Baghaei et al., 2022). Multiple pro-inflammatory interleukins (IL), including IL-1β, regulate the biological function of liver-resident cells and induce the recruitment of immune cells to the liver (Gieling et al., 2009; Masola et al., 2019).
Previously, we reported that inflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α levels were positively correlated with the degree of liver fibrosis (Lee et al., 2018a). These inflammatory cytokines increased fibroblast growth factor-21 levels for protective effects on IL-1β-induced growth retardation of Huh-7 cells through the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathways (Lee et al., 2018a). Although it has been reported that inflammatory cytokines, including TGF-β, IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α, can induce fibrosis, most studies have focused on TGF-β and TNF-α (Yang and Seki, 2015; Fabregat et al., 2016) and few have determined the signaling pathways involved in the regulation of HSC activation by IL-1β. Therefore, here, we investigated the effect of the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-1β on the proliferation and signaling pathways in LX-2 cells, an HSC cell line. We found that IL-1β increased growth rate and α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) expression through the JNK, p38, and NF-κB signaling and protein kinase B (AKT) activation. JNK, p38, and NF-κB signals were activated at early time points after IL-1β treatment and then converged at AKT. Thus, we establish that the AKT signaling pathway can be used as a target for alleviating liver fibrosis by the inflammatory cytokine IL-1β.
The reagents used in the study were obtained from the indicated suppliers: IL-1β, IL-6, TGF-β1, and TNF-α from R&D Systems (Minneapolis, MN, USA); antibodies against α-SMA from Abcam (Cambridge, UK); antibodies against glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor-alpha (IκB-α), and phosphorylated (p)-IκB-α were from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA, USA); antibodies against AKT, p-AKT, p38, p-p38, JNK, p-JNK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 1/2, and p-ERK 1/2 were from Cell Signaling Technology (Danvers, MA, USA). Chemical inhibitors for NF-κB (Bay 11-7082; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), JNK (SP600125; MedChemExpress, Princeton, NJ, USA), p38 (SB202109; MedChemExpress), phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K; LY294002; Sigma-Aldrich), and AKT (AKTI-1/2; Selleck Chemicals, Houston, TX, USA) were also used. All other materials were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich unless indicated otherwise.
HSC line, LX-2, was purchased from Millipore (Burlington, MA, USA) and maintained in Dulbecco’s minimal essential medium supplemented with 3% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and penicillin/streptomycin (all from Gibco BRL, Rockville, MD, USA) at 37°C and 5% CO2. After 24 h, LX-2 cells were treated with IL-1β (0.5 to 20 ng/mL), IL-6 (10 ng/mL), and TNF-α (10 ng/mL), or TGF-β1 (1 ng/mL) and cultured for additional 24 h to analyze growth rate and α-SMA expression. To analyze the role of the signaling molecules, 20 min before IL-1β treatment, LX-2 cells were treated with Bay 11-7082 (1 µM), SP600125 (5 µM), SB202109 (2 µM), LY294002 (1 µM), or AKTI-1/2 (1 µM).
To detect the level of α-SMA expression, LX-2 cells were grown on glass coverslips and exposed to TGF-β, IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α for 48 h. The cells were then washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, permeabilized with 0.2% Triton X-100 for 10 min at room temperature, and blocked with 3% FBS in PBS for 30 min. They were incubated overnight with a primary antibody specific for α-SMA (1:100; Abcam) at 4°C. For fluorescence labeling, cells were incubated with Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated secondary antibody (1:100; Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) for 1 h at room temperature. The unbound secondary antibody was removed by washing, and the cells were mounted in ProLong™ Gold Antifade Mountant with DAPI (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole) (Invitrogen). The cells were observed and photographed under a fluorescent microscope (Eclipse TS2R, Nikon, Japan).
Cellular DNA content was analyzed using CycleTEST plus DNA reagent Kit (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, LX-2 cells were trypsinized, neutralized with Dulbecco’s minimal essential medium, and centrifuged at 2000 rpm for 5 min. Cells were washed twice with the buffer solution provided in the Kit, and Solutions A, B, and C were sequentially treated according to the manufacturer’s instructions. DNA contents were analyzed on a flow cytometer (BD FACSAria III, BD Biosciences).
Cells were lysed in Laemmli sample buffer (62.5 mM Tris-HCl [pH 6.8], 34.7 mM SDS, 10% (v/v) glycerol, and 5% (v/v) β-mercaptoethanol), boiled for 5 min, subjected to separation by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and transferred to an Immobilon membrane (Millipore). The membrane was blocked with 5% skimmed-milk in Tris-HCl-buffered saline containing 0.05% (v/v) Tween 20 (TBST buffer) for 30 min; it was then incubated overnight with primary antibodies against α-SMA, GAPDH, PCNA, IκB-α, and p-IκB-α at a dilution of 1:1000 or AKT, p-AKT, p38, p-p38, JNK, p-JNK, ERK ½, and p-ERK ½ at a dilution of 1:2000 and 4°C. The membrane was washed thrice for 5 min with TBST buffer, and then horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies (1:5000; Cell Signaling Technology) were added and allowed to react for 1 h. The membrane was washed thrice with TBST buffer and protein bands were visualized using the EZ-Western Lumi Pico or Femto kit (Dogen, Seoul, Korea) and detected using the ChemiDoc XRS+ system (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). The intensity of immunoreactive bands was quantified using densitometry with ImageJ, and relative protein expression was normalized against GAPDH.
Methylthiazolyldiphenyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay
LX-2 cells were plated at a density of 8 × 103 cells/cm2 in 96-well plates and cultured for 24 h. The cells were then treated with IL-1β (0.5 to 20 ng/mL), IL-6 (10 ng/mL), TNF-α (10 ng/mL) and cultured for an additional 24 h. Each inhibitor was added 20 min before IL-1β treatment to determine their effect in inhibiting the signals activated by IL-1β. MTT dissolved in PBS was added to each well (final concentration: 5 mg/mL), and the cells were further incubated at 37°C for 2 h. MTT formazan was dissolved in 100 μL dimethyl sulfoxide following incubation for an additional 15 min with shaking. Subsequently, the optical density of each well was measured at 570 nm using a microplate reader (Molecular Devices; San Jose, CA, USA).
All experiments were performed three times. The data are expressed as the mean ± SD. P-values were determined using a paired 2-tailed Student’s t-test (Mann–Whitney U test). All statistical analyses were performed with GraphPad Prism 7.0 software (GraphPad Inc., La Jolla, CA). Significance was set at P ≤ 0.05.
Activation of LX-2 cells by pro-inflammatory cytokines
We previously reported that the expression of inflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α was increased in human liver tissues during liver fibrosis progression. Additionally, IL-1β inhibited the growth of Huh-7 cells (Lee et al., 2018a). Therefore, we investigated whether IL-1β could regulate the activity of HSCs. First, α-SMA expression was detected in LX-2 cells treated with IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α and was compared to α-SMA expression in TGF-β1-treated LX-2 cells. We found that 10 ng/mL IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α increased the expression of α-SMA by 3.79-, 2.94-, and 2.66-fold, respectively, which is lower than that induced by TGF-β1 (6.35-fold, 1 ng/mL), with IL-1β inducing the most considerable increase (Fig. 1A). In addition, the expression was α-SMA was similar to the immunoblotting result of immunocytochemical analysis (Fig. 1B). Up to 10 ng/mL of IL-1β could increase the expression of α-SMA in a dose-dependent manner (Fig. 2A). The expression of PCNA, a eukaryotic replication marker, gradually increased with the IL-1β concentration (Fig. 2A). IL-1β also increased the proliferation of LX-2 cells (Fig. 2B). In the cell cycle analysis, IL-1β decreased the G1 population of LX-2 cells, but those in S and G2/M-stages increased slightly (Fig. 2C). These results indicate that IL-1β induces an increase in α-SMA expression to activate HSCs, thereby increasing their proliferation as well. This finding suggests that the inflammatory response plays a vital role in exacerbating liver fibrosis.
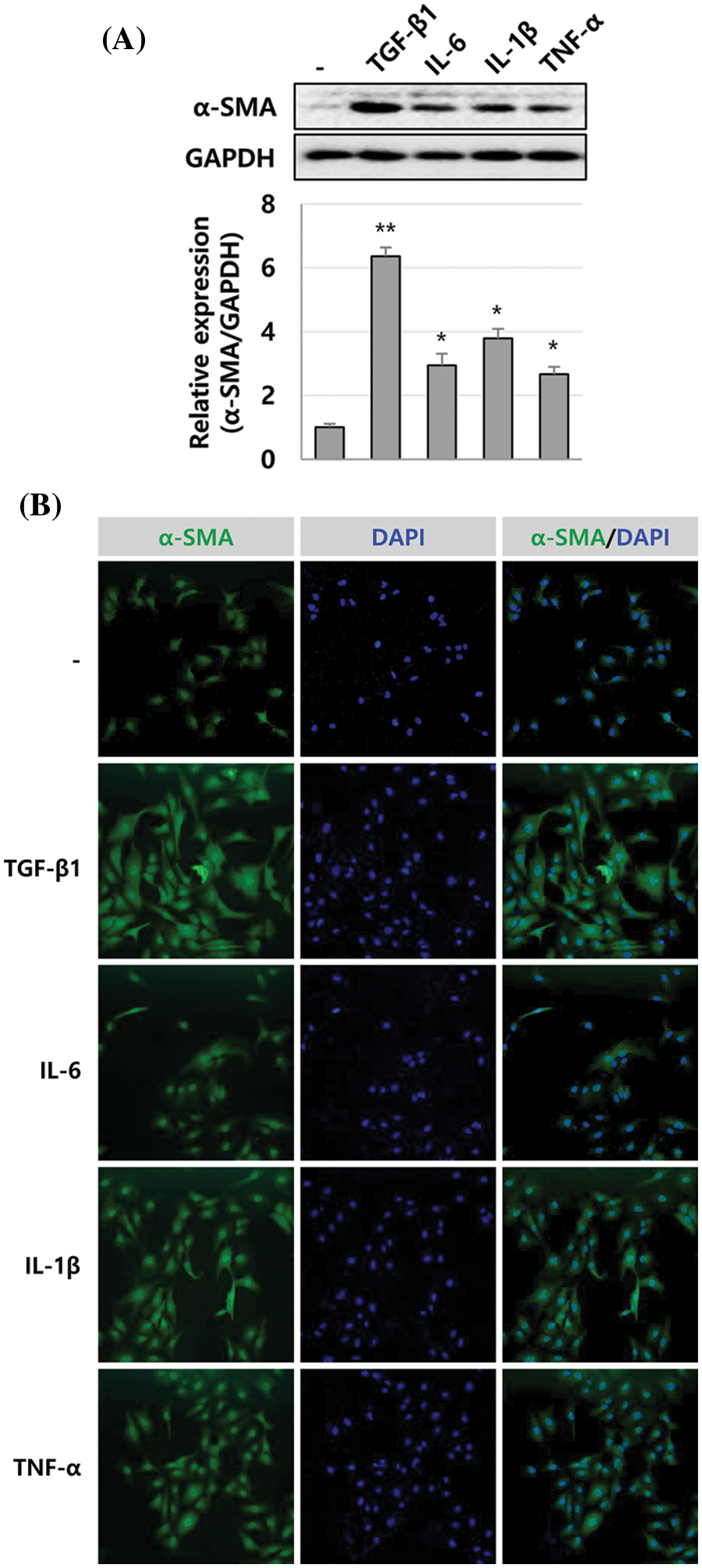
Figure 1: α-SMA expression in LX-2 cells induced by inflammatory cytokines. The expression level of α-SMA was compared in LX-2 cells treated with TGF-β1, IL-6, IL-1β, or TNF-α for 24 h, observed through immunoblotting (A) and immunocytochemical analysis (B). The intensity of α-SMA expression was quantified using densitometry with Image J, and its relative expression was normalized against that of GAPDH. *P ≤ 0.05 and **P ≤ 0.01.
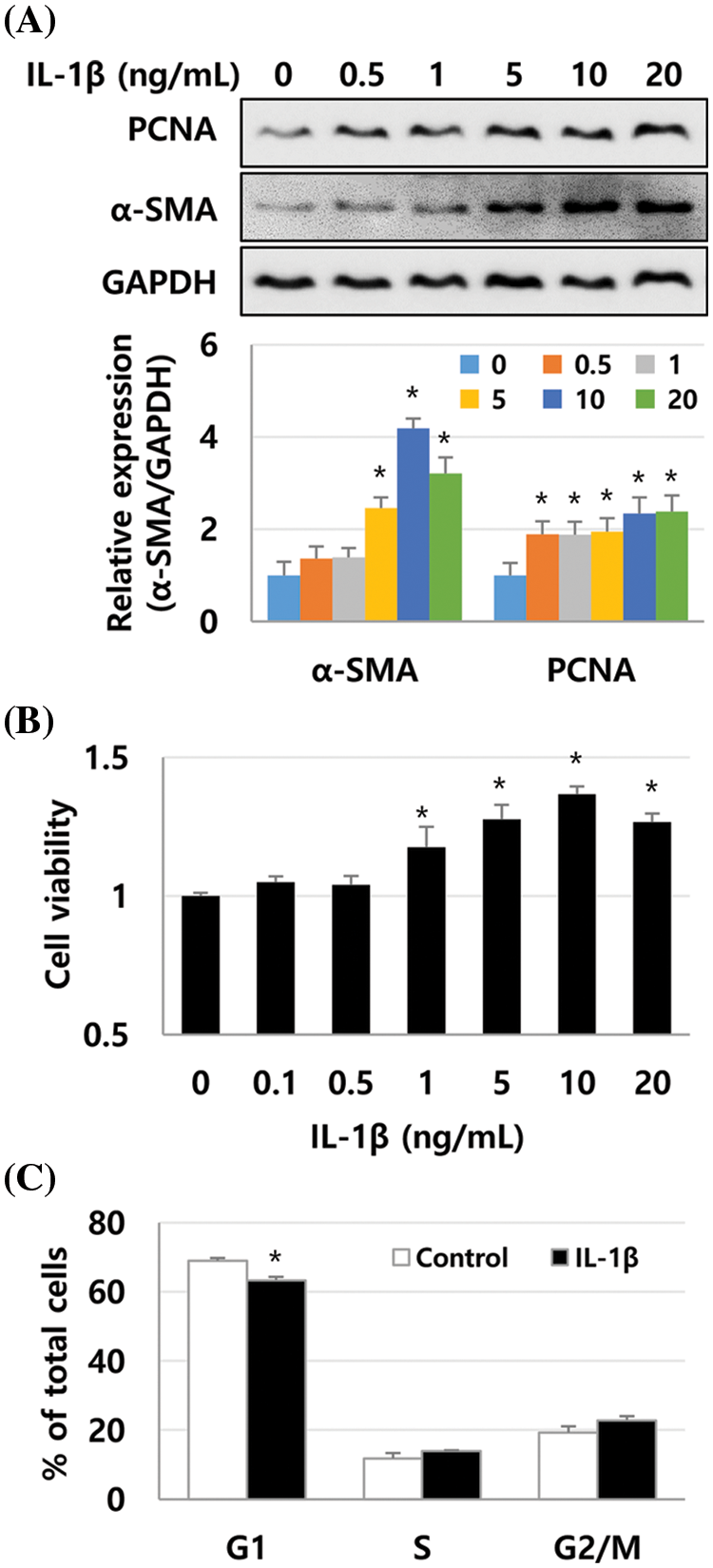
Figure 2: Proliferation and α-SMA expression in IL-1β-treated LX-2 cells increases in a dose-dependent manner. LX-2 cells were treated with up to 20 ng/mL of IL-1β for 1 day, and the expression of PCNA and α-SMA was detected using immunoblotting. Their proliferation was analyzed using the MTT assay. (A) α-SMA expression in IL-1β-treated LX-2 cells. (B) Increased proliferation of IL-1β-treated LX-2 cells. (C) Cell cycle analysis of LX-2 cells treated with IL-1β at 10 ng/mL. Data are presented as the mean ± SD of four independent experiments. *P ≤ 0.05.
Signaling pathway activated by interleukin-1β in LX-2 cells
Next, we investigated whether IL-1β activated NF-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs, i.e., p38 and JNK), which are involved in liver diseases via IL-1 family cytokines, in LX-2 cells (Tsutsui et al., 2015). Moreover, levels of ERK and AKT, which can regulate cell proliferation, were analyzed after treating LX-2 cells with 10 ng/mL IL-1β. After IL-1β treatment, phosphorylation of JNK and p38 was detected approximately between 5 and 60 min and peaked between 15 and 30 min. However, phosphorylation of ERK in LX-2 cells gradually decreased in a time-dependent manner. In addition, IκB-α expression decreased from 15 to 60 min, indicating that NF-κB was activated simultaneously (Fig. 3). The activity of NF-kB was observed to gradually increase again after 3 h (Fig. 3). The phosphorylation of IκB-α increased 1.4-fold at 5 min (Fig. 3) compared to the control, and its phosphorylation was observed to be more significant within 5 min (Suppl. Fig. 1). The second cycle of NF-κB activation was observed to increase gradually after 3 h (Fig. 3). In addition, AKT phosphorylation was observed at 30 min and continued until 48 h. The expression of α-SMA increased significantly after 24 h of IL-1β treatment (Fig. 3). In other words, IL-1β activated p38, JNK, and NF-κB, followed by AKT in LX-2 cells and also increased the expression of α-SMA.
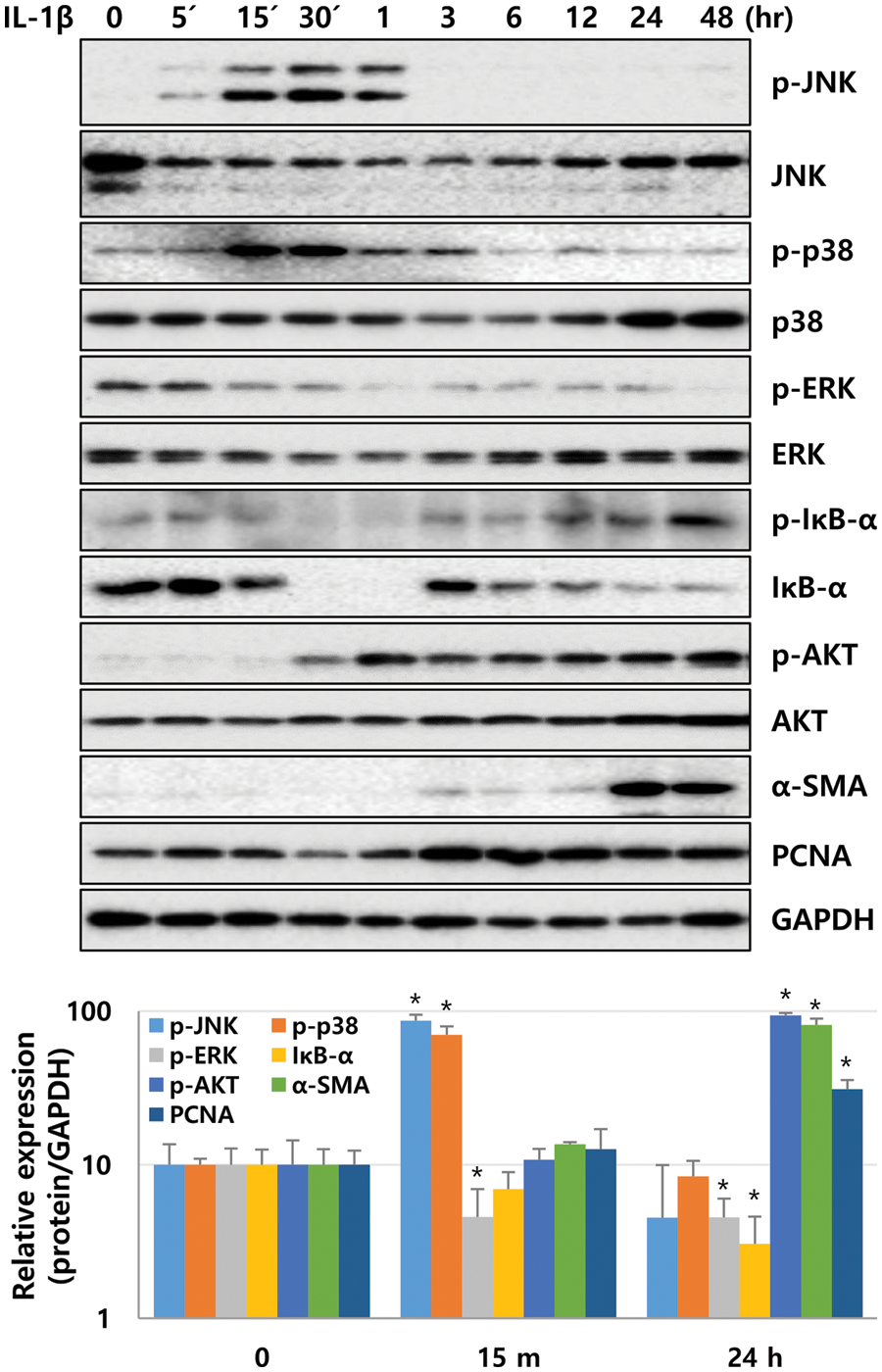
Figure 3: Signaling molecules activated by IL-1β in LX-2 cells. After IL-1β treatment, LX-2 cell lysates were obtained at time points as indicated, and phosphorylation and expression levels of signaling molecules were analyzed by immunoblotting. *P ≤ 0.05.
Protein kinase B, a key molecule regulating IL-1β-induced LX-2 activation
To analyze the signaling cascade activated by IL-1β in LX-2 cells, we used chemical inhibitors to investigate the possible role of the p38, JNK, NF-κB, and AKT in the IL-1β-induced signaling pathways. LX-2 cells were treated with each inhibitor 20 min prior to IL-1β treatment. The changes in the expression of p-p38, p-JNK, and IκB-α activated between 5 and 60 min were analyzed in cell lysates recovered 15 min after IL-1β treatment. After 24 h of IL-1β treatment, samples were analyzed for the changes in AKT activity and α-SMA expression. All inhibitors for p38, JNK, NF-κB, and AKT suppressed IL-1β-induced α-SMA expression. In particular, AKTI-1/2, a potent and selective AKT inhibitor, significantly reduced the expression of α-SMA to the control levels (Fig. 4A). The NF-κB inhibitor, Bay 11-7082, inhibited IκB-α degradation and AKT phosphorylation, whereas the p38 inhibitor SB202109 reduced p38 and AKT phosphorylation. SP600125, a JNK inhibitor, inhibited JNK and AKT phosphorylation, partially inhibited IκB degradation, and decreased p38 activity (Fig. 4A). Therefore, p38, JNK, and NF-κB inhibitors can all inhibit AKT phosphorylation, and these results suggest that the activities of p38, JNK, and NF-κB converge at AKT in LX-2 cells. In addition, AKT inhibitors AKTI-1/2 and LY294002 downregulated the IL-1β-induced α-SMA expression without modulating p-p38, p-JNK, and IκB-α activities (Fig. 4A). These results suggest that AKT acts as a key modulator when the inflammatory cytokine IL-1β regulates ECM production by LX-2 cells.
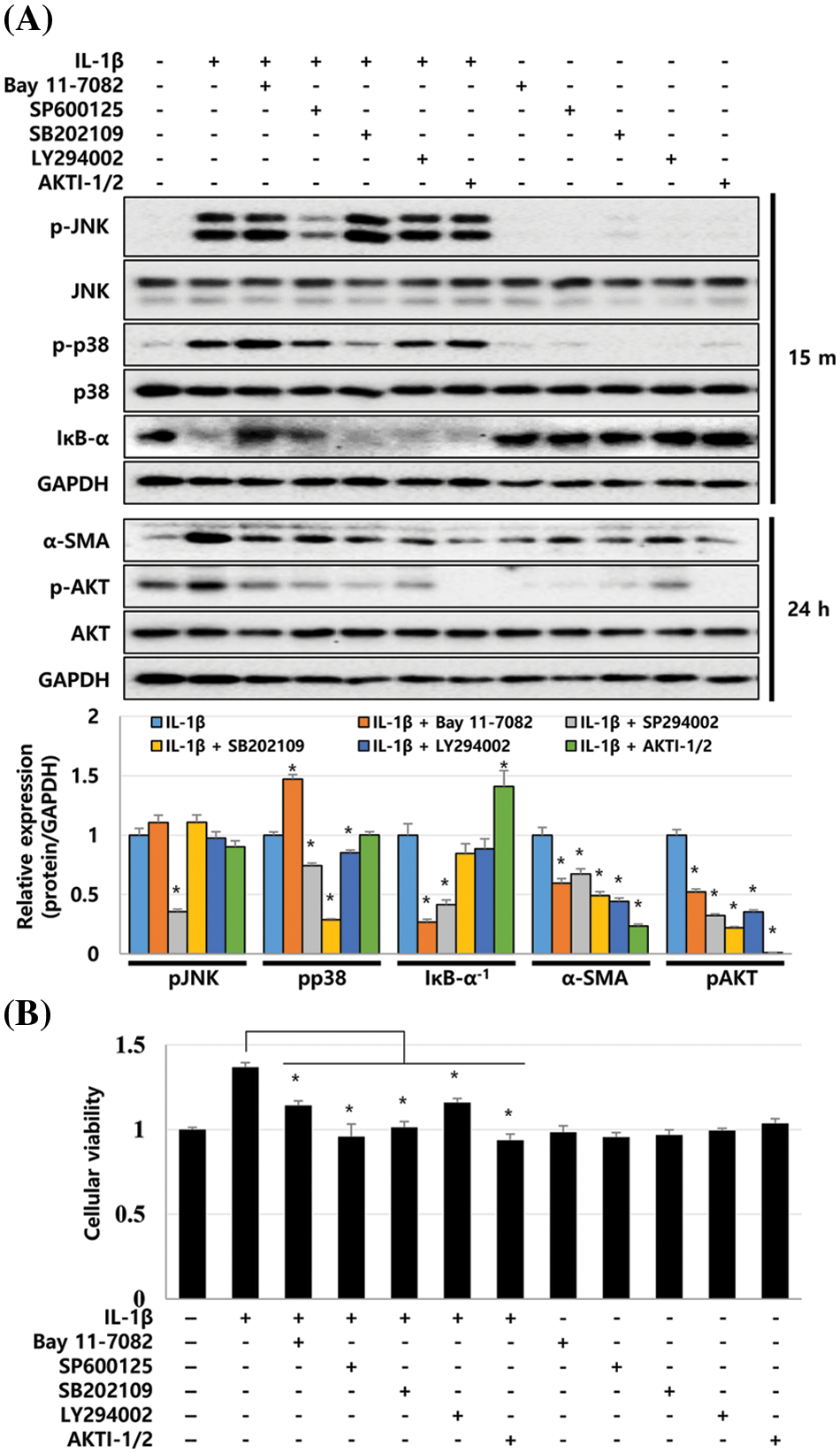
Figure 4: Signaling cascades activated in IL-1β-treated LX-2 cells. LX-2 cells were treated with each inhibitor 20 min prior to IL-1β treatment. Cell lysates were recovered 15 min or 24 h after IL-1β treatment, and then, the phosphorylation and expression levels of signaling molecules were analyzed using immunoblotting. (A) Phosphorylation and expression levels of signaling molecules after treatment with inhibitors and/or IL-1β. The intensity of signaling molecules was quantified using densitometry with Image J, and relative expression was normalized against GAPDH. (B) Decrease in LX-2 proliferation after treatment with inhibitors and/or IL-1β. Data are presented as the mean ± SD of four independent experiments. *P ≤ 0.05.
Next, we investigated whether p38, JNK, NF-κB, and AKT inhibitors affect the IL-1β-induced proliferation of LX-2 cells. According to the MTT assay, p38, JNK, NF-κB, and AKT inhibitors decreased the proliferation of LX-2 cells induced by IL-1β (Fig. 4B). These results suggest that p38, JNK, NF-κB, and AKT signaling pathways are involved in IL-1β-induced ECM production by and proliferation of LX-2 cells (Fig. 5).
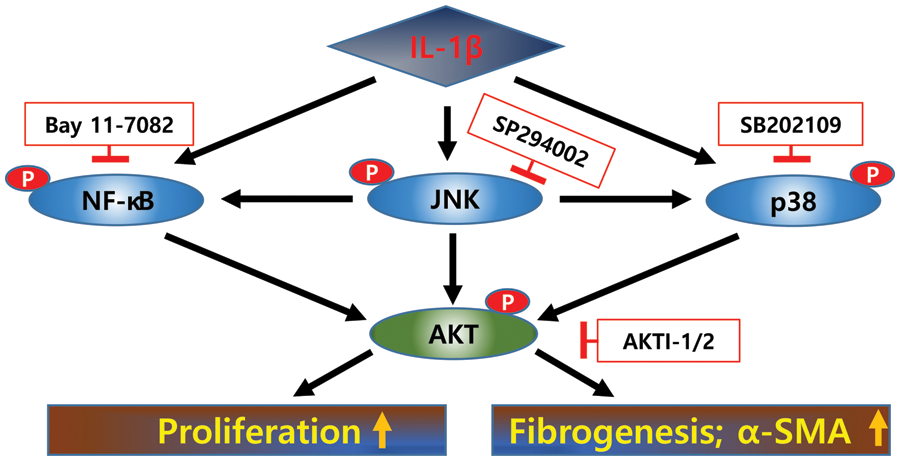
Figure 5: Signaling pathways activated by IL-1β in LX-2 cells. IL-1β increases the expression of α-SMA in LX-2 cells and their proliferation rate. After IL-1β treatment, p38, JNK, and NF-κB were activated at early time points, and these signals converged at AKT, resulting in increased proliferation of and α-SMA expression in LX-2 cells.
This study demonstrates that the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-1β is positively correlated with the proliferation and ECM production of HSCs through JNK, p38, NF-κB, and AKT signals. JNK, p38, and NF-κB signals converged at AKT phosphorylation, leading to LX-2 activation by IL-1β. Each inhibitor of JNK, p38, and NF-κB partially decreased the expression of α-SMA, but AKTI-1/2, a potent and selective AKT inhibitor, significantly reduced the expression of α-SMA to the control levels. Therefore, the AKT signaling pathway can be used as a target for alleviating liver fibrosis by IL-1β.
In idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), the PI3K/AKT signaling pathways are considered master regulators (Kulkarni et al., 2011; Wang et al., 2022). Therefore, PI3K/AKT inhibitors are currently used to evaluate the pre-clinical and clinical benefits for IPF (Zhang et al., 2016; Lin et al., 2019; Lukey et al., 2019). Omipalisib (GSK2126458), a potent PI3K/mTOR inhibitor, reduced TGF-β-induced fibroblast proliferation and collagen I synthesis by inhibiting PI3K activity and AKT phosphorylation in the blood and lungs of IPF patients (Lukey et al., 2019). In addition, inhibition of the FAK/AKT/β-catenin pathway is associated with the anti-fibrotic effects of the herbal medicine artesunate in LX-2 cells (Lv et al., 2018). In our results, AKT phosphorylation was observed in IL-1β-treated LX-2 cells from 30 min onwards and continued until 48 h. Inhibition of AKT activity reduced the expression of α-SMA in LX-2 cells to the control levels, suggesting that AKT activation is an essential step for lung and liver fibrosis. Glycogen synthase kinase (GSK)-3β is a vital signaling mediator that participates in various biological events, including embryonic development, cell differentiation, apoptosis, and ECM accumulation (Frame and Cohen, 2001; Xiao et al., 2017; Liu et al., 2018; Zheng et al., 2020). In the fibrotic process, GSK-3β can play pro-fibrotic or anti-fibrotic roles, depending on the upstream modulators or downstream effectors (Zheng et al., 2020). AKT can regulate fibrosis by phosphorylating the Ser9 site of GSK-3β, which leads to its inactivation (Wang et al., 2016; Zhang et al., 2020). Kim and colleagues reported that thymosin beta-4 regulates the activation of LX-2 cells via the phosphorylation of GSK-3β, an inactive form (Kim et al., 2017). Similarly, Ser9 phosphorylation of GSK-3β was observed to increase after 5 min in IL-1β-treated LX-2 cells, but its phosphorylation increased and decreased repeatedly until day 2 (Suppl. Fig. 2). These data suggest that AKT increases ECM production of LX-2 cells independent of phosphorylated GSK-3β (Ser9).
The proliferation and excessive ECM production of HSCs after liver damage are critical events in the progression of liver fibrosis. IL-1β expression is significantly increased in patients with suspected hepatic fibrosis and positively correlates with the fibrosis stage (Lee et al., 2018a). IL-1β also participates in HSC proliferation and ECM component expression (Gieling et al., 2009; Luo et al., 2009; Morita et al., 2019). Gieling et al. (2009) reported that IL-1 is an important mediator in the early phase of liver injury and controls the progression from liver injury to fibrogenesis through the activation of HSCs in vivo. In addition, Reiter et al. (2016) observed that the IL-1 receptor antagonist, anakinra, regulates HSC proliferation and suggested the possibility of treating liver fibrosis by antagonizing IL-1 expression. In our results, the inhibition of IL-1β-activated AKT, p38, JNK, and NF-κB signaling, and reduced HSC proliferation as well as α-SMA expression.
Collectively, IL-1β regulates both HSC proliferation and ECM production through the activation of AKT, p38, JNK, and NF-κB, where AKT acts as a downstream signal for p38, JNK, and NF-κB. Since IL-1β can be considered a therapeutic target for liver cirrhosis, IL-1β antagonism or inhibition of IL-1β-activated signaling pathways could be viable therapeutic strategies to alleviate liver fibrosis. Further studies should focus on evaluating the anti-fibrotic effects of IL-1β antagonism or inhibition of IL-1β-activated signaling pathways in vivo. Additionally, other molecules and signaling pathways should be explored through overexpression or specific inhibition of target genes that may contribute to liver fibrosis.
Our results suggest that JNK, p38, and NF-κB signals could converge at AKT phosphorylation, leading to LX-2 activation by IL-1β. Therefore, the AKT signaling pathway can be used as a target for alleviating liver fibrosis by the inflammatory cytokine IL-1β.
Availability of Data and Materials: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Author Contribution: Study conception and design: Fatema Tuj Saima, Young Woo Eom; data collection: Yongdae Yoon, Soonjae Hwang, Young Woo Eom; analysis and interpretation of results: Moon Young Kim, Soon Koo Baik; draft manuscript preparation: Young Woo Eom. All authors reviewed the results and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Ethics Approval: Not applicable.
Funding Statement: This work was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Education (2021R1I1A1A01056265).
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to report regarding the present study.
References
Baghaei K, Mazhari S, Tokhanbigli S, Parsamanesh G, Alavifard H, Schaafsma D, Ghavami S (2022). Therapeutic potential of targeting regulatory mechanisms of hepatic stellate cell activation in liver fibrosis. Drug Discovery Today 27: 1044–1061. DOI 10.1016/j.drudis.2021.12.012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Bartneck M, Koppe C, Fech V, Warzecha KT, Kohlhepp M, Huss S, Weiskirchen R, Trautwein C, Luedde T, Tacke F (2021). Roles of CCR2 and CCR5 for hepatic macrophage polarization in mice with liver parenchymal cell-specific NEMO deletion. Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology 11: 327–347. DOI 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2020.08.012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Blaner WS, O’Byrne SM, Wongsiriroj N, Kluwe J, D’Ambrosio DM, Jiang H, Schwabe RF, Hillman EM, Piantedosi R, Libien J (2009). Hepatic stellate cell lipid droplets: A specialized lipid droplet for retinoid storage. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1791: 467–473. DOI 10.1016/j.bbalip.2008.11.001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Fabregat I, Moreno-Caceres J, Sanchez A, Dooley S, Dewidar B, Giannelli G, ten Dijke P, Consortium IL (2016). TGF-β signalling and liver disease. FEBS Journal 283: 2219–2232. DOI 10.1111/febs.13665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Frame S, Cohen P (2001). GSK3 takes centre stage more than 20 years after its discovery. Biochemical Journal 359: 1–16. DOI 10.1042/bj3590001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Friedman SL (2000). Molecular regulation of hepatic fibrosis, an integrated cellular response to tissue injury. Journal of Biological Chemistry 275: 2247–2250. DOI 10.1074/jbc.275.4.2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Friedman SL (2004). Mechanisms of disease: Mechanisms of hepatic fibrosis and therapeutic implications. Nature Clinical Practice Gastroenterology & Hepatology 1: 98–105. DOI 10.1038/ncpgasthep0055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Friedman SL (2008). Hepatic stellate cells: Protean, multifunctional, and enigmatic cells of the liver. Physiological Reviews 88: 125–172. DOI 10.1152/physrev.00013.2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Geerts A (2001). History, heterogeneity, developmental biology, and functions of quiescent hepatic stellate cells. Seminars in Liver Disease 21: 311–335. DOI 10.1055/s-2001-17550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Gieling RG, Wallace K, Han YP (2009). Interleukin-1 participates in the progression from liver injury to fibrosis. American Journal of Physiology 296: G1324–1331. DOI 10.1152/ajpgi.90564.2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Hellerbrand C, Jobin C, Licato LL, Sartor RB, Brenner DA (1998). Cytokines induce NF-κB in activated but not in quiescent rat hepatic stellate cells. American Journal of Physiology 275: G269–278. DOI 10.1152/ajpgi.1998.275.2.G269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Hinz B, Phan SH, Thannickal VJ, Galli A, Bochaton-Piallat ML, Gabbiani G (2007). The myofibroblast: One function, multiple origins. American Journal of Pathology 170: 1807–1816. DOI 10.2353/ajpath.2007.070112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Hinz B, Phan SH, Thannickal VJ, Prunotto M, Desmouliere A, Varga J, de Wever O, Mareel M, Gabbiani G (2012). Recent developments in myofibroblast biology: Paradigms for connective tissue remodeling. American Journal of Pathology 180: 1340–1355. DOI 10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.02.004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Hung C, Linn G, Chow YH, Kobayashi A, Mittelsteadt K, Altemeier WA, Gharib SA, Schnapp LM, Duffield JS (2013). Role of lung pericytes and resident fibroblasts in the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 188: 820–830. DOI 10.1164/rccm.201212-2297OC. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Kalluri R, Neilson EG (2003). Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and its implications for fibrosis. Journal of Clinical Investigation 112: 1776–1784. DOI 10.1172/JCI200320530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Kim J, Hyun J, Wang S, Lee C, Lee JW, Moon EY, Cha H, Diehl AM, Jung Y (2017). Thymosin beta-4 regulates activation of hepatic stellate cells via hedgehog signaling. Scientific Reports 7: 3815. DOI 10.1038/s41598-017-03782-x. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Kis K, Liu X, Hagood JS (2011). Myofibroblast differentiation and survival in fibrotic disease. Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine 13: e27. DOI 10.1017/S1462399411001967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Kramann R, Schneider RK, DiRocco DP, Machado F, Fleig S, Bondzie PA, Henderson JM, Ebert BL, Humphreys BD (2015). Perivascular Gli1+ progenitors are key contributors to injury-induced organ fibrosis. Cell Stem Cell 16: 51–66. DOI 10.1016/j.stem.2014.11.004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Kulkarni AA, Thatcher TH, Olsen KC, Maggirwar SB, Phipps RP, Sime PJ (2011). PPAR-γ ligands repress TGFβ-induced myofibroblast differentiation by targeting the PI3K/Akt pathway: Implications for therapy of fibrosis. PLoS One 6: e15909. DOI 10.1371/journal.pone.0015909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Lee KJ, Jang YO, Cha SK, Kim MY, Park KS, Eom YW, Baik SK (2018a). Expression of fibroblast growth factor 21 and β-klotho regulates hepatic fibrosis through the nuclear factor-κB and c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathways. Gut and Liver 12: 449–456. DOI 10.5009/gnl17443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Lee M, Lee Y, Song J, Lee J, Chang SY (2018b). Tissue-specific role of CX3CR1 expressing immune cells and their relationships with human disease. Immune Network 18: e5. DOI 10.4110/in.2018.18.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Lin S, Jin J, Liu Y, Tian H, Zhang Y et al. (2019). Discovery of 4-methylquinazoline based PI3K inhibitors for the potential treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 62: 8873–8879. DOI 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b00969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Liu W, Zhang L, Xuan K, Hu C, Li L, Zhang Y, Jin F, Jin Y (2018). Alkaline phosphatase controls lineage switching of mesenchymal stem cells by regulating the LRP6/GSK3β complex in hypophosphatasia. Theranostics 8: 5575–5592. DOI 10.7150/thno.27372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Lukey PT, Harrison SA, Yang S, Man Y, Holman BF et al. (2019). A randomised, placebo-controlled study of omipalisib (PI3K/mTOR) in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. European Respiratory Journal 53: 18011992. DOI 10.1183/13993003.01992-2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Luo DD, Fielding C, Phillips A, Fraser D (2009). Interleukin-1 beta regulates proximal tubular cell transforming growth factor beta-1 signalling. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 24: 2655–2665. DOI 10.1093/ndt/gfp208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Lv J, Bai R, Wang L, Gao J, Zhang H (2018). Artesunate may inhibit liver fibrosis via the FAK/Akt/β-catenin pathway in LX-2 cells. BMC Pharmacology and Toxicology 19: 64. DOI 10.1186/s40360-018-0255-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Masola V, Carraro A, Granata S, Signorini L, Bellin G et al. (2019). In vitro effects of interleukin (IL)-1 beta inhibition on the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of renal tubular and hepatic stellate cells. Journal of Translational Medicine 17: 12. DOI 10.1186/s12967-019-1770-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Morita W, Snelling SJB, Wheway K, Watkins B, Appleton L, Carr AJ, Dakin SG (2019). ERK1/2 drives IL-1β-induced expression of TGF-β1 and BMP-2 in torn tendons. Scientific Reports 9: 19005. DOI 10.1038/s41598-019-55387-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Mueller L, Goumas FA, Affeldt M, Sandtner S, Gehling UM et al. (2007). Stromal fibroblasts in colorectal liver metastases originate from resident fibroblasts and generate an inflammatory microenvironment. American Journal of Pathology 171: 1608–1618. DOI 10.2353/ajpath.2007.060661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Reiter FP, Wimmer R, Wottke L, Artmann R, Nagel JM et al. (2016). Role of interleukin-1 and its antagonism of hepatic stellate cell proliferation and liver fibrosis in the Abcb4-/- mouse model. World Journal of Hepatology 8: 401–410. DOI 10.4254/wjh.v8.i8.401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sahin H, Borkham-Kamphorst E, Kuppe C, Zaldivar MM, Grouls C et al. (2012). Chemokine Cxcl9 attenuates liver fibrosis-associated angiogenesis in mice. Hepatology 55: 1610–1619. DOI 10.1002/hep.25545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Tomasek JJ, Gabbiani G, Hinz B, Chaponnier C, Brown RA (2002). Myofibroblasts and mechano-regulation of connective tissue remodelling. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 3: 349–363. DOI 10.1038/nrm809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Trivedi P, Wang S, Friedman SL (2021). The power of plasticity-metabolic regulation of hepatic stellate cells. Cell Metabolism 33: 242–257. DOI 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.10.026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Tsutsui H, Cai X, Hayashi S (2015). Interleukin-1 family cytokines in liver diseases. Mediators of Inflammation 2015: 630265. DOI 10.1155/2015/630265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Wang J, Hu K, Cai X, Yang B, He Q, Wang J, Weng Q (2022). Targeting PI3K/AKT signaling for treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B 12: 18–32. DOI 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.07.023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Wang C, Jin H, Wang N, Fan S, Wang Y et al. (2016). Gas6/Axl Axis contributes to chemoresistance and metastasis in breast cancer through Akt/GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling. Theranostics 6: 1205–1219. DOI 10.7150/thno.15083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Willis BC, duBois RM, Borok Z (2006). Epithelial origin of myofibroblasts during fibrosis in the lung. Proceedings of the American Thoracic Society 3: 377–382. DOI 10.1513/pats.200601-004TK. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Wynn TA (2007). Common and unique mechanisms regulate fibrosis in various fibroproliferative diseases. Journal of Clinical Investigation 117: 524–529. DOI 10.1172/JCI31487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Xiao D, Huang J, Pan Y, Li H, Fu C et al. (2017). Chromatin remodeling factor LSH is upregulated by the LRP6-GSK3β-E2F1 axis linking reversely with survival in gliomas. Theranostics 7: 132–143. DOI 10.7150/thno.17032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Yang YM, Seki E (2015). TNFα in liver fibrosis. Current pathobiology Reports 3: 253–261. DOI 10.1007/s40139-015-0093-z. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Zeisberg EM, Tarnavski O, Zeisberg M, Dorfman AL, McMullen JR et al. (2007). Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition contributes to cardiac fibrosis. Nature Medicine 13: 952–961. DOI 10.1038/nm1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Zhang YE (2017). Non-smad signaling pathways of the TGF-β family. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology 9: a022129. DOI 10.1101/cshperspect.a022129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Zhang C, Wei S, Sun WP, Teng K, Dai MM et al. (2020). Super-enhancer-driven AJUBA is activated by TCF4 and involved in epithelial-mesenchymal transition in the progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Theranostics 10: 9066–9082. DOI 10.7150/thno.45349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Zhang XL, Xing RG, Chen L, Liu CR, Miao ZG (2016). PI3K/Akt signaling is involved in the pathogenesis of bleomycininduced pulmonary fibrosis via regulation of epithelialmesenchymal transition. Molecular Medicine Reports 14: 5699–5706. DOI 10.3892/mmr.2016.5960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Zheng H, Yang Z, Xin Z, Yang Y, Yu Y, Cui J, Liu H, Chen F (2020). Glycogen synthase kinase-3β: A promising candidate in the fight against fibrosis. Theranostics 10: 11737–11753. DOI 10.7150/thno.47717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
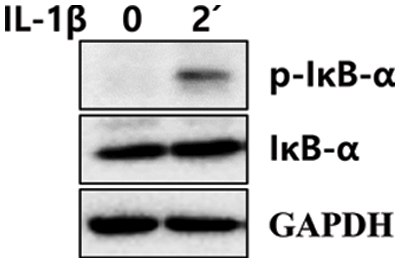
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE S1: Phosphorylation of IκB-α in IL-1β-treated LX-2 cells. After IL-1β treatment for 2 min, LX-2 cell lysates were obtained, and phosphorylation of IκB-α was analyzed using immunoblotting.
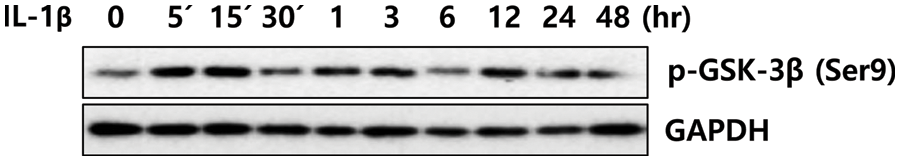
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE S2: Phosphorylation of GSK-3β (Ser9) in IL-1β-treated LX-2 cells. After IL-1β treatment for 24 h, LX-2 cell lysates were obtained, and phosphorylation of GSK-3β (Ser9) was analyzed using immunoblotting.
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools