 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Evaluation of combined detection of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 and glutathione peroxidase 4 in primary hepatic carcinoma and preliminary exploration of pathogenesis
Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, The Second Hospital of Nanjing, Nanjing Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanjing, 210003, China
* Corresponding Author: AIDONG GU. Email:
BIOCELL 2023, 47(12), 2609-2615. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2023.042472
Received 31 May 2023; Accepted 26 July 2023; Issue published 27 December 2023
Abstract
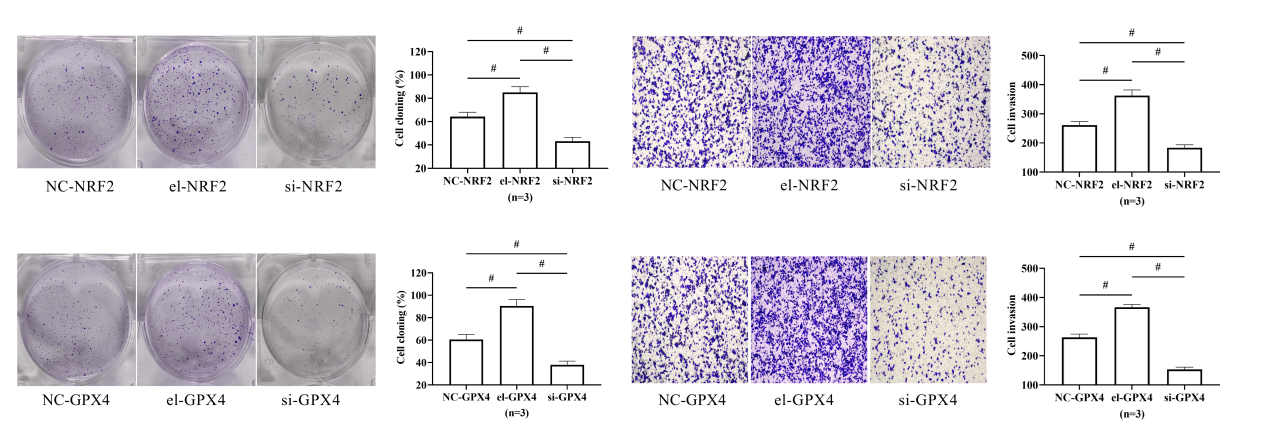
Objective: This study aims to analyze the clinical significance and mechanism of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2) and glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) in primary hepatic carcinoma (PHC). Methods: The expression of NRF2 and GPX4 in peripheral blood of patients with PHC was determined to analyze the diagnostic value of the two combined for PHC. The prognostic significance of NRF2 and GPX4 was evaluated by 3-year follow-up. Human liver epithelial cells THLE-2 and human hepatocellular carcinoma cells HepG2 were purchased, and the expression of NRF2 and GPX4 in the cells was determined. NRF2 and GPX4 aberrant expression vectors were constructed and transfected into HepG2, and changes in cell proliferation and invasion capabilities were observed. Results: The expression of NRF2 and GPX4 in patients with PHC was higher than that in patients with LC or VH (p < 0.05), and the two indicators combined was excellent in diagnosing PHC. Moreover, patients with high expression of NRF2 and GPX4 had a higher risk of death (p < 0.05). In in vitro experiments, both NRF2 and GPX4 expression was elevated in HepG2 (p < 0.05). HepG2 activity was enhanced by increasing the expression of the two, vice versa (p < 0.05). Conclusion: NRF2 and GPX4 combined is excellent in diagnosing PHC, and promotes the malignant development of PHC.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools