 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Inhibition of VEGF-A expression in hypoxia-exposed fetal retinal microvascular endothelial cells by exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells
1 Department of Ophthalmology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Jinan University, Jinan University, Guangzhou, 510630, China
2 Department of Ophthalmology, Guangdong Women and Children Hospital, Guangzhou, 511400, China
3 Department of Ophthalmology, The Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Jinan University, Jinan University, Dongguan, 523000, China
4 Graduate School, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, 510000, China
5 Lab Center, Guangdong Cord Blood Bank, Guangzhou, 510000, China
6 Guangdong Eye Institute, Department of Ophthalmology, Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital (Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences), Southern
Medical University, Guangzhou, 510000, China
* Corresponding Authors: Jingxiang Zhong, ; Xianqiong Luo,
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Perspectives on Stem Cells and Regenerative Medicine)
BIOCELL 2023, 47(11), 2485-2494. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2023.044177
Received 23 July 2023; Accepted 16 October 2023; Issue published 27 November 2023
Abstract
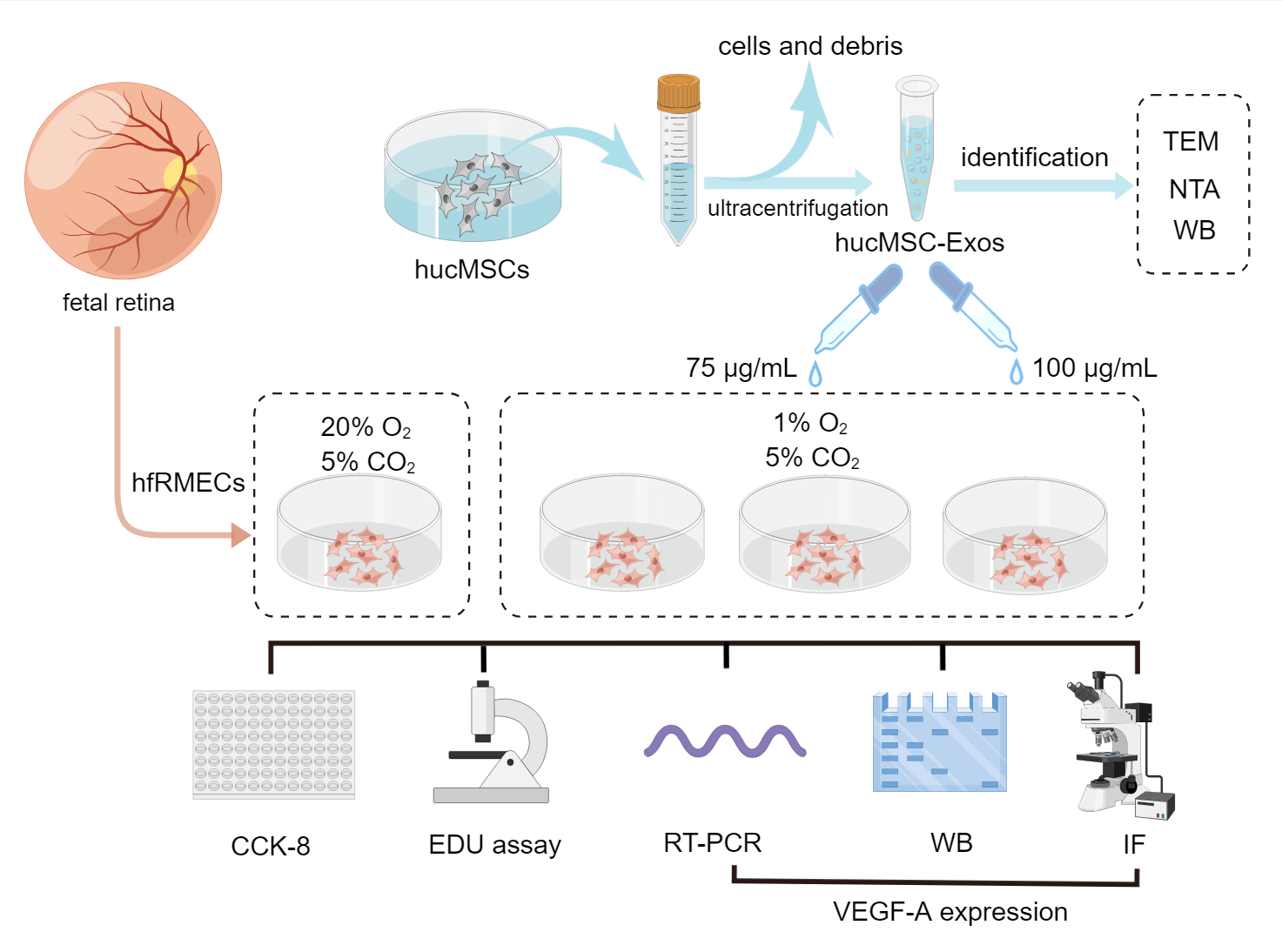
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the potential of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell (hucMSC)-derived exosomes (hucMSC-Exos) in inhibiting hypoxia-induced cell hyper proliferation and overexpression of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) in immature human fetal retinal microvascular endothelial cells (hfRMECs). Methods: Exosomes were isolated from hucMSCs using cryogenic ultracentrifugation and characterized through various techniques, including transmission electron microscopy, nanoparticle tracking analysis, bicinchoninic acid assays, and western blotting. The hfRMECs were identified using von Willebrand factor (vWF) co-staining and divided into four groups: a control group cultured under normoxic condition, a hypoxic model group, a hypoxic group treated with low-concentration hucMSC-Exos (75 μg/mL) and a hypoxic group treated with high-concentration hucMSC-Exos (100 μg/mL). Cell viability and proliferation were assessed using Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay and EdU (5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine) assay respectively. Expression levels of VEGF-A were evaluated using RT-PCR, western blotting and immunofluorescence. Results: Hypoxia significantly increased hfRMECs’ viability and proliferation by upregulating VEGF-A levels. The administration of hucMSC-Exos effectively reversed this response, with the high-concentration group exhibiting greater efficacy compared to the lowconcentration group. Conclusion: In conclusion, hucMSC-Exos can dose-dependently inhibit hypoxia-induced hyperproliferation and VEGF-A overexpression in immature fetal retinal microvascular endothelial cells.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools