 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Diagnostic and classification value of immune-related lncRNAs in dilated cardiomyopathy
1 Information Center, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, 610041, China
2 Laboratory of Cardiovascular Diseases, Regenerative Medicine Research Center, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, 610041, China
3 Health Management Center, General Practice Medical Center, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, 610041, China
4 Department of Cardiology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, 610041, China
* Corresponding Authors: Xiaojing Liu, ; Junteng Zhou,
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Subcellular Organelles and Cellular Molecules: Localization, Detection, Prediction, and Diseases)
BIOCELL 2023, 47(11), 2517-2533. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2023.043864
Received 14 July 2023; Accepted 08 September 2023; Issue published 27 November 2023
Abstract
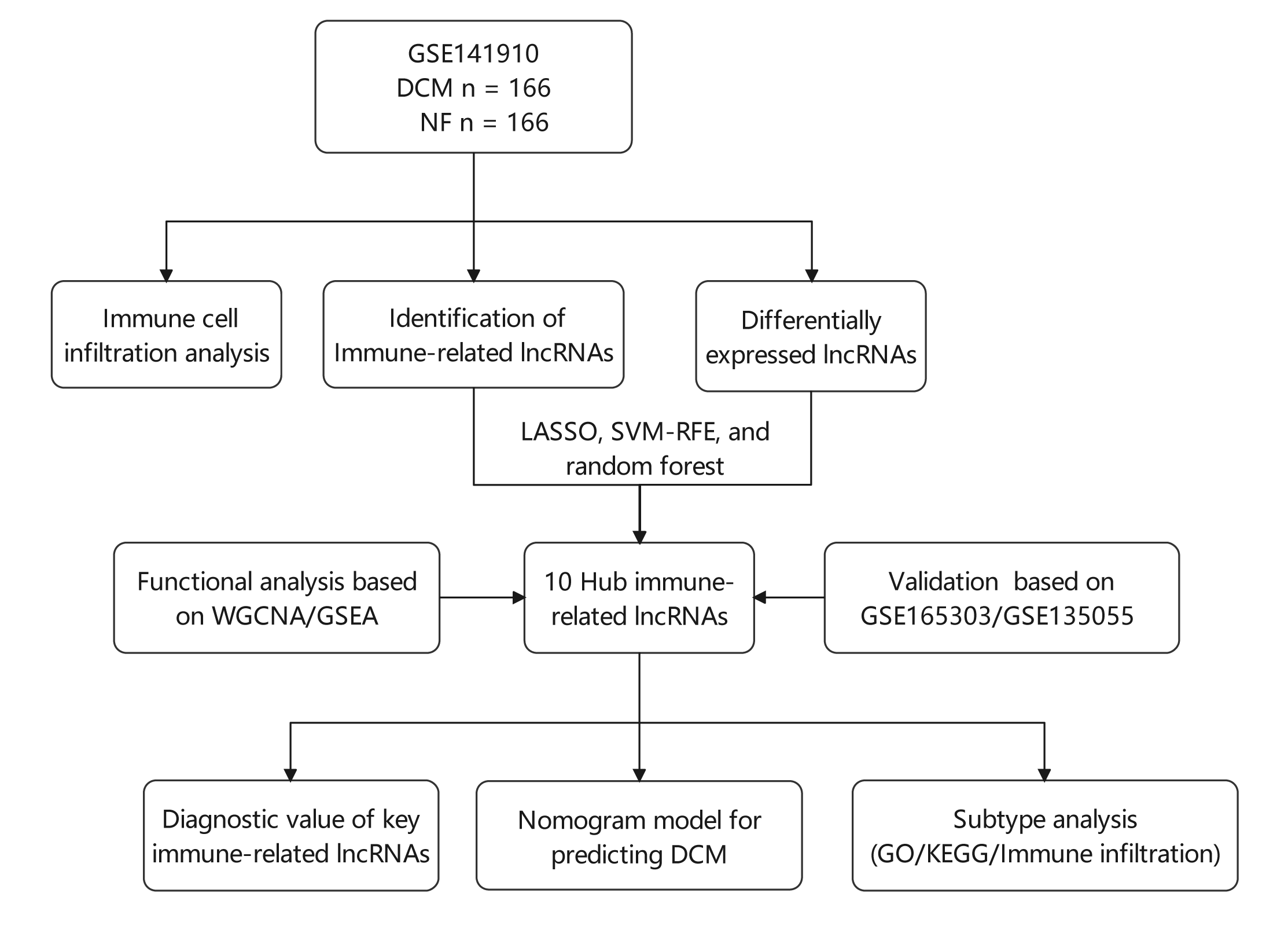
Background: Various physiological mechanisms are linked to dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) development, including oxidative stress, immune irregularities, inflammation, fibrosis, and genetic changes. However, precise molecular drivers of DCM, especially regarding abnormal immune responses, remain unclear. This study investigates immune-related long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in DCM’s diagnostic and therapeutic potential. Methods: GSE141910, GSE135055, and GSE165303 datasets were acquired from the GEO database. LASSO, SVM-RFE, and random forest algorithms identified DCM-associated immune-related lncRNAs. Diagnostic capabilities were assessed by Nomogram and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. Multivariate linear regression explored lncRNA correlations with ejection fraction. Single-sample gene set enrichment analysis (ssGSEA) gauged immune cell infiltration/functions. Functional enrichment analyses were performed using Gene set variation analysis (GSVA), gene ontology (GO), and the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG). Consensus clustering categorized DCM cases. Results: Ten immune-related lncRNAs emerged: C10orf71-AS1, FHAD1-AS1, SCIRT, FNDC1-AS1, MELTFAS1, LOC101928834, GDNF-AS1, DCXR-DT, C3orf36, and LOC107985323. These lncRNAs, tied to immunomodulation, showed promising DCM diagnostic accuracy. Adjusted for confounders, they independently correlated with ejection fraction. Using lncRNA expression, DCM patients were grouped into subtypes. Subtype C1 displayed a higher level of immune cell infiltration and immune checkpoint expression compared to subtype C2, emphasizing the variations in the immune microenvironment. Conclusion: This study identifies ten immune-related lncRNAs for further exploration in DCM diagnosis and subtyping. Based on expression patterns, we propose two potential DCM subtypes. Notably, findings are preliminary and hypothesis-generating, demanding validation and further investigation. This research provides insights into DCM diagnosis and classification.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material FileCite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools