 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
NR4A1 enhances glycolysis in hypoxia-exposed pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells by upregulating HIF-1α expression
1 Cardiovascular Department, The Third Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha, 410013, China
2 Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, The Second Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, 410011, China
* Corresponding Authors: CHENYANG CHEN. Email: ; JIANG LI. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Cellular Signal Transduction in Biological Activities)
BIOCELL 2023, 47(11), 2423-2433. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2023.044459
Received 31 July 2023; Accepted 27 September 2023; Issue published 27 November 2023
Abstract
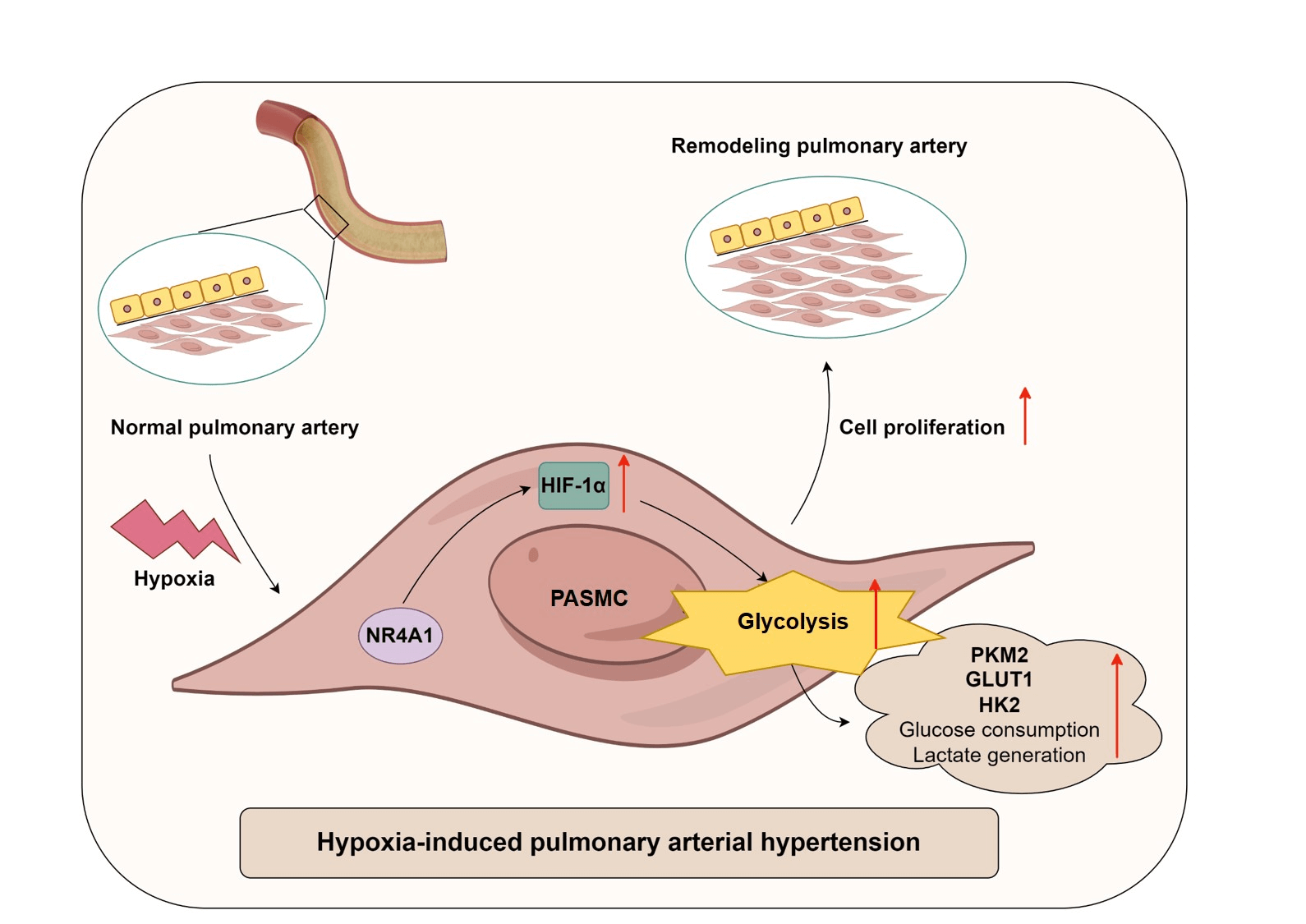
Background: Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a chronic and progressive disease that is strongly associated with dysregulation of glucose metabolism. Alterations in nuclear receptor subfamily 4 group A member 1 (NR4A1) activity alter the outcome of PAH. This study aimed to investigate the effects of NR4A1 on glycolysis in PAH and its underlying mechanisms. Methods: This study included twenty healthy volunteers and twenty-three PAH patients, and plasma samples were collected from the participants. To mimic the conditions of PAH in vitro, a hypoxia-induced model of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell (PASMC) model was established. The proliferation of PASMCs was assessed using CCK8 assays. Results: Levels of NR4A1, hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α), and various glycolysis-related enzymes were measured. In addition, extracellular glucose and lactate production were assessed. The interaction between NR4A1 and HIF-1α was evaluated by co-immunoprecipitation assays. Levels of NR4A1 and HIF-1α was increased in PAH patients, and exposure to hypoxia resulted in increased levels of NR4A1 and HIF-1α in PASMCs. NR4A1 interacted with HIF-1α. NR4A1 overexpression enhanced hypoxia-induced expression of HIF-1α, GLUT1, PKM2, HK2, and CD36, decreased glucose levels, increased lactate levels and promoted hypoxic PASMC viability. Conversely, silencing NR4A1 decreased hypoxia-induced expression of HIF-1α, GLUT1, PKM2, HK2, and CD36, promoted glucose production, reduced lactate levels and inhibited hypoxic PASMC viability. Furthermore, overexpression of HIF-1α reversed the regulation of glycolysis caused by NR4A1 knockdown. Conclusion: NR4A1 enhances glycolysis in hypoxia-induced PASMCs by upregulating HIF-1α. Our findings indicate that the management of NR4A1 activity may be a promising strategy for PAH therapy.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools