 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
SIRT2 interacts with DDX24 to promote nasopharyngeal carcinoma growth
Department of Radiotherapy, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, China
* Corresponding Author: WENQI LIU. Email:
BIOCELL 2023, 47(11), 2445-2452. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2023.042512
Received 02 June 2023; Accepted 08 September 2023; Issue published 27 November 2023
Abstract
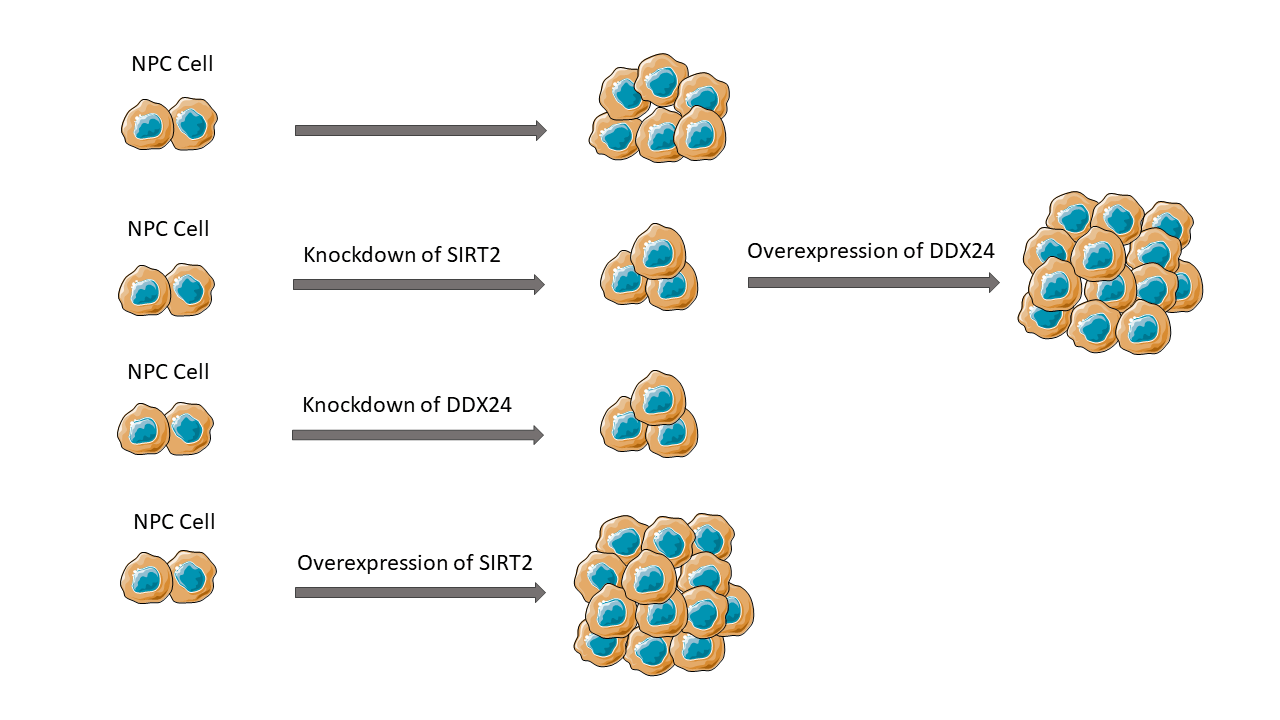
Background: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is one of the most prevalent cancers in Southeast Asia. Sirtuin 2 (SIRT2) is a member of the NAD+-dependent deacetylase family and has been shown to play important roles in numerous biological processes. However, Its function in NPC remains uncertain. The primary aim of this study is to clarify the role of SIRT2 in NPC. Methods: In this research, we examined the effect of SIRT2 silencing on NPC cell proliferation and colony formation using vitro NPC cell lines. Co-immunoprecipitation and mass spectrometry was applied to identify SIRT2-interacting proteins in NPC cells. Results: In comparison to nasopharyngeal epithelial NP69 cells, SIRT2 was up-regulated in multiple NPC cell lines, particularly in CNE2 cells. SIRT2 knockdown abrogated CNE2 cell proliferation and colony formation, whereas SIRT2 overexpression promoted HNE1 cell proliferation and colony formation. The SIRT2-interacting proteins were gathered in gene expression and regulation processes including RNA processing and translation. Among the SIRT2-interacting proteins, there were multiple DEAD-box (DDX) family members. Of note, silencing of DDX24 phenocopied the effect of SIRT2 knockdown on NPC growth. Overexpression of DDX24 restored SIRT2-depleted CNE2 cells to proliferative and colony formation. Conclusions: Our study indicates that SIRT2 can interact with DDX24 to enhance NPC growth. The clinical relevance of SIRT2 and DDX24 in NPC warrants further investigation.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools