 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Hsa_circ_0036740 in familial adenomatous polyposis: Immune regulation and neutrophil effects in CRC based on high-throughput assay
Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Meizhou People’s Hospital, Meizhou, 514031, China
* Corresponding Author: EN LI. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Bioinformatics Study of Diseases)
BIOCELL 2023, 47(11), 2409-2422. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2023.031186
Received 19 May 2023; Accepted 21 June 2023; Issue published 27 November 2023
Abstract
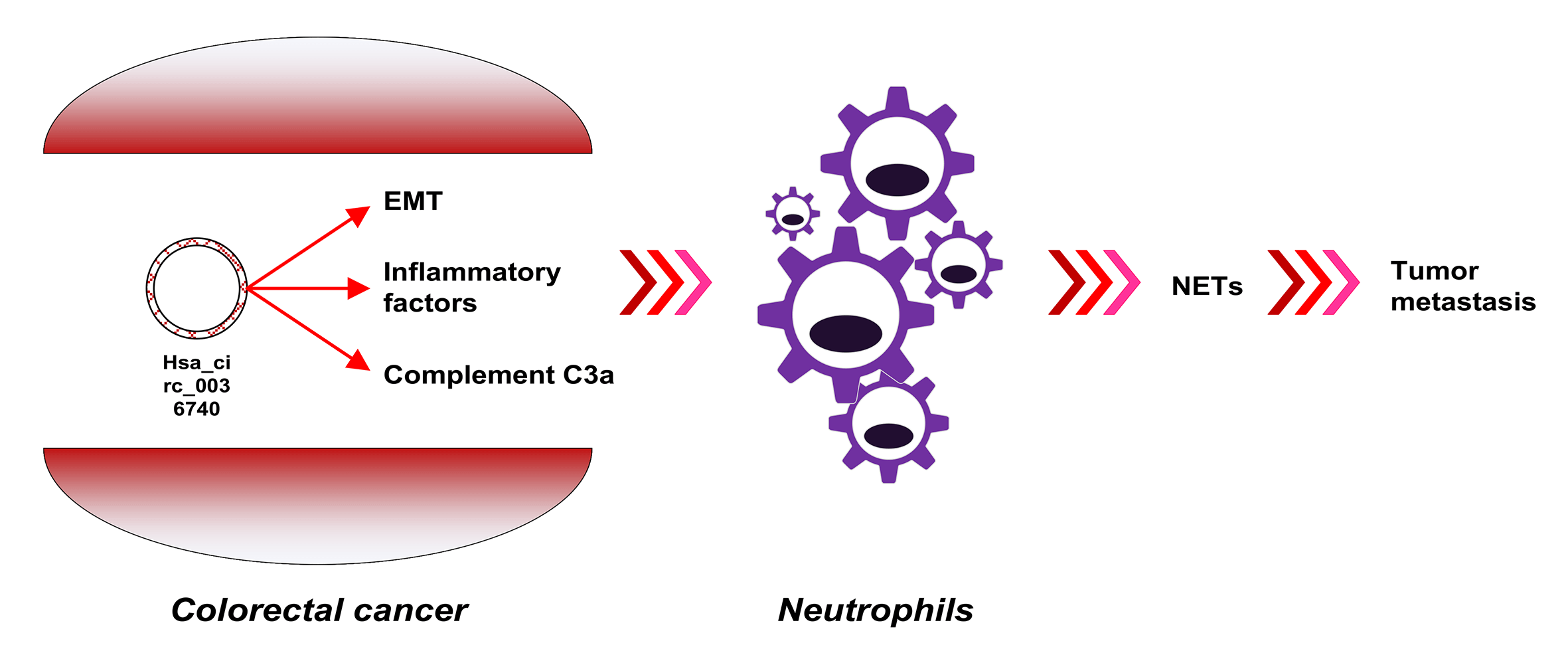
Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) is an autosomal dominant disease with a high probability of becoming cancerous. Many RNAs potentially associated with FAP have not been identified. In this study, a circRNA (circular RNA) expression profile of FAP was established using a circRNA microarray, and differentially expressed circRNAs were verified by RT-qPCR. The effects of hsa_circ_0036740 on the malignant behavior of tumor cells (proliferation, apoptosis, and epithelial mesenchymal transition) and the levels of C3A complement protein expression were evaluated. Moreover, neutrophils were isolated and co-cultured with colorectal cancer cells (CRCs), followed by measurements of MPO-DNA, citrullinated histone H3, interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, and IL-8 levels. Nuclear translocation of arginine deiminase 4 (PAD4) was observed using immunofluorescence assays. Based on the high-throughput assay, 238 downregulated circRNAs, and 38 upregulated circRNAs were identified. A Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes enrichment analysis suggested that immune regulation might be involved in FAP. A total of 10 DECs (differentially expressed circular RNAs) were identified by RT-qPCR, and among them, hsa_circ_0036740 showed the highest fold-change in upregulation. Results of gain-of- and loss-of-function studies revealed that hsa_circ_0036740 enhanced the malignant behavior of tumor cells, such as metastasis, proliferation, and apoptosis, with an increasing level of C3A complement. Moreover, hsa_circ_0036740 also significantly increased neutrophil extracellular trap formation and inflammation in neutrophils, as shown by an increased expression of PAD4. In conclusion, this study revealed the expression profiles of circRNAs in FAP and confirmed the possible involvement of hsa_circ_0036740 in the immune regulation mediated by neutrophils. Finally, hsa_circ_0036740 was suggested as a new therapeutic target for CRC.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material FileCite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools