 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Molecular basis of COVID-19, ARDS and COVID-19-associated ARDS: Diagnosis pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies
1 Biopharmaceutical Research Lab, Anusandhan Kendra-1, SASTRA Deemed-to-be University, Thanjavur, 613401, India
2 School of Chemical and Biotechnology, SASTRA Deemed-to-be University, Thanjavur, 613401, India
* Corresponding Author: SENTHIL VISAGA AMBI. Email:
BIOCELL 2023, 47(11), 2335-2350. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2023.029379
Received 15 February 2023; Accepted 25 August 2023; Issue published 27 November 2023
Abstract
The novel coronavirus pneumonia (COVID-19) is spreading worldwide and threatening people greatly. The routes by which SARS-CoV-2 causes lung injury have grown to be a major concern in the scientific community since patients with new Coronavirus, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) have a high likelihood of developing acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in severe cases. The mortality rate of COVID-19 has increased over the period due to rapid spread, and it becomes crucial to understand the disease epidemiology, pathogenic mechanisms, and suitable treatment strategies. ARDS is a respiratory disorder and is one of the clinical manifestations observed in patients with severe COVID-19. In this scenario, it is important to address this problem to develop suitable treatment strategies. This review attempts to present the prevalence of ARDS in COVID-19 patients and their predictive causes and risk factors, highlighting the contrasting features of COVID-19-induced ARDS with typical ARDS. This review also presents insights into the association between SARS-CoV-2 and lung damage while exploring the potential COVID-19 mechanisms in ARDS from the perspective of the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 protein, cytokine storm, immune responses, and other signaling pathways. The review also discusses the diagnosis strategies, pathogenesis, risk factors, and treatment options of COVID-19-related ARDS.Graphic Abstract
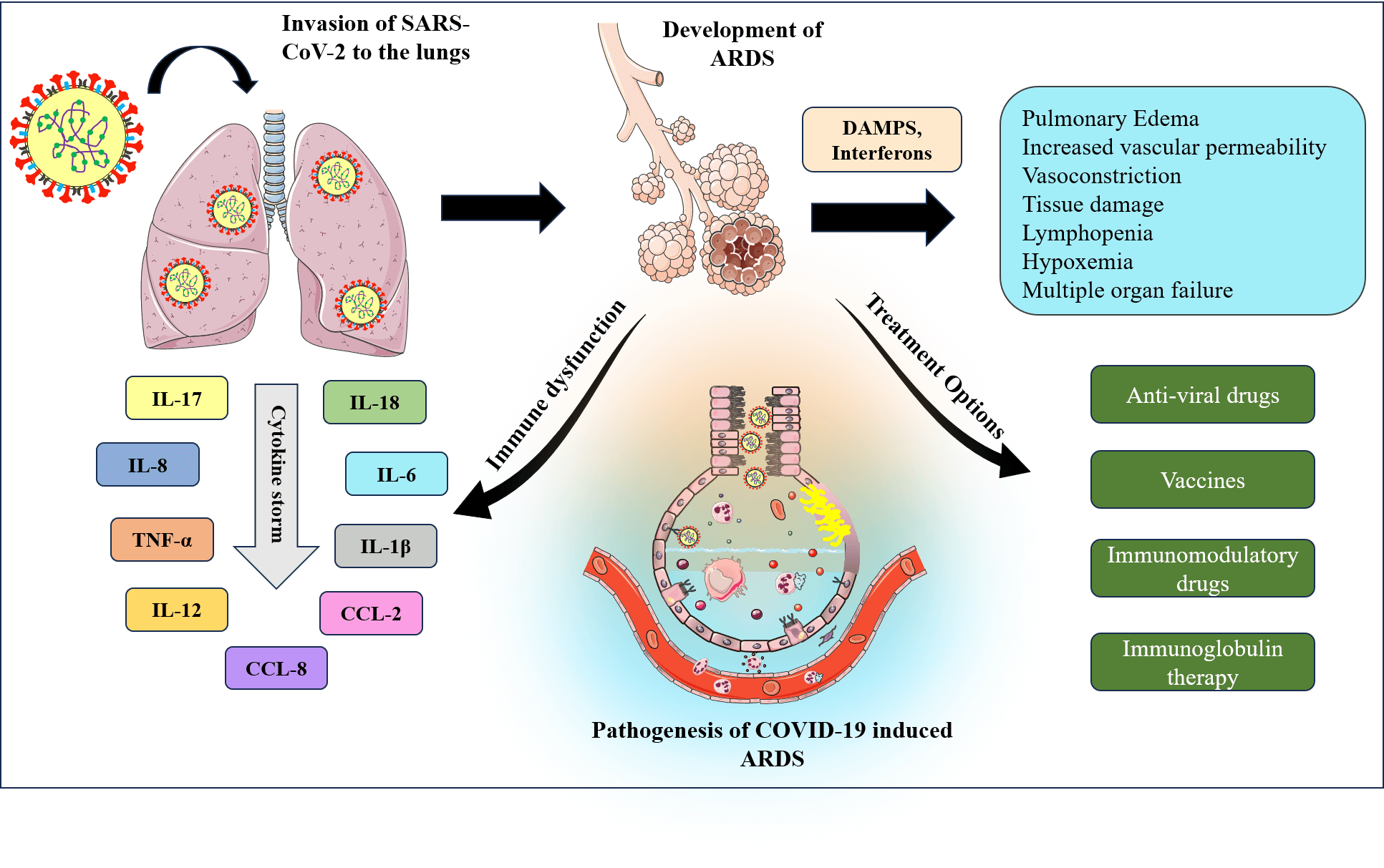
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools