 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Exploring exosomes to provide evidence for the treatment and prediction of Alzheimer’s disease
1 Edmond H. Fischer Signal Transduction Laboratory, School of Life Sciences, Jilin University, Changchun, 130012, China
2 Department of General Surgery, The Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, 130041, China
* Corresponding Author: LINLIN ZENG. Email:
BIOCELL 2023, 47(10), 2163-2176. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2023.031226
Received 23 May 2023; Accepted 22 June 2023; Issue published 08 November 2023
Abstract
Exosomes are extracellular vesicles with a 30–150 nm diameter originating from endosomes. In recent years, scientists have regarded exosomes as an ideal small molecule carrier for the targeted treatment of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) across the blood-brain barrier due to their nanoscale size and low immunogenicity. A large amount of evidence shows that exosomes are rich in biomarkers, and it has been found that the changes in biomarker content in blood, cerebrospinal fluid, and urine are often associated with the onset of AD patients. In this paper, some recent advances in the use of exosomes in the treatment of AD are reviewed, and various exosome markers and some latest detection methods are summarized to provide some evidence for the detection or treatment of AD by exosomes.Graphic Abstract
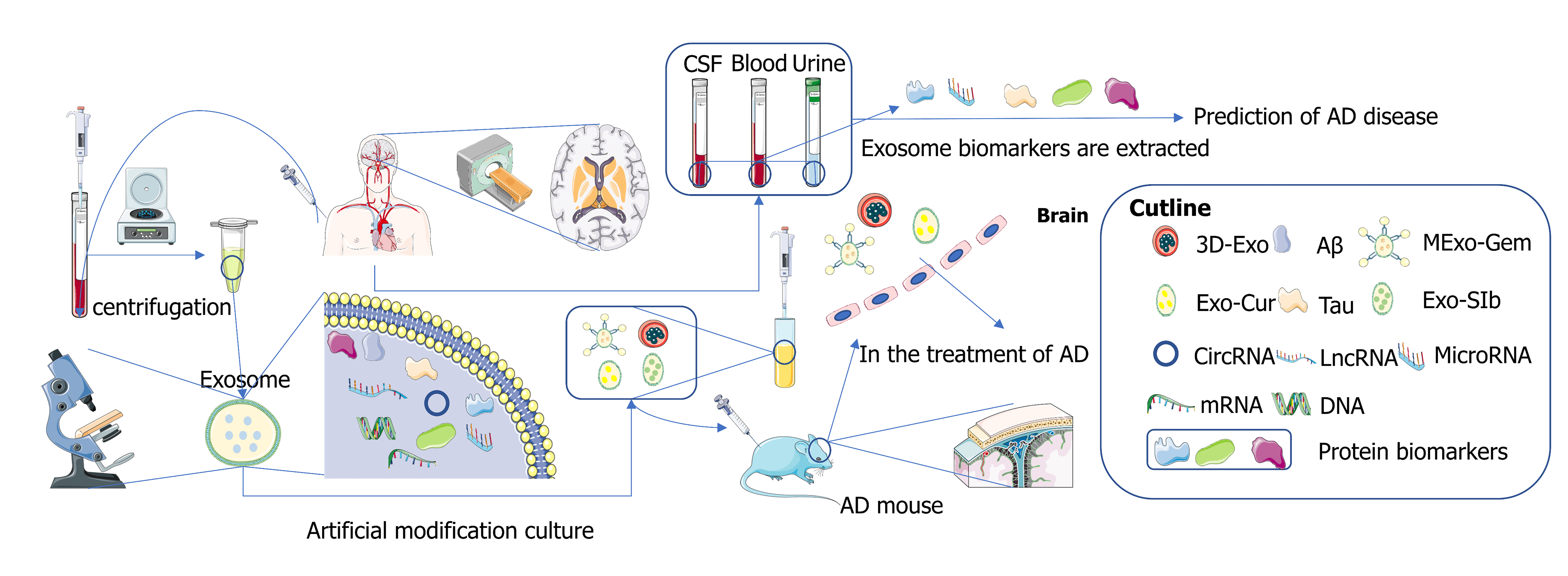
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools