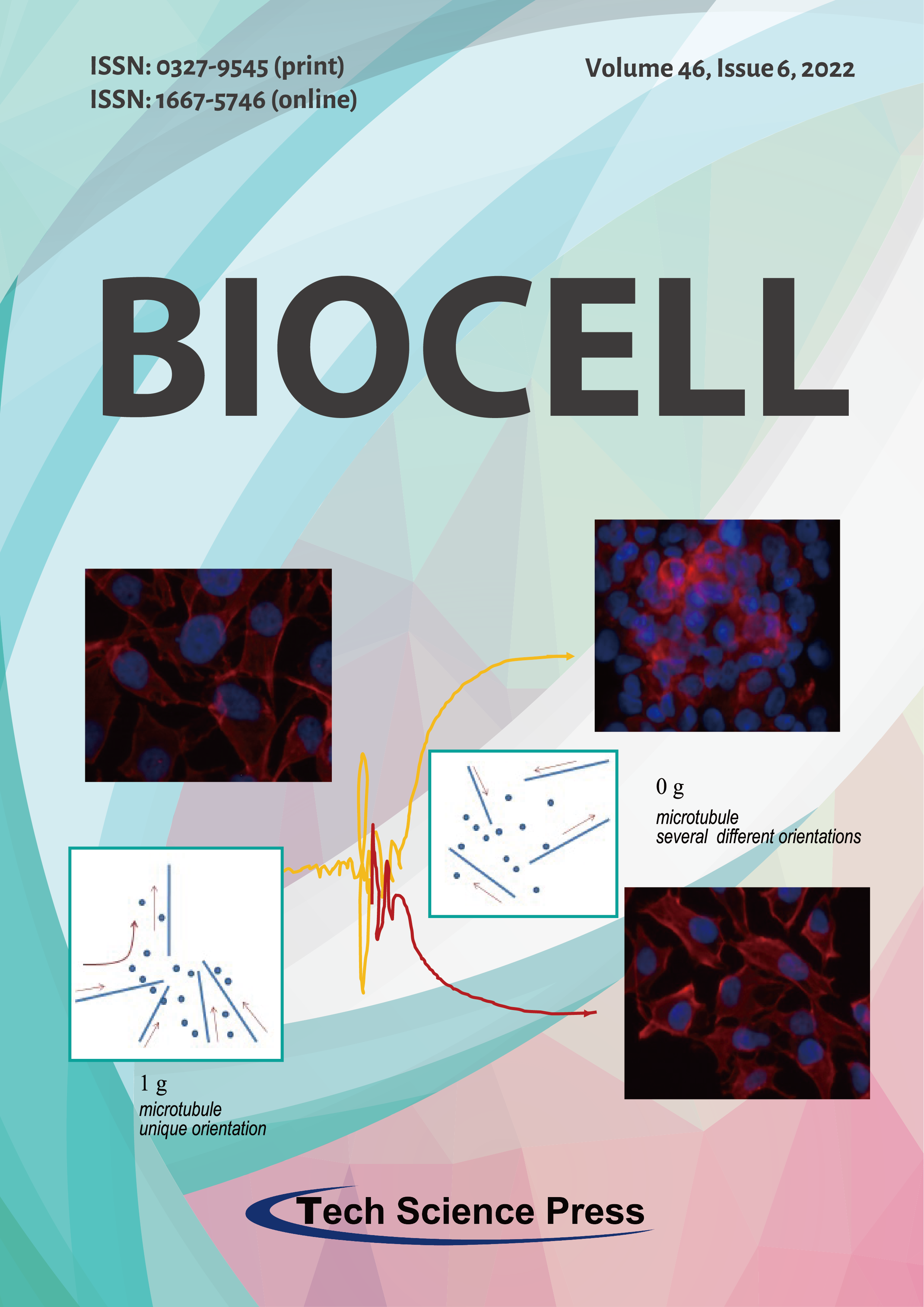
Several microenvironment-related cues interfere with the non-linear dynamics that govern cytoskeleton architecture, namely by fostering symmetry breakings and transitions across different phenotypes. Such process induces a whole-coherent adaptive response, involving the reprogramming of biochemical and gene-expression patterns. In weightlessness conditions, the removal of the gravity constraints disrupts the gravity-oriented process through which microfilaments and microtubules organize themselves into a specified shape. In absence of gravity, cytoskeleton remodeling is an everlasting phenomenon (due to non-equilibrium dynamics), which will lead to an endless rearrangement, while cells are oscillating in between different morphological (and functional) configurations, thus promoting the emergence of novel phenotypes.
View this paper