DOI:10.32604/biocell.2021.015899

| BIOCELL DOI:10.32604/biocell.2021.015899 |  |
| Review |
Ubiquitin-like posttranslational modifications in NAFLD progression and treatment
1Key Laboratory of Laboratory Medicine of Jiangsu Province, School of Medicine, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang, 212013, China
2The Affiliated Third Hospital of Zhenjiang, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang, 212013, China
*Address correspondence to: Yongmin Yan, yym@ujs.edu.cn; Youwen Tan, tyw915@sina.com
Received: 22 January 2021; Accepted: 10 March 2021
Abstract: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a long-lasting condition that affects the liver, destroying its function. Liver injury can cause steatosis and inflammation, and further activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) often leads to the development of nonalcoholic liver fibrosis. The patient with NAFLD is at risk of developing advanced liver disease and complications, such as liver failure, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and portal hypertension. Although our understanding of the cellular and molecular mechanisms of NAFLD has greatly improved in recent years, treatment remains limited. Analysis and characterization of protein posttranslational modifications (PTMs) could improve our understanding of NAFLD pathology and leading to the development of new and more effective treatments. In recent years, a number of studies have described how ubiquitin-like (Ubl)-PTMs change during NAFLD and how treatments targeting specific enzymes mediating these Ubl-PTMs can improve various liver diseases, particularly in relation to NAFLD and nonalcoholic liver fibrosis. New strategies for evaluating modified proteomes could provide novel insights into the roles of Ubl-PTMs in NAFLD progression and the therapeutic value of targeting the proteins involved in these Ubl-PTMs.
Keywords: NAFLD; Neddylation; Nonalcoholic liver fibrosis; Ubiquitination; SUMOylation
NAFLD is a long-lasting condition that affects the liver, destroying its ability to regenerate after injury and triggering wound healing reactions (Giannitrapani et al., 2014). NAFLD progression involves multiple cell types and mediators (Fig. 1) and is a major global public health problem, with about 800 million cases worldwide and about 2 million deaths each year (Marcellin and Kutala, 2018; Parola and Pinzani, 2019). Additionally to the global prevalence of NAFLD and its risk factors, including obesity, metabolic syndrome, and type 2 diabetes, means that the prevalence of chronic liver disease (CLD) is expected to continue to increase (Adams and Lindor, 2007).
Although our understanding of the cellular and molecular mechanisms of NAFLD has greatly improved in recent years, treatment for NAFLD remains limited. Analysis and charact-erization of the protein posttranslational modifications (PTMs) could improve our understanding of NAFLD pathology and lead to the development of new and more effective treatments. In recent years, many studies have described that alterations in ubiquitin-like (Ubl)-PTMs occur during the NAFLD process and that targeting the specific enzymes that mediate these Ubl-PTMs could improve NAFLD. Therefore, this review discusses NAFLD, nonalcoholic liver fibrosis, and treatment strategies, including the roles of Ubl-PTMs and their value in the development of new potential treatments.
The most common PTMs include ubiquitination, neddylation, SUMOylation, phosphorylation, acetylation, glycosylation, and hydroxylation. Many PTMs are mediated by ubiquitination, an important system for processing abnormally folded or damaged proteins. Unlike ubiquitination that is mainly involved in protein degradation, neddylation and SUMOylation have diverse roles, including directly or indirectly affecting ubiquitination and stabilizing protein levels (Figs. 2 and 3). Ubiquitination, SUMOylation, and neddylation are crucial post-translational modifications that control a wide range of biological processes, including DNA repair, transcriptional regulation, inflammation, protein stability, and cell cycle progression (Husnjak and Dikic, 2012; Yao et al., 2020; Zeng et al., 2020).
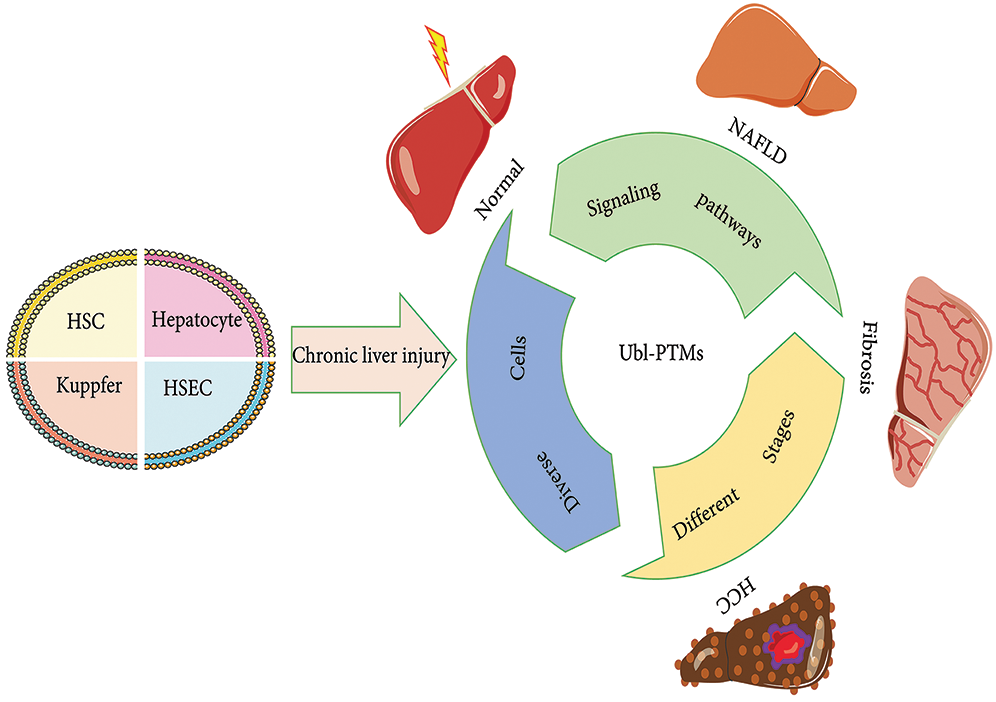
Figure 1: Initiation, progression, and resolution of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) involving Ubl-PTMs. NAFLD is a long-lasting condition that affects the liver, destroying its function. Liver injury can cause steatosis (hepatocytes), inflammation (hepatocytes and Kupfer cells), liver cell necrosis, angiogenesis (HSEC), wound healing responses, and accumulation of extracellular matrix (ECM) protein (HSCs). Liver fibrosis usually recovers after eliminating the pathogenic factors. However, if the damage persists and a chronic reaction is established, liver fibrosis can develop into cirrhosis, which may eventually lead to loss of liver function and potential loss of reversibility. At this stage, if the pathogenic factors are not withdrawn, the patient is at risk of developing advanced liver disease and complications, such as liver failure, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and portal hypertension. Abbreviation: CLD, chronic liver disease; NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; HSEC, liver sinusoidal endothelial cell; HSC, hepatic stellate cell; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma.
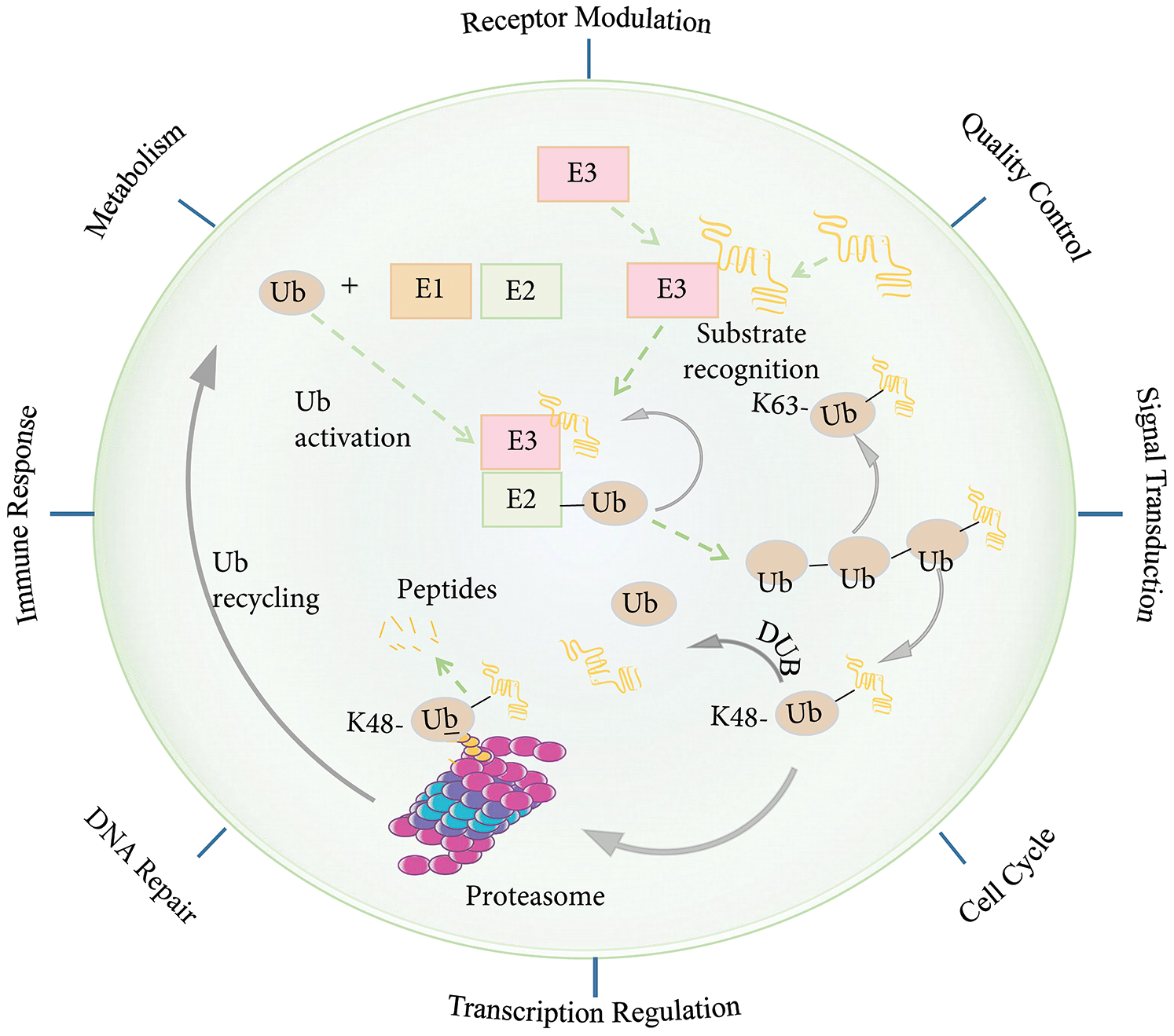
Figure 2: The ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS). Protein degradation by the ubiquitin-proteasome system involves several steps. First, a Ub activating enzyme (E1) activates ubiquitin (Ub) in an ATP-dependent manner and connects it to the Ub-conjugating enzyme (E2). A Ub ligating enzyme (E3) then mediates the transfer of the activated Ub to the target protein. There are different forms of ubiquitination. For example, K11-/K48 linked polyubiquitin chains generally target substrates for degradation by the 26S proteosome, whereas K63-linked polyubiquitin chains induce receptor modulation, quality control, signal transduction, cell cycle, transcription regulation, immune response, metabolism, and DNA damage repair activation. The process of ubiquitination can be reversed by deubiquitin enzymes (DUBs). Abbreviation: Ub, ubiquitin; E1, Ub activating enzyme; E2, Ub coupling enzyme; E3, Ub ligase; DUB, deubiquitinating enzyme.
Ubiquitin (Ub) is a small 76-amino acid protein and is a member of the Ubl protein. Ubiquitination is reversible and is involved in the main cellular processes that define cellular phenotypes and behaviors. In the cell, deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) offset ubiquitination (Wilson et al., 2015). A variety of proteins containing Ub-binding domains can recognize Ub chains and mediate the downstream effects of the Ub signals (Husnjak and Dikic, 2012; Ramanathan and Ye, 2012). The addition of Ub to a target protein is controlled by the coordinated activities of three types of enzymes: Ub-activating enzymes (E1), Ub-conjugating enzymes (E2), and Ub ligases (E3) (Wilson et al., 2015). First, the C-terminal glycine of Ub is covalently linked to the catalytic cysteine of the E1 enzyme for activation. It is then passed to the E2 Ub-conjugating enzyme to form an E2-Ub thioester. The E2-Ub thioester then coordinates with the E3 Ub ligase to transfer the Ub to the target protein (Wenzel et al., 2011). The most characteristic form of ubiquitination involves a K48-linked poly-Ub chain, which targets the protein in question for processing or degradation by the 26S proteasome. In contrast, the K63-linked poly-Ub chain does not target the protein to the 26S proteasome. Instead, this modification is functionally similar to phosphorylation in that it can regulate multiple signaling events, including nuclear factor (NF)-κB activation (Heride et al., 2014). A substrate can undergo mono-ubiquitination or polyubiquitination through different mechanisms. The diversity of the ubiquitination topology is determined by different E2 and E3 enzyme combinations. The reversible nature of ubiquitination is very important for the termination of signaling events, editing Ub modifications, and Ub recovery (Kulathu and Komander, 2012; Wenzel et al., 2011).
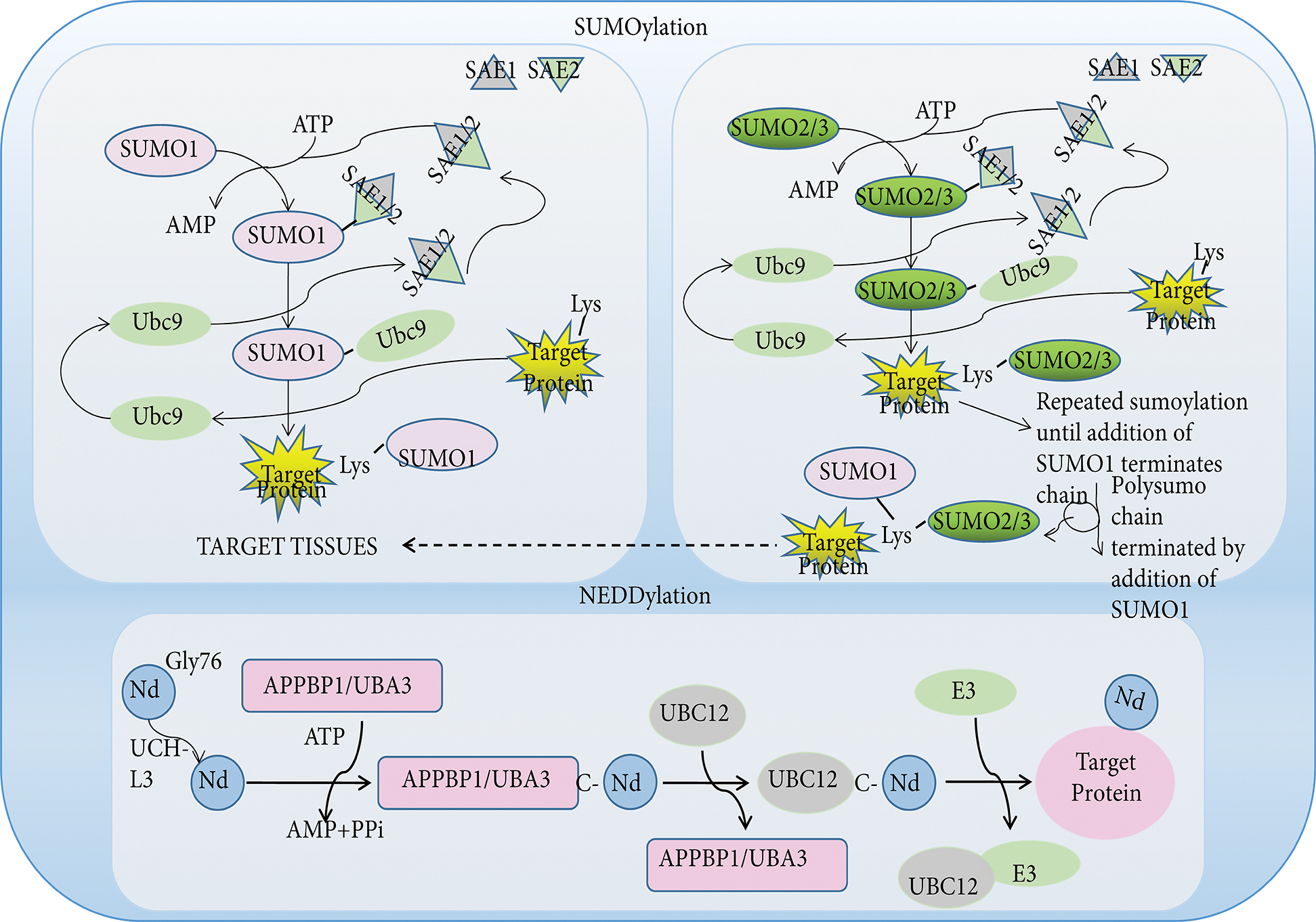
Figure 3: The pathway of SUMOylation and NEDDylation. Like ubiquitin, SUMO and NEDD8 proteins are small protein tags that are conjugated to proteins to modify their function. Three different SUMO proteins, SUMO1, SUMO2, SUMO3, are conjugated to proteins. These SUMO proteins have distinct functions, with SUMO1 conjugated to proteins as a monomer, while SUMO2 and SUMO3 are conjugated to proteins as higher molecular weight polymer with SUMO1 terminating further SUMO addition. SUMO proteins are first activated by adenylation by one enzyme complex (SAE1/SAE2), then transferred to the terminal amino group of a lysine side chain in target proteins. The Nedd8 precursor molecule is activated by the hydrolysis of glycine at 76 by UCH-L3. The mature NEDD8 molecule can form a high-energy thioester bond with the active site of UBA3 cysteine through its C-terminal glycine. Activated Nedd8 is then transferred to UBC12 and forms an isopeptide bond with the lysine residue of the substrate. Abbreviation: NEDD8, neural precursor cell expressed developmentally downregulated-8; SUMO, small ubiquitin-like modifiers; SAE, sumo-activating enzyme.
Ubiquitin-like proteins (Ubls) are a family of small proteins involved in PTMs, whose name is derived from ubiquitin, the first discovered member of the family. In addition to ubiquitin, the human genome encodes at least eight different Ubl families (Cappadocia and Lima, 2018).
Neural precursor cell-expressed developmentally downregulated 8 (NEDD8) is composed of 81 amino acids and is covalently bound to target proteins to participate proteins PTM, in a process known as Neddylation (Dye and Schulman, 2007; Mendoza et al., 2003). Similar to the multienzyme cascade of ubiquitination, the enzymes involved in the neddylation reaction include Nedd8 activating enzymes 1, Nedd8 conjugating enzymes 2, and Nedd8 ligase enzymes 3. E3 ligase enzymes come from a variety of families, including the Cullin-Ring family and the non-Cullin Hect family. However, neddylation is mainly linked to Cullin-Ring family C-terminal residues, thereby activity Cullin activities and regulating target protein ubiquitination levels (Dye and Schulman, 2007; Rabut and Peter, 2008).
Small ubiquitin-related modifier (SUMO) is a highly conserved post-translational modification protein found in eukaryotes (Cappadocia and Lima, 2018). To date, at least five SUMO isoforms have been identified, including SUMO1, SUMO2, SUMO3, SUMO4, and SUMO5 (Pichler et al., 2017). All SUMO proteins undergo the same enzymatic catalysis of binding and dissociating with the substrate. SUMOylation is achieved through the cooperative action of three enzymes: ubiquitin-activating enzyme (E1), ubiquitin-transferring enzyme (E2), and ubiquitin ligase (E3). Specifically, the E1 activating enzyme catalyzes the formation of thioester bonds between the SUMO active cysteine and UBA2 in an ATP-dependent manner and subsequently transfers to the E2 binding enzyme in order to form E2-SUMO thioesters. The E3 ligase then recruits E2-SUMO thioesters and substrates to form complexes to increase specificity (Dohmen, 2004; Gareau and Lima, 2010). However, the E2 enzyme can specifically recognize SUMO and bind it to the substrate without E3 ligase action (Hoeller et al., 2007). Furthermore, SUMOylation may also influence ubiquitination and protein stability indirectly.
NAFLD etiology and pathophysiology
NAFLD is one of the most important public health issues worldwide in the 21st century. In recent years, with the acceleration of urbanization and changes in people’s lifestyles and diet, the incidence of NAFLD has rapidly grown. NAFLD is now recognized as the most common form of CLD in adults and children worldwide (Nobili et al., 2016; Perumpail et al., 2017). NAFLD occurs as the result of a combination of genetic, environmental, and other factors, and its pathogenesis is very complicated. The most well-known the theories of NAFLD development is the “second strike” theory proposed by Day and James (Day and James, 1998). The second-strike theory describes the formation of simple fatty liver in hepatocytes caused by insulin resistance and lipid metabolism disorders are the first attack. The second attack involves the processes of oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation damage caused by various means, leading to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, liver fibrosis, and fatty cirrhosis (Koyama and Brenner, 2017).
The forms of NAFLD include simple fatty liver and NASH caused by liver lipid accumulation, and typical pathological features vary based on the underlying pathogenesis. Studies have shown that simple fatty liver is a benign disease, but NASH (involving hepatocellular injury and inflammatory responses) can progress to more severe conditions, including liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, or liver cancer (Brown and Kleiner, 2016). Although several drugs are being evaluated for NASH treatment, none have yet been approved.
Ubiquitination involves Ub activation (E1), binding (E2), ligation (E3), and various eukaryotic physiological processes are regulated by the continuous action of the three types that mediate these steps. Over the past few decades, extensive studies have been conducted on PTMs, particularly Ub-mediated PTMs, and their roles in the development and progression of NAFLD (Tab. 1).
E3 Ub ligases are important across the entire UPS. Therefore, many studies have explored the role of various E3 Ub ligases in NAFLD and their potential mechanisms of action. A recent study showed that tripartite motif 8 (TRIM8), an E3 Ub ligase, can directly bind to and ubiquitinate transforming growth factor β-activated kinase 1 (TAK1) to promote its phosphorylation and the activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)/p53 and NF-κB signaling. In mice, this exacerbates NASH and complications associated with a high-fat diet (HFD) and genetic defects (ob/ob) (Yan et al., 2017). In a study of obese mice, upregulated KCTD17 (which is involved in ubiquitination) in the liver binds phosphorylated PHLPP2 and leads to its degradation, causing lipogenesis regulatory gene upregulation and promotion of hepatic steatosis (Kim et al., 2017). The three PPAR subtypes, PPARα, PPARγ, and PPARβ/δ, play integral roles in inflammation and metabolic signal network integration, and they have been widely investigated as targets for the treatment of metabolic diseases (Gross et al., 2016). Several E3 Ub ligases are involved in PPARγ polyubiquitination during fat differentiation (Kim et al., 2013; Li et al., 2016; Watanabe et al., 2015). Additionally, the MDM2 E3 Ub ligase can interact with PPARα and regulate its transcriptional activity at the cellular level (Gopinathan et al., 2009). In recent in vivo and in vitro experiments, progestin and adipoQ receptor 3 (PAQR3) were found to promote PPARα HUWE1 E3 Ub ligase-mediated ubiquitination to negatively regulating PPARα. Moreover, loss of PAQR3 alleviated hepatic steatosis in HFD-fed mice (Zhao et al., 2018). In the liver, insulin-induced gene (Insig) proteins negatively regulate sterol regulatory element-binding protein (SREBP)-1C-induced lipid synthesis, and AMPK regulates energy metabolism in response to changes in physiological and nutritional status. Han et al. (2019) found that Insig protein stability involves Thr222 phosphorylation by AMPK and that this phosphorylation prevents the E3 Ub ligase glycoprotein 78 (GP78) from ubiquitinating Insig proteins and causing their degradation. Thus, Insig proteins can negatively regulate SREBP-1C and lipid synthesis-related gene expression (Han et al., 2019). Additionally, knockout of the MKRN1 E3 Ub ligase can reverse NAFLD by preventing AMPK ubiquitination to allow AMPK activation, thereby promoting glucose consumption and inhibiting lipid accumulation (Lee et al., 2018). Several recent studies have focused on Parkin, a component of the multiprotein E3 Ub ligase complex that is associated with liver lipid accumulation. Earlier studies reported that Parkin knockout in mice prevented liver lipid accumulation by inhibiting β-catenin degradation (Lee et al., 2019). Similarly, in HFD-fed mice, Parkin 2 knockout protected against diet-induced obesity by increasing AMPK activation and improving insulin sensitivity in the liver (Edmunds et al., 2019).
E3 Ub ligases and DUBs play important roles in proteolysis and assembly via protein ubiquitination and deubiquitination, respectively. In the highly dynamic process of ubiquitination metabolism, DUBs catalyze the removal of ubiquitin from target proteins. Relatively few recent studies have examined the role of DUBs in NAFLD. Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 10 (USP10) is associated with environmental stress responses (Takahashi et al., 2013), tumor growth (Lin et al., 2013), inflammation (Niu et al., 2013), and cell metabolism (Deng et al., 2016). USP10 expression is significantly reduced in patients with NAFLD, obese mice, and palmitate-treated hepatocytes (Luo et al., 2018). Furthermore, USP10 overexpression significantly inhibits metabolic dysfunction in mice by inhibiting the ubiquitination and degradation of sirtuin 6 (SIRT6). This ameliorates hepatic steatosis and inhibits the development of NAFLD in HFD-fed ob/ob mice (Luo et al., 2018). Additionally, ubiquitin-specific protease 14 (USP14) is a DUB that is essential for the protease/antiprotease balance. USP14 can directly interact with and enhance the stability of fatty acid synthase (FAS), which plays an important role in liver steatosis (Liu et al., 2018). Liu et al. (2019) reported that liver-specific knockout of USP14 in obese mice eliminated the effect of ER stress on glucose metabolism and improved hyperglycemia and glucose tolerance. USP14 was proposed as a potential therapeutic target for obesity. In conclusion, Ubl-PTMs play a variety of roles in fatty acid oxidation, synthesis, oxidative stress, and insulin resistance, which are pivotal in the development and progression of NAFLD. These insights reveal many opportunities for the development of relevant drugs.
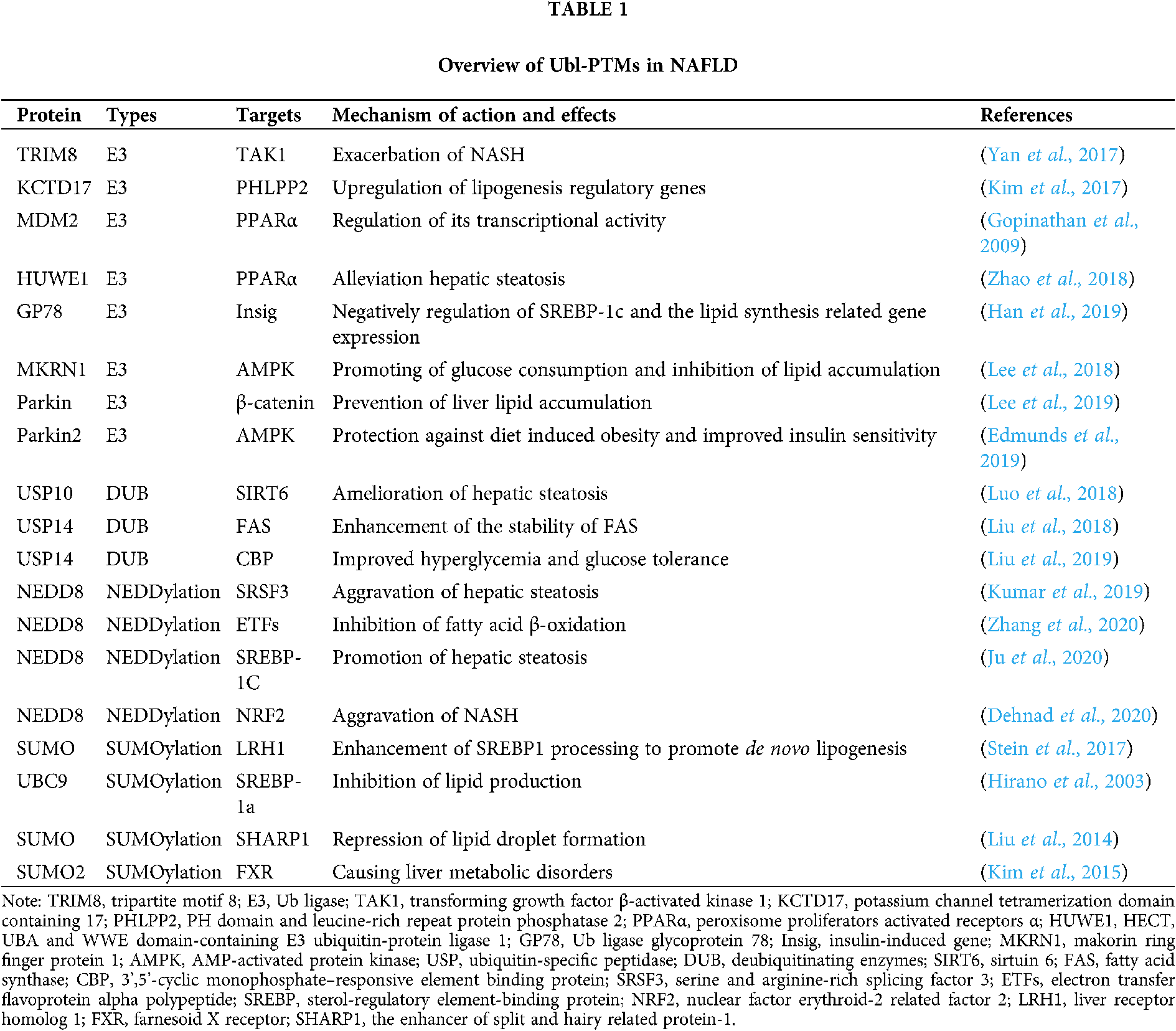
NEDD8 and SUMO-mediated PTMs in NAFLD
Ubl proteins are a small family of proteins including NEDD8 and SUMO, which are involved in ubiquitin-mediated PTMs. The relevance of NEDD8 and SUMO in NAFLD has been extensively studied (Tab. 1). For example, SRSF3 degradation via lysin11 neddylation partially contributes to the aggravation of hepatic steatosis and prevention of SRSF3 degradation in vivo to protect mice from NAFLD (Kumar et al., 2019). Furthermore, another study revealed that mouse models with liver-specific deficiency of NEDD8 or of ubiquitin-like modifier activating enzyme 3 (UBA3), which inhibits electron transfer flavoprotein alpha polypeptide (ETF), exhibit neonatal death with spontaneous fatty liver. This occurs through the inability of impaired ETFs, stability and inhibition of fatty acid β-oxidation (Zhang et al., 2020). Recently, it was reported that neddylation of SREBP-1c regulated by the human homolog of mouse double minute 2 (HDM2) competes with its ubiquitination and stabilizes SREBP-1c protein levels, eventually promoting hepatic steatosis (Ju et al., 2020). Additionally, exposure to high AGEs promotes an AGER1/RAGE imbalance to promote NRF2 degradation via cullin3 neddylation, eventually causing AGER1 downregulation and NASH aggravation (Dehnad et al., 2020).
Similar studies have examined SUMOylation. For example, in the liver, liver receptor homolog 1 (LRH1) is an important triglyceride metabolism regulator. Mice expressing a SUMOylation-defective LRH1 mutant developed NAFLD and early signs of NASH. Mechanistically, this occurred via reduced expression of oxysterol binding protein-like 3 (OSBPL3) and enhanced SREBP1 processing to promote de novo lipogenesis (Stein et al., 2017). Similarly, modification of SREBP-1α at lys123 and lys418 by UBC9, a SUMO-1-conjugating enzyme, reduced its transcription activity and inhibited lipid production (Hirano et al., 2003). Furthermore, SHARP1 SUMOylation can repress lipid droplet formation (Liu et al., 2014). Additionally, Farnesoid X receptor acetylation inhibits SUMO2-mediated farnesoid X receptor (FXR) SUMOylation in obese mice, eventually causing liver metabolic disorders (Kim et al., 2015). These data indicate that neddylation and SUMOylation perform their important roles in NAFLD through competitive combination with ubiquitination substrates.
Therapeutic strategies targeting Ubl-PTMs in NAFLD
Although it was thought that NAFLD was a benign condition, we now know that it may progress, causing more advanced liver injury that is sometimes accompanied by complications such as HCC and liver failure. Additionally, NAFLD has important deleterious effects in patients with diabetes, increasing the risk of cardiovascular complications. Many recent studies have explored new drugs for treating liver disease, such as NAFLD (Fig. 4).
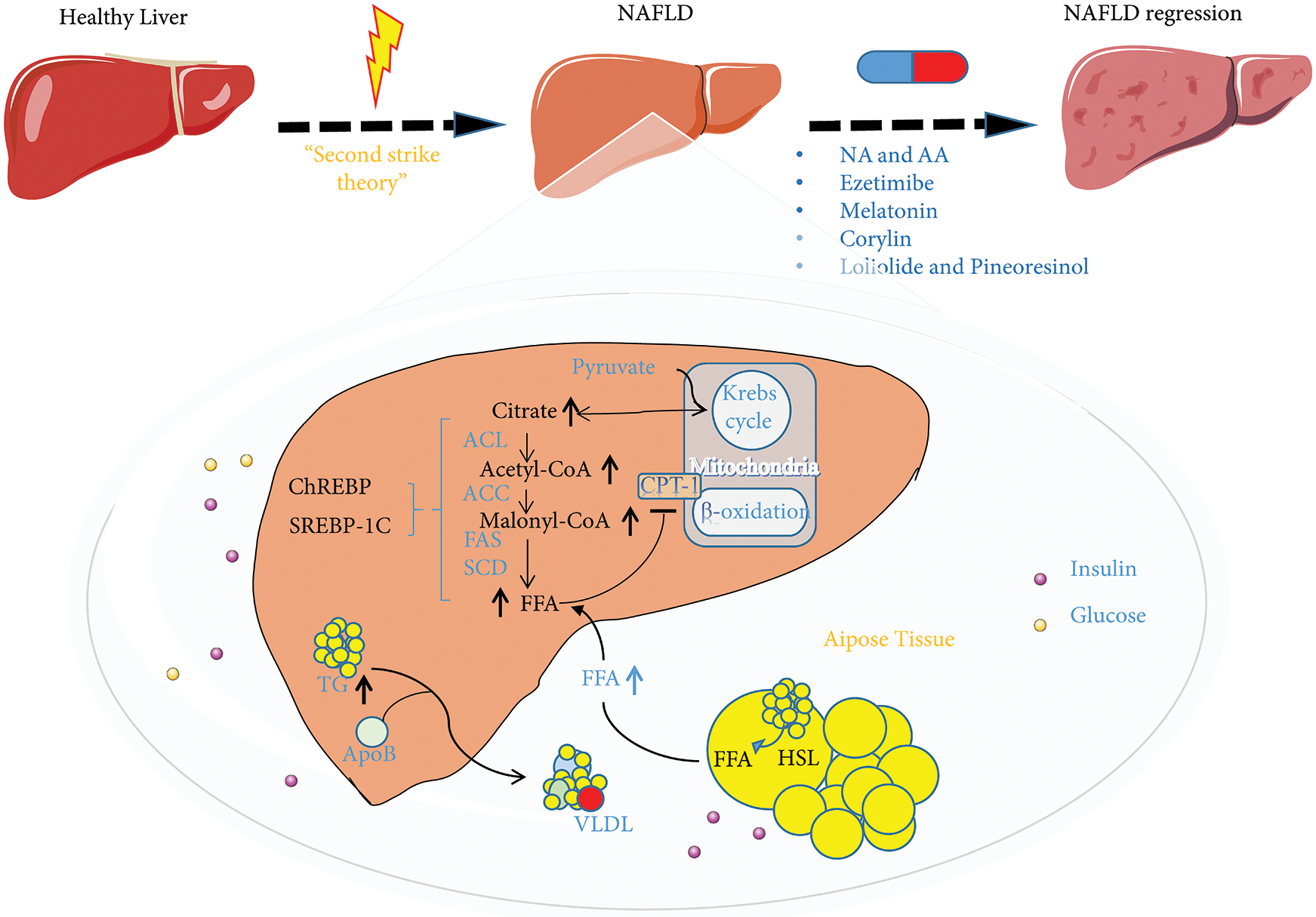
Figure 4: The ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) and inhibitors in regulating nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) metabolism. NAFLD is considered to be the result of metabolic disorders. Lipid metabolism disorders are caused by one or more abnormalities in the liver that disrupt the regulation of fatty acid absorption mediated by CD36 and LDLR, synthesis mediated by SREBP1, ChREBP, SCD, and FAS, β-oxidation mediated by CPT-1, and the secretion of very-low-density lipoprotein (ApoB). Nicotinic acid and arachidonic acid, ezetimibe, melatonin, corylin, loliolide, and pineoresinol supplementation can restore the state of lipid metabolism disorders. Abbreviation: NA, nicotinic acid; AA, arachidonic acid; ACL, ATP citrate lyase; ACC, acetyl CoA carboxylase; FAS, fatty acid synthetase; SCD, stearoyl CoA desaturase; HSL, hormone-sensitive lipase; LDLR, low-density lipoprotein receptor; SREBP1, sterol-regulatory element-binding proteins; CPT-1, carnitine palmitoyltransferase1; ChREBP, carbohydrate response element-binding protein.
Nicotinic acid (NA), a naturally occurring form of vitamin B3, is a precursor of NAD+ and its analog NADP, both of which play vital roles in energy metabolism (Godin et al., 2012). In addition to being a nutritional factor, NA has been used for decades as a broad-spectrum lipid-regulating agent, and it was the first lipid-regulating agent identified for the prevention of cardiovascular disease (Karpe and Frayn, 2004). Recent studies have reported the effect of NA dietary supplementation on the development of the fatty liver. NA supplementation significantly increased hepatic levels of total NAD, NAD+, NADH, cytochrome P450 4A1 (CYP4A1), and acyl-CoA oxidase 1, while reducing the level of FAS and the CYP4A1 ubiquitination. Nevertheless, NA supplementation clearly increased fatty acid oxidation and decreased de novo fatty acid formation in the liver, which can improve fatty liver (Li et al., 2014).
Lysimachia vulgaris (LV) is a medicinal plant traditionally used to treat gastrointestinal conditions, including diarrhea and dysentery, and for hemostasis and wound sterilization (Kim et al., 2019). Recently, in HFD-fed mice, LV extract reduced fat metabolism and restored liver function to control levels. Two LV extract compounds, loliolide and pinoresinol, were identified in the dichloromethane fraction and significantly reduced the expression of lipogenic factors. Importantly, these compounds inhibit fat production by enhancing ubiquitination to increase the degradation of liver X receptors (LXRs). Thus, loliolide and pinoresinol are potential therapeutic candidates for NAFLD as they increase LXR ubiquitination and reduce fat production (Kim et al., 2019).
Ezetimibe can treat hypercholesterolemia by inhibiting cholesterol absorption (Altmann et al., 2004). Long-term combination therapy involving ezetimibe and acarbose significantly increased hepatic expression of microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTP) and PPARα compared to the monotherapies (Nozaki et al., 2009). Recently, in a laboratory NAFLD model, ezetimibe inhibited NAFLD development by reducing hepatic reactive oxygen species production and preventing MTP ubiquitination and degradation by reducing S-phase kinase-associated protein 2 (SKP2) E3 Ub ligase and cell division cycle protein 20 (CDC20) levels and promoting hepatic lipid release (Wang et al., 2014).
Melatonin (N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine) is closely related to glucose and lipid metabolism (Pan et al., 2006; Yin et al., 2018). Recent research has revealed the role of melatonin in the pathogenesis and development of NAFLD. In the HFD-induced NAFLD mouse model, melatonin activates the β-arrestin 1 scaffold protein, allowing it to bind to apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) and inhibit ASK1 deubiquitination by tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors (TRAFs). In this manner, melatonin protects against the development of NAFLD (Li et al., 2019).
Other research has shown that arachidonic acid can selectively decrease the ACSL4 protein levels in hepatocytes by increasing its ubiquitination (Kan et al., 2014). Considering the important role of ACSL4 in fatty acid metabolism regulation, arachidonic acid is considered an attractive therapeutic agent for NAFLD, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic syndrome, and further studies are needed. In a mice experiment, the selective HSP90β inhibitor, corylin, specifically promoted mature SREBP ubiquitination and proteasome degradation through the AKT-GSK3β- FBW37 pathway, reducing the lipid content of hepatocytes (Zheng et al., 2019). Selective HSP90β inhibitors, such as corylin, may be useful for treating metabolic diseases.
Nonalcoholic Liver Fibrosis Etiology and Pathophysiology
Liver injury can lead to steatosis and inflammation, and further activation of HSCs often leads to the development of nonalcoholic liver fibrosis. Liver fibrosis is a reversible wound healing response to various chronic liver injuries. Liver fibrosis is characterized by excessive extracellular matrix protein deposition and structural disruption of the liver (Hernandez-Gea and Friedman, 2011). HSCs are the main cell source of matrix components and play a vital role in the development and maintenance of liver fibrosis (Novo et al., 2014; Puche et al., 2013). HSCs can be transformed from static cells, which are rich in vitamin A, into highly proliferative myofibroblasts, which are the key to stress fibers accumulation and thus contribute to the development of fibrosis (Friedman, 2008). Although liver fibrosis is reversible (Fallowfield, 2011), and patients usually recover after the pathogenic factors are eliminated, if the damage persists and a chronic reaction is established, cirrhosis can develop (Yoon et al., 2016). At this stage, if the pathogenic factors are not eliminated, the patient is at risk of developing advanced liver disease and complications, including portal hypertension, hepatic failure, and HCC (Parola and Pinzani, 2019; Yoon et al., 2016), which are major causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide (Seki and Brenner, 2015). Basic research over the past two decades has provided many clues to explain the cellular and molecular mechanisms of liver fibrosis and has led to the development of anti-fibrosis therapies.
Ub-mediated PTMs in nonalcoholic liver fibrosis
Ubiquitination is associated with the pathogenesis of multiple diseases in humans, including nonalcoholic liver fibrosis. In recent years, several studies have described changes related to Ub cascade intermediates during nonalcoholic liver fibrosis and how targeting the specific enzymes that mediate Ub-mediated PTMs can improve fibrosis, mainly in the liver.
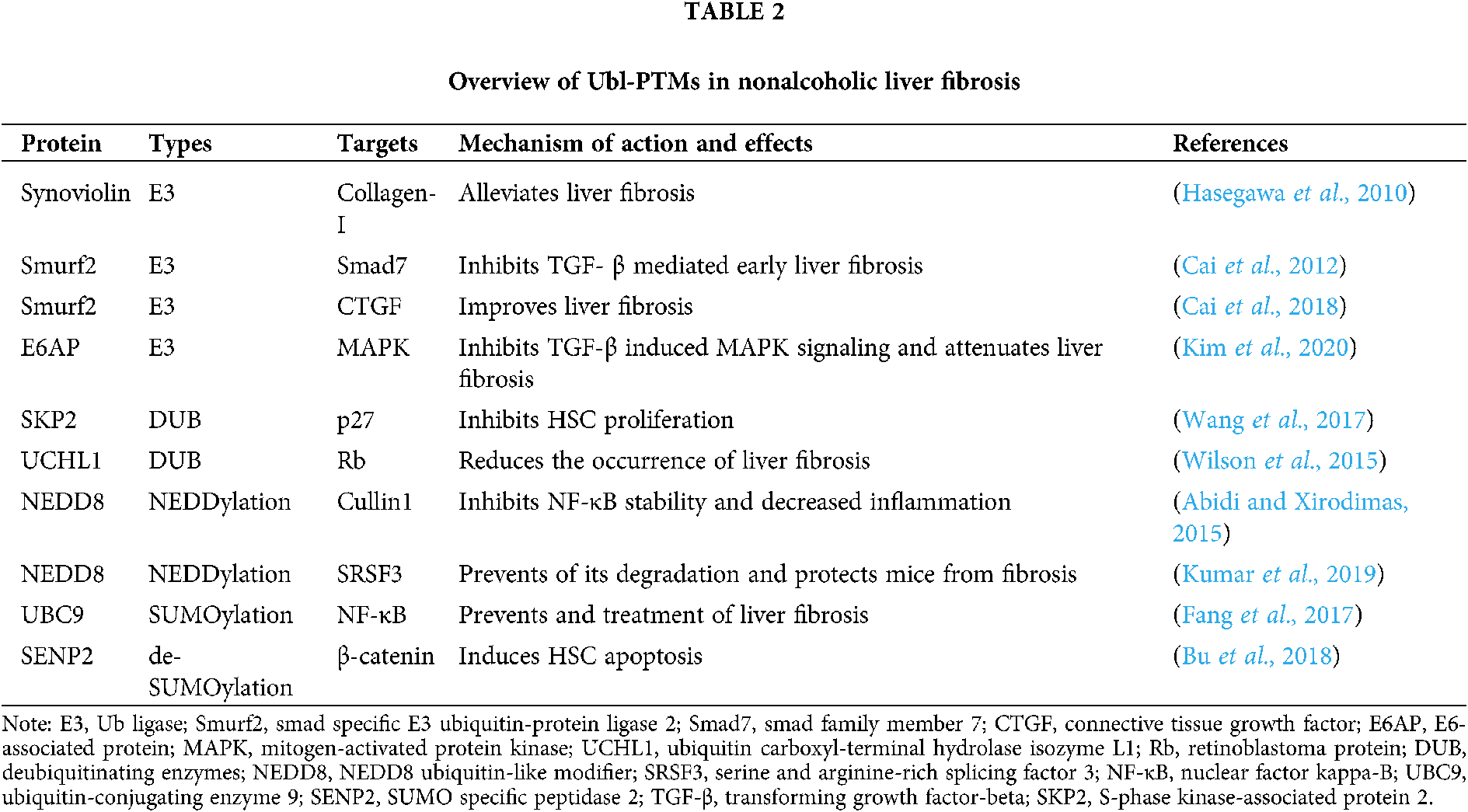
Ub is a marker of nonalcoholic liver fibrosis, often being detected at the border of, or within, the fibrous matrix (Banner et al., 2000; Guy et al., 2012). Ubiquitination in liver fibrosis has been studied by many researchers (Tab. 2). For example, the synoviolin E3 Ub ligase is closely related to collagen I maturation, and reducing synoviolin expression can help to alleviate liver fibrosis (Hasegawa et al., 2010). The Smurf2 E3 Ub ligase is homologous to the E6-associated protein (E6AP) C-terminus (HECT)-type E3 Ub ligase and regulates transforming growth factor (TGF)-β signaling via the UPS. Cai et al., (2012) found that Smurf2 interacts with the Smad7 adaptor protein to mediate ubiquitination-dependent degradation of TGF-β type I receptor (TβRI) thereby inhibiting TGF-β-mediated early liver fibrosis. In another study, Smurf2 overexpression in the liver improved liver fibrosis by inhibiting connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) (Cai et al., 2018). Moreover, the role of the E6AP E3 Ub ligase in cell processes such as proliferation and stress has been extensively studied. In particular, miR-302c downregulation in HSCs leads to TGF-β-induced E6AP upregulation, E6AP inhibits TGF-β-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling, thereby attenuating liver fibrosis (Kim et al., 2020). Recent studies have also found that co-culture of mesenchymal stem cells with HSCs can inhibit HSC proliferation and promote HSC apoptosis by reducing SKP2 E3 Ub ligase levels, thereby reducing p27 ubiquitination and increasing p27 stability (Wang et al., 2017). Additionally, Wilson et al. (2015) showed that pharmacological inhibition of ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase isozyme L1 (UCHL1) in CCl4-treated and bile duct-ligated mice or in vitro UCHL1 knockdown in cultured HSCs reduces the occurrence of liver fibrosis. These convincing findings related to ubiquitination in nonalcoholic liver fibrosis have prompted researchers to further evaluate the roles of Ub-mediated PTMs in nonalcoholic liver fibrosis.
NEDD8 and SUMO-mediated PTMs in nonalcoholic liver fibrosis
The relevance of neddylation and SUMOylation in non-alcoholic liver fibrosis and in the development of treatments for nonalcoholic liver fibrosis have been extensively studied (Tab. 2). Zubite-Franco et al. (2016) described for the first time the increase in the neddylation proteome in patients with liver fibrosis and in mouse models of liver fibrosis induced by CCl4 and bile duct ligation (Zubiete-Franco et al., 2016). In these mouse models, neddylation inhibition leads to decreased inflammation, which can partly be explained by the lack of cullin-1 NEDDylation. Cullin-1 is a component of SCFβ-TrCP (an E3 Ub ligase complex), and lack of cullin-1 nedd-ylation means that the complex cannot ubiquitinate and degrade IKB. This promotes NF-κB stability in the cytoplasm (Abidi and Xirodimas, 2015). Consistent with this evidence, other researchers have recently shown that in vivo inhibition of the serine-rich splicing factor 3 (SRSF3) neddylation and the resultant prevention of its degradation protect mice from liver fibrosis (Kumar et al., 2019).
SUMOylation is a highly dynamic process that enables rapid global changes in the SUMOylation state of the proteome in response to both internal and external stimuli (Psakhye and Jentsch, 2012; Yang et al., 2012). A recent study reported that UBC9, the only identified E2 SUMO-conjugating enzyme, is a potential therapeutic target for the prevention and treatment of liver fibrosis (Fang et al., 2017). Another study used the de-SUMOylation enzyme SENP2 as a key protein to induce HSC apoptosis via Wnt/β-catenin signaling inhibition, thereby reducing CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in mice (Fang et al., 2017). Various members of the TGF-β/Smad canonical pathway, which is common to fibrotic processes, are SUMOylated (Bu et al., 2018), although no specific research has been conducted on the liver. Overall, neddylation and SUMOylation are highly dynamic processes that have beneficial and pathological effects on cell physiology depending on the protein substrate, cell type, and environment.
Therapeutic strategies targeting Ubl-PTMs in nonalcoholic liver fibrosis
Over the past few decades, our increasing understanding of the role of Ubl-PTMs in disease has led to the development of many therapeutic agents related to these modifications (Hendriks and Vertegaal, 2016; Liu et al., 2016; Veggiani et al., 2019; Wertz and Murray, 2019; Zhou et al., 2017). However, only some of these agents have been tested in nonalcoholic liver fibrosis (Fig. 5).
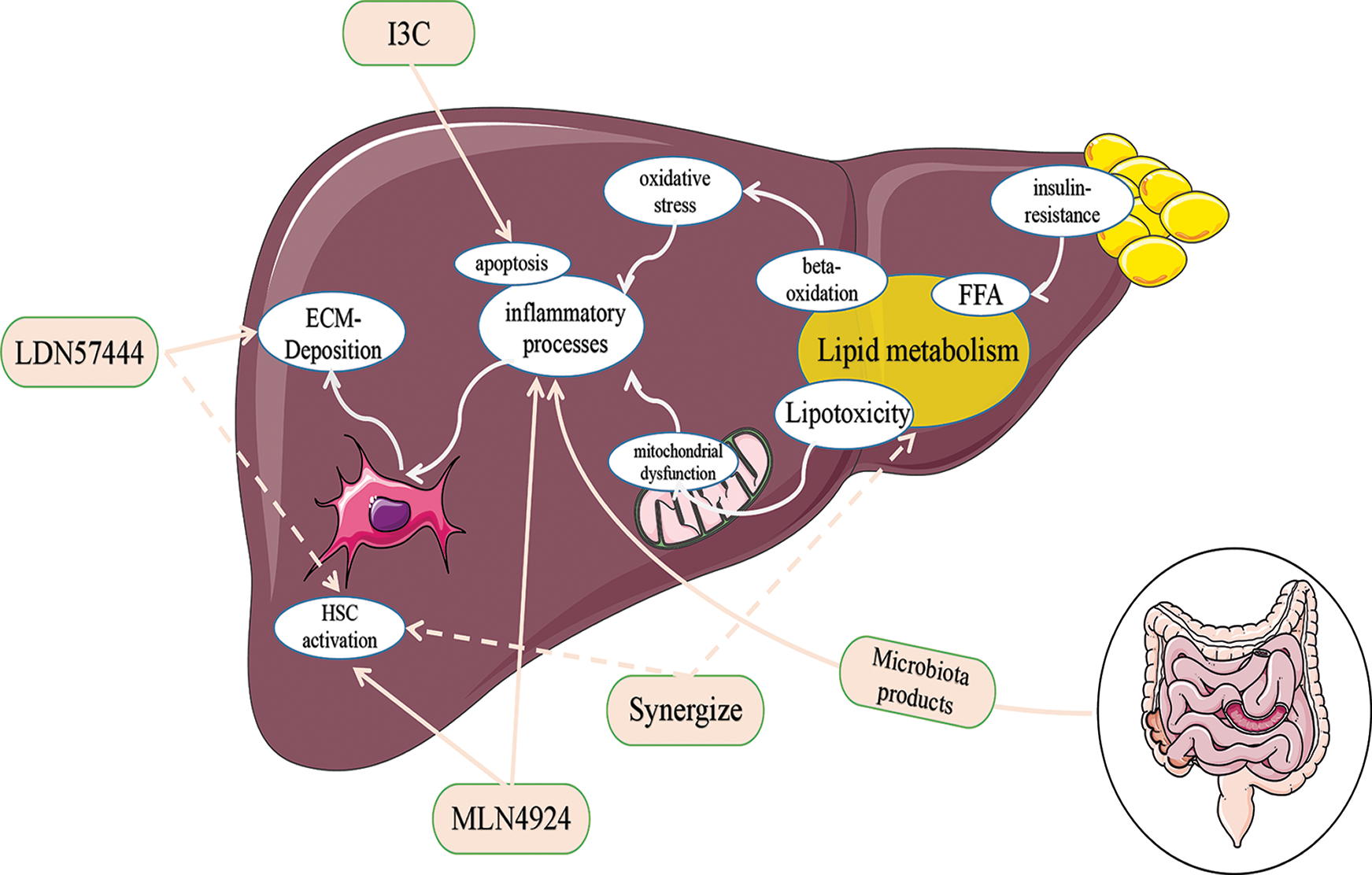
Figure 5: Pharmacological inhibitors of the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) and targets for nonalcoholic liver fibrosis.
Liver fibrosis is an excessive wound healing response to various chronic liver injuries and is characterized by excessive extracellular matrix protein deposition. Hepatic stellate cells (HCSs) are the main cell source of matrix components and can be activated by multiple factors, including lipotoxicity, oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and inflammation, and plays a vital role in the development and maintenance of liver fibrosis. LDN57444, MLN4924, I3C, and synergize supplementation can inhibit HSC activation and improve ECM-deposition, respectively, by acting on different influencing factors. Abbreviation: I3C, Indole-3-Carbinol; ECM, extracellular matrix; FFA, free fatty acids; HSC, hepatic stellate cell.
Furthermore, treatment strategies related to neddylation and SUMOylation in nonalcoholic liver fibrosis have been evaluated. Preclinical studies conducted in mouse models have shown that MLN4924 (also known as pevonedistat), a small-molecule inhibitor of neddylation mediated by NEDD8-activating enzyme E1 regulatory subunit (NAE1), can reverse liver fibrosis (Li et al., 2017). Additionally, recent research has investigated the combination of a SUMOylation inhibitor and FXR agonist obeticholic acid (OCA) for the treatment of liver fibrosis. Using a SUMOylation inhibitor makes the FXRs responsive to OCA and leads to perilipin-1 upregulation. This stabilizes lipid droplets and enhances the efficacy of OCA against HSC activation and fibrosis. The combination therapy of a SUMOylation inhibitor and OCA can significantly reduce liver fibrosis induced by CCL4, bile duct ligation, and more importantly, NASH (Zubiete-Franco et al., 2016).
Ubl-PTMs regulate various physiological processes in eukaryotic cells and have pivotal roles in NAFLD and nonalcoholic liver fibrosis. Liver injury can cause steatosis and inflammation, and further activation of HSCs often leads to the development of nonalcoholic liver fibrosis. The patient with NAFLD is at risk of developing advanced liver disease and complications, such as liver failure, HCC, and portal hypertension. In recent years, research exploring the role of Ubl-PTMs in NAFLD progression has made significant progress, and many therapeutic agents related to these modifications have been developed.
In this review, we summarize the important roles of ubiquitination, SUMOylation, and NEDDylation of three Ubl-PTMs in NAFLD and nonalcoholic liver fibrosis. The individual and combined effects of these processes on substrate proteins are of great significance for disease development. Ubl-PTMs can be used both as drug targets and as promising prognostic biomarkers. We believe that the development of Ubl-related drugs for NAFLD progression is a promising area of research.
Availability of Data and Materials: Not applicable.
Author Contribution: Conception and design of the work (Yongmin Yan), Funding (Yongmin Yan and Youwen Tan), Fuji Yang wrote the manuscript, Fuji Yang & Yan Huang produced the figures and tables. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics Approval: Not applicable.
Funding Statement: This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81670549), Jiangsu Provincial Key Research and Development Program (BE2020775), Zhenjiang Key Research and Development Program (SH2020002), Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD), 333 Talent Project of Jiangsu Province, Six Talent Peaks Project of Jiangsu Province and the Backbone Teacher of the Blue Project in Jiangsu Province.
Conflicts of Interest: Fuji Yang, Yan Huang, Youwen Tan, and Yongmin Yan have no conflict to declare.
Abidi N, Xirodimas DP (2015). Regulation of cancer-related pathways by protein NEDDylation and strategies for the use of NEDD8 inhibitors in the clinic. Endocrine-Related Cancer 22: T55–T70. DOI 10.1530/ERC-14-0315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Adams LA, Lindor KD (2007). Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Annals of Epidemiology 17: 863–869. DOI 10.1016/j.annepidem.2007.05.013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Altmann SW, Davis HR, Murgolo N, Graziano MP (2004). Niemann-Pick C1 Like 1 protein is critical for intestinal cholesterol absorption. Science 303: 1201–1204. DOI 10.1126/science.1093131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Banner BF, Savas L, Tortorelli K, Bonkovsky HL (2000). Ubiquitin as a marker of cell injury in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. American Journal of Clinical Pathology 114: 860–866. DOI 10.1309/4UBB-BF78-F55V-50KA. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Brown GT, Kleiner DE (2016). Histopathology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Metabolism-clinical and Experimental 65: 1080–1086. DOI 10.1016/j.metabol.2015.11.008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Bu FT, Chen Y, Yu HX, Chen X, Yang Y, Pan XY, Wang Q, Wu YT, Huang C, Meng XM, Li J (2018). SENP2 alleviates CCl4-induced liver fibrosis by promoting activated hepatic stellate cell apoptosis and reversion. Toxicology Letters 289: 86–98. DOI 10.1016/j.toxlet.2018.03.010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Cai Y, Huang G, Ma L, Dong L, Chen S, Shen X, Zhang S, Xue R, Sun D, Zhang S (2018). Smurf2, an E3 ubiquitin ligase, interacts with PDE4B and attenuates liver fibrosis through miR-132 mediated CTGF inhibition. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta-Molecular Cell Research 1865: 297–308. DOI 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2017.10.011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Cai Y, Zhou CH, Fu D, Shen XZ (2012). Overexpression of Smad ubiquitin regulatory factor 2 suppresses transforming growth factor-beta mediated liver fibrosis. Journal of Digestive Diseases 13: 327–334. DOI 10.1111/j.1751-2980.2012.00592.x. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Cappadocia L, Lima CD (2017). Ubiquitin-like protein conjugation: Structures, chemistry, and mechanism. Chemical Reviews 118: 889–918. DOI 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Day CP, James OF (1998). Steatohepatitis: A tale of two hits? Gastroenterology 114: 842–845. DOI 10.1016/S0016-5085(98)70599-2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Dehnad A, Fan W, Jiang JX, Fish SR, Li Y (2020). AGER1 downregulation associates with fibrosis in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and type 2 diabetes. Journal of Clinical Investigation 130: 4320–4330. [Google Scholar]
Deng M, Yang X, Qin B, Liu T, Zhang H, Guo W, Lee SB, Kim JJ, Yuan J, Pei H, Wang L, Lou Z (2016). Deubiquitination and Activation of AMPK by USP10. Molecular Cell 61: 614–624. DOI 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.01.010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Dohmen RJ (2004). SUMO protein modification. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1695: 113–131. DOI 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2004.09.021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Dye BT, Schulman BA (2007). Structural mechanisms underlying posttranslational modification by ubiquitin-like proteins. Annual Review of Biophysics and Biomolecular Structure 36: 131–150. DOI 10.1146/annurev.biophys.36.040306.132820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Edmunds LR, Huckestein BR, Kahn M, Zhang D, Chu Y, Zhang Y, Wendell SG, Shulman GI, Jurczak MJ (2019). Hepatic insulin sensitivity is improved in high-fat diet-fed Park2 knockout mice in association with increased hepatic AMPK activation and reduced steatosis. Physiological Reports 7: e14281. DOI 10.14814/phy2.14281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Fallowfield JA (2011). Therapeutic targets in liver fibrosis. American Journal of Physiology–Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology 300: G709–G715. DOI 10.1152/ajpgi.00451.2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Fang SF, Yuan J, Shi Q, Xu T, Fu Y, Wu Z, Guo W (2017). Downregulation of UBC9 promotes apoptosis of activated human LX-2 hepatic stellate cells by suppressing the canonical NF-kappaB signaling pathway. PLoS One 12: e0174374. DOI 10.1371/journal.pone.0174374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Friedman SL (2008). Hepatic stellate cells: Protean, multifunctional, and enigmatic cells of the liver. Physiological Reviews 88: 125–172. DOI 10.1152/physrev.00013.2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Gareau JR, Lima CD (2010). The SUMO pathway: Emerging mechanisms that shape specificity, conjugation and recognition. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 11: 861–871. DOI 10.1038/nrm3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Giannitrapani L, Soresi M, Bondi ML, Montalto G, Cervello M (2014). Nanotechnology applications for the therapy of liver fibrosis. World Journal of Gastroenterology 20: 7242–7251. DOI 10.3748/wjg.v20.i23.7242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Godin AM, Ferreira WC, Rocha LTS, Ferreira RG, Paiva ALL, Merlo LA, Nascimento EB, Bastos LFS, Coelho MM (2012). Nicotinic acid induces antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects in different experimental models. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior 101: 493–498. DOI 10.1016/j.pbb.2012.02.012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Gopinathan L, Hannon DB, Peters JM, Vanden Heuvel JP (2009). Regulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha by MDM2. Toxicological Sciences 108: 48–58. DOI 10.1093/toxsci/kfn260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Gross B, Pawlak M, Lefebvre P, Staels B (2016). PPARs in obesity-induced T2DM, dyslipidaemia and NAFLD. Nature Reviews Endocrinology 13: 36–49. DOI 10.1038/nrendo.2016.135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Guy CD, Suzuki A, Burchette JL, Brunt EM, Abdelmalek MF, Cardona D, McCall SJ, Belt P, Ferrell LD, Diehl AM (2012). Costaining for keratins 8/18 plus ubiquitin improves detection of hepatocyte injury in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Human Pathology 43: 790–800. DOI 10.1016/j.humpath.2011.07.007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Han YM, Hu Z, Cui A, Liu Z, Ma F, Xue Y, Liu Y, Zhang F, Zhao Z, Yu Y, Gao J, Wei C, Li J, Fang J, Li J, Fan JG, Song BL, Li Y (2019). Post-translational regulation of lipogenesis via AMPK-dependent phosphorylation of insulin-induced gene. Nature Communications 10: 35. DOI 10.1038/s41467-019-08585-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Hasegawa D, Fujii R, Yagishita N, Matsumoto N, Aratani S, Izumi T, Azakami K, Nakazawa M, Fujita H, Sato T, Araya N, Koike J, Tadokoro M, Suzuki N, Nagata K, Senoo H, Friedman SL, Nishioka K, Yamano Y, Itoh F, Nakajima T (2010). E3 ubiquitin ligase synoviolin is involved in liver fibrogenesis. PLoS One 5: e13590. DOI 10.1371/journal.pone.0013590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Hendriks IA, Vertegaal ACO (2016). A comprehensive compilation of SUMO proteomics. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 17: 581–595. DOI 10.1038/nrm.2016.81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Heride C, Urbe S, Clague MJ (2014). Ubiquitin code assembly and disassembly. Current Biology 24: R215–R220. DOI 10.1016/j.cub.2014.02.002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Hernandez-Gea V, Friedman SL (2011). Pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. Annual Review of Pathology: Mechanisms of Disease 6: 425–456. DOI 10.1146/annurev-pathol-011110-130246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Hirano Y, Murata S, Tanaka K, Shimizu M, Sato R (2003). Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins are negatively regulated through SUMO-1 modification independent of the ubiquitin/26 S proteasome pathway. Journal of Biological Chemistry 278: 16809–16819. DOI 10.1074/jbc.M212448200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Hoeller D, Hecker CM, Wagner S, Rogov V, Dotsch V, Dikic I (2007). E3-independent monoubiquitination of ubiquitin-binding proteins. Molecular Cell 26: 891–898. DOI 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.05.014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Husnjak K, Dikic I (2012). Ubiquitin-binding proteins: decoders of ubiquitin-mediated cellular functions. Annual Review of Biochemistry 81: 291–322. DOI 10.1146/annurev-biochem-051810-094654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Ju UI, Jeong DW, Seo J, Park JB, Park JW, Suh KS, Kim JB, Chun YS (2020). Neddylation of sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c is a potential therapeutic target for nonalcoholic fatty liver treatment. Cell Death & Disease 11: 883. DOI 10.1038/s41419-020-2472-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Kan CF, Singh AB, Stafforini DM, Azhar S, Liu J (2014). Arachidonic acid downregulates acyl-CoA synthetase 4 expression by promoting its ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. Journal of Lipid Research 55: 1657–1667. DOI 10.1194/jlr.M045971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Karpe F, Frayn KN (2004). The nicotinic acid receptor-a new mechanism for an old drug. Lancet 363: 1892–1894. DOI 10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16359-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Kim DH, Xiao Z, Kwon S, Sun X, Ryerson D, Tkac D, Ma P, Wu SY, Chiang CM,Zhou E, Xu HE, Palvimo JJ, Chen LF, Kemper B, Kemper JK (2015). A dysregulated acetyl/SUMO switch of FXR promotes hepatic inflammation in obesity. EMBO Journal 34: 184–199. DOI 10.15252/embj.201489527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Kim JH, Park KW, Lee EW, Jang WS, Seo J, Shin S, Hwang KA, Song J (2014). Suppression of PPARγ through MKRN1-mediated ubiquitination and degradation prevents adipocyte differentiation. Cell Death & Differentiation 21: 594–603. DOI 10.1038/cdd.2013.181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Kim JY, Kim KM, Yang JH, Cho SS, Kim SJ, Park SJ, Ahn SG, Lee GH, Yang JW, Lim SC, Kang KW, Ki SH (2020). Induction of E6AP by microRNA-302c dysregulation inhibits TGF-beta-dependent fibrogenesis in hepatic stellate cells. Scientific Reports 10: 512. DOI 10.1038/s41598-019-57322-w. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Kim K, Ryu D, Dongiovanni P, Ozcan L, Nayak S, Ueberheide B, Valenti L, Auwerx J, Pajvani UB (2017). Degradation of PHLPP2 by KCTD17, via a glucagon-dependent pathway, promotes hepatic steatosis. Gastroenterology 153: 1568–1580. DOI 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.08.039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Kim SY, Lee JY, Jhin C, Shin JM, Kim M, Ahn HR, Yoo G, Son YJ, Jung SH, Nho CW (2019). Reduction of hepatic lipogenesis by loliolide and pinoresinol from Lysimachia vulgaris via degrading liver X receptors. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 67: 12419–12427. DOI 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b01488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Koyama Y, Brenner DA (2017). Liver inflammation and fibrosis. Journal of Clinical Investigation 127: 55–64. DOI 10.1172/JCI88881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Kulathu Y, Komander D (2012). Atypical ubiquitylation-the unexplored world of polyubiquitin beyond Lys48 and Lys63 linkages. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 13: 508–523. DOI 10.1038/nrm3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Kumar D, Das M, Sauceda C, Ellies LG, Kuo K, Parwal P (2019). Degradation of splicing factor SRSF3 contributes to progressive liver disease. Journal of Clinical Investigation 129: 4477–4491. DOI 10.1172/JCI127374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Lee DH, Park MH, Hwang CJ, Kim Y, Hwang DY, Han SB, Hong JT (2019). Parkin deficiency prevents chronic ethanol-induced hepatic lipid accumulation through beta-catenin accumulation. Cell Communication and Signaling 17: 299. DOI 10.1186/s12964-019-0424-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Lee MS, Han HJ, Han SY, Kim IY, Chae S, Lee CS, Kim SE, Yoon SG, Park JW, Kim JH, Shin S, Jeong M, Ko A, Lee HY, Oh KJ, Lee YH, Bae KH, Koo SH, Kim JW, Seong JK, Hwang D, Song J (2018). Loss of the E3 ubiquitin ligase MKRN1 represses diet-induced metabolic syndrome through AMPK activation. Nature Communications 9: 675. DOI 10.1038/s41467-018-05721-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Li B, Cong M, Zhu Y, Xiong Y, Jin W, Wan Y, Zhou Y, Ao Y, Wang H (2017). Indole-3-carbinol induces apoptosis of hepatic stellate cells through K63 de-ubiquitination of RIP1 in rats. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry 41: 1481–1490. DOI 10.1159/000470650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Li DJ, Tong J, Li YH, Meng HB, Ji QX, Zhang GY, Zhu JH, Zhang WJ, Zeng FY, Huang G, Hua X, Shen FM, Wang P (2019). Melatonin safeguards against fatty liver by antagonizing TRAFs-mediated ASK1 deubiquitination and stabilization in a beta-arrestin-1 dependent manner. Journal of Pineal Research 67: e12611. [Google Scholar]
Li JJ, Wang R, Lama R, Wang X, Floyd Z, Park E, Liao F (2016). Ubiquitin ligase NEDD4 regulates PPARgamma stability and adipocyte differentiation in 3T3-L1 cells. Scientific Reports 6: 779. DOI 10.1038/srep38550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Li Q, Xie G, Zhang W, Zhong W, Sun X, Jia W, Zhou Z (2014). Dietary nicotinic acid supplementation ameliorates chronic alcohol-induced fatty liver in rats. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 38: 1982–1992. DOI 10.1111/acer.12396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Lin Z, Yang H, Tan C, Li J, Liu Z, Quan Q, Kong S, Ye J, Gao B, Fang D (2013). USP10 antagonizes c-Myc transcriptional activation through SIRT6 stabilization to suppress tumor formation. Cell Reports 5: 1639–1649. DOI 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.11.029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Liu B, Jiang S, Li M, Xiong X, Zhu M, Li D, Zhao L, Qian L, Zhai L, Li J, Lu H, Sun S, Lin J, Lu Y, Li X, Tan M (2018). Proteome-wide analysis of USP14 substrates revealed its role in hepatosteatosis via stabilization of FASN. Nature Communications 9: 373. DOI 10.1038/s41467-018-07185-y. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Liu B, Wang T, Mei W, Li D, Cai R, Zuo Y, Cheng J (2014). Small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) protein-specific protease 1 de-SUMOylates Sharp-1 protein and controls adipocyte differentiation. Journal of Biological Chemistry 289: 22358–22364. DOI 10.1074/jbc.M114.571950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Liu B, Zhang Z, Hu Y, Lu Y, Li D, Liu J, Liao S, Hu M, Wang Y, Zhang D, Chen Y, Qian Q, Lv X, Wu D, Tan M, Hu C, Xiong X, Li X (2019). Sustained ER stress promotes hyperglycemia by increasing glucagon action through the deubiquitinating enzyme USP14. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 116: 21732–21738. DOI 10.1073/pnas.1907288116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Liu S, Long J, Yuan B, Zheng M, Xiao M, Xu J, Lin X, Feng XH (2016). SUMO modification reverses inhibitory effects of Smad Nuclear Interacting Protein-1 in TGF-β responses. Journal of Biological Chemistry 291: 24418–24430. DOI 10.1074/jbc.M116.755850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Luo PC, Qin C, Lu J, Zhang J (2018). Ubiquitin-Specific Peptidase 10 (USP10) inhibits hepatic steatosis, insulin resistance, and inflammation through Sirt6. Hepatology 68: 1786–1803. DOI 10.1002/hep.30062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Marcellin P, Kutala BK (2018). Liver diseases: A major, neglected global public health problem requiring urgent actions and large-scale screening. Liver International 38: 2–6. DOI 10.1111/liv.13682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Mendoza HM, Shen LN, Botting C, Lewis A, Chen J, Ink B, Hay RT (2003). NEDP1, a highly conserved cysteine protease that deNEDDylates Cullins. Journal of Biological Chemistry 278: 25637–25643. DOI 10.1074/jbc.M212948200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Niu J, Shi Y, Xue J, Miao R, Huang S, Wang T, Wu J, Fu M, Wu ZH (2013). USP10 inhibits genotoxic NF-kappaB activation by MCPIP1-facilitated deubiquitination of NEMO. EMBO Journal 32: 3206–3219. DOI 10.1038/emboj.2013.247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Nobili V, Alisi A, Newton KP, Schwimmer JB (2016). Comparison of the phenotype and approach to pediatric vs adult patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 150: 1798–1810. DOI 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.03.009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Novo E, Cannito S, Paternostro C, Bocca C, Miglietta A, Parola M (2014). Cellular and molecular mechanisms in liver fibrogenesis. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics 548: 20–37. DOI 10.1016/j.abb.2014.02.015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Nozaki YC, Fujita K, Terauchi YS, Nakajima A (2009). Long-term combination therapy of ezetimibe and acarbose for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Journal of Hepatology 51: 548–556. DOI 10.1016/j.jhep.2009.05.017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Pan M, Song Y, Xu J, Gan H (2006). Melatonin ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver induced by high-fat diet in rats. Journal of Pineal Research 41: 79–84. DOI 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2006.00346.x. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Parola M, Pinzani M (2019). Liver fibrosis: Pathophysiology, pathogenetic targets and clinical issues. Molecular Aspects of Medicine 65: 37–55. DOI 10.1016/j.mam.2018.09.002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Perumpail BJ, Khan MA, Yoo ER, Cholankeril G, Kim D, Ahmed A (2017). Clinical epidemiology and disease burden of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World Journal of Gastroenterology 23: 8263–8276. DOI 10.3748/wjg.v23.i47.8263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Pichler A, Fatouros C, Lee H, Eisenhardt N (2017). SUMO conjugation-a mechanistic view. Biomolecular Concepts 8: 13–36. DOI 10.1515/bmc-2016-0030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Psakhye I, Jentsch S (2012). Protein group modification and synergy in the SUMO pathway as exemplified in DNA repair. Cell 151: 807–820. DOI 10.1016/j.cell.2012.10.021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Puche JE, Saiman Y, Friedman SL (2013). Hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis. Comprehensive Physiology 3: 1473–1492. [Google Scholar]
Rabut G, Peter M (2008). Function and regulation of protein neddylation. ‘Protein modifications: Beyond the usual suspects’ review series. EMBO Reports 9: 969–976. DOI 10.1038/embor.2008.183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Ramanathan HN, Ye Y (2011). Cellular strategies for making monoubiquitin signals. Critical Reviews in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 47: 17–28. DOI 10.3109/10409238.2011.620943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Seki E, Brenner DA (2015). Recent advancement of molecular mechanisms of liver fibrosis. Journal of Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic Sciences 22: 512–518. DOI 10.1002/jhbp.245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Stein S, Lemos V, Xu P, Demagny H, Wang X, Ryu D, Jimenez V (2017). Impaired SUMOylation of nuclear receptor LRH-1 promotes nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Journal of Clinical Investigation 1: 2. [Google Scholar]
Takahashi M, Higuchi M, Matsuki H, Yoshita M, Ohsawa T, Oie M, Fujii M (2013). Stress granules inhibit apoptosis by reducing reactive oxygen species production. Molecular and Cellular Biology 33: 815–829. DOI 10.1128/MCB.00763-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Veggiani G, Gerpe MCR, Sidhu SS, Zhang W (2019). Emerging drug development technologies targeting ubiquitination for cancer therapeutics. Pharmacology & Therapeutics 199: 139–154. DOI 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2019.03.003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Wang L, Bai G, Chen F (2017). Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells suppress the proliferation of hepatic stellate cells by inhibiting the ubiquitination of p27. Biochemistry and Cell Biology 95: 628–633. DOI 10.1139/bcb-2017-0127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Wang X, Sugimoto K, Ikegami H, Rakugi H (2014). Novel effect of ezetimibe to inhibit the development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Fatty Liver Shionogi mouse. Hepatology Research 44: 102–113. DOI 10.1111/hepr.12092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Watanabe M, Takahashi H, Tanaka KJ, Hatakeyama S (2015). The E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIM23 regulates adipocyte differentiation via stabilization of the adipogenic activator PPARγ. eLife 4: 557. DOI 10.7554/eLife.05615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Wenzel DM, Stoll KE, Klevit RE (2011). E2s: Structurally economical and functionally replete. Biochemical Journal 433: 31–42. DOI 10.1042/BJ20100985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Wertz IE, Murray JM (2019). Structurally-defined deubiquitinase inhibitors provide opportunities to investigate disease mechanisms. Drug Discovery Today: Technologies 31: 109–123. DOI 10.1016/j.ddtec.2019.02.003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Wilson CL, Murphy LB, Leslie J, Kendrick S, French J, Fox CR, Sheerin NS, Fisher A, Robinson JH, Tiniakos DG, Gray DA, Oakley F, Mann DA (2015). Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase 1: A novel functional marker for liver myofibroblasts and a therapeutic target in chronic liver disease. Journal of Hepatology 63: 1421–1428. DOI 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.07.034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Yan FJ, Zhang X, Huang Z, Li H (2017). The E3 ligase tripartite motif 8 targets TAK1 to promote insulin resistance and steatohepatitis. Hepatology 65: 1492–1511. DOI 10.1002/hep.28971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Yang W, Thompson JW, Moseley MA, Paschen W (2011). Analysis of oxygen glucose-deprivation-induced changes in SUMO3 conjugation using SILAC-based quantitative proteomics. Journal of Proteome Research 11: 1108–1117. DOI 10.1021/pr200834f. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Yao J, Liang X, Liu Y, Zheng M (2020). Neddylation: A versatile pathway takes on chronic liver diseases. Frontiers in Medicine 7: 117. DOI 10.3389/fmed.2020.586881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Yin J, Li Y, K. RW, Yin Y (2018). Melatonin reprogramming of gut microbiota improves lipid dysmetabolism in high-fat diet-fed mice. Journal of Pineal Research 65: e12524. DOI 10.1111/jpi.12524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Yoon Y, Friedman SL, Lee YA (2016). Antifibrotic therapies: Where are we now? Seminars in Liver Disease 36: 087–098. DOI 10.1055/s-0036-1571295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Zeng M, Liu W, Hu Y, Fu N (2020). Sumoylation in liver disease. Clinica Chimica Acta 510: 347–353. DOI 10.1016/j.cca.2020.07.044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Zhang X, Zhang YL, Qiu G, Pian L, Guo L, Cao H, Liu J (2020). Hepatic neddylation targets and stabilizes electron transfer flavoproteins to facilitate fatty acid β-oxidation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 4: 5. [Google Scholar]
Zhao ZL, Xu D, Liao L, Chen Y (2018). Hepatic PPARa function is controlled by polyubiquitination and proteasome-mediated degradation through the coordinated actions of PAQR3 and HUWE1. Hepatology 68: 289–303. DOI 10.1002/hep.29786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Zheng ZG, Zhang X, Liu XX, Jin XX, Dai L, Cheng HM, Jing D, Thu PM, Zhang M, Li H, Zhu J, Liu C, Xue B, Li Y, Chen L, Peng C, Zhu W, Wang L, Liu J, Li HJ, Li P, Xu X (2019). Inhibition of HSP90beta improves lipid disorders by promoting mature SREBPs degradation via the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Theranostics 9: 5769–5783. DOI 10.7150/thno.36505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Zhou YJ, Ji CM, Cao M, Guo M, Huang W, Ni W, Meng L, Yang H, Wei J (2017). Inhibitors targeting the SUMOylation pathway: A patent review 2012-2015. International Journal of Molecular Medicine 41: 3–12. [Google Scholar]
Zubiete-Franco I, Fernández-Tussy P, Barbier-Torres L, Simon J, Fernández-Ramos D, Lopitz-Otsoa F, de Davalillo SL, Duce AM, Iruzubieta P, Taibo D, Crespo J, Caballeria J, Villa E, Aurrekoetxea I, Aspichueta P, Varela Rey M, Lu SC, Mato JM, Beraza N, Delgado TC, Martnez Chantar ML (2016). Deregulated neddylation in liver fibrosis. Hepatology 65: 694–709. DOI 10.1002/hep.28933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 | This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. |