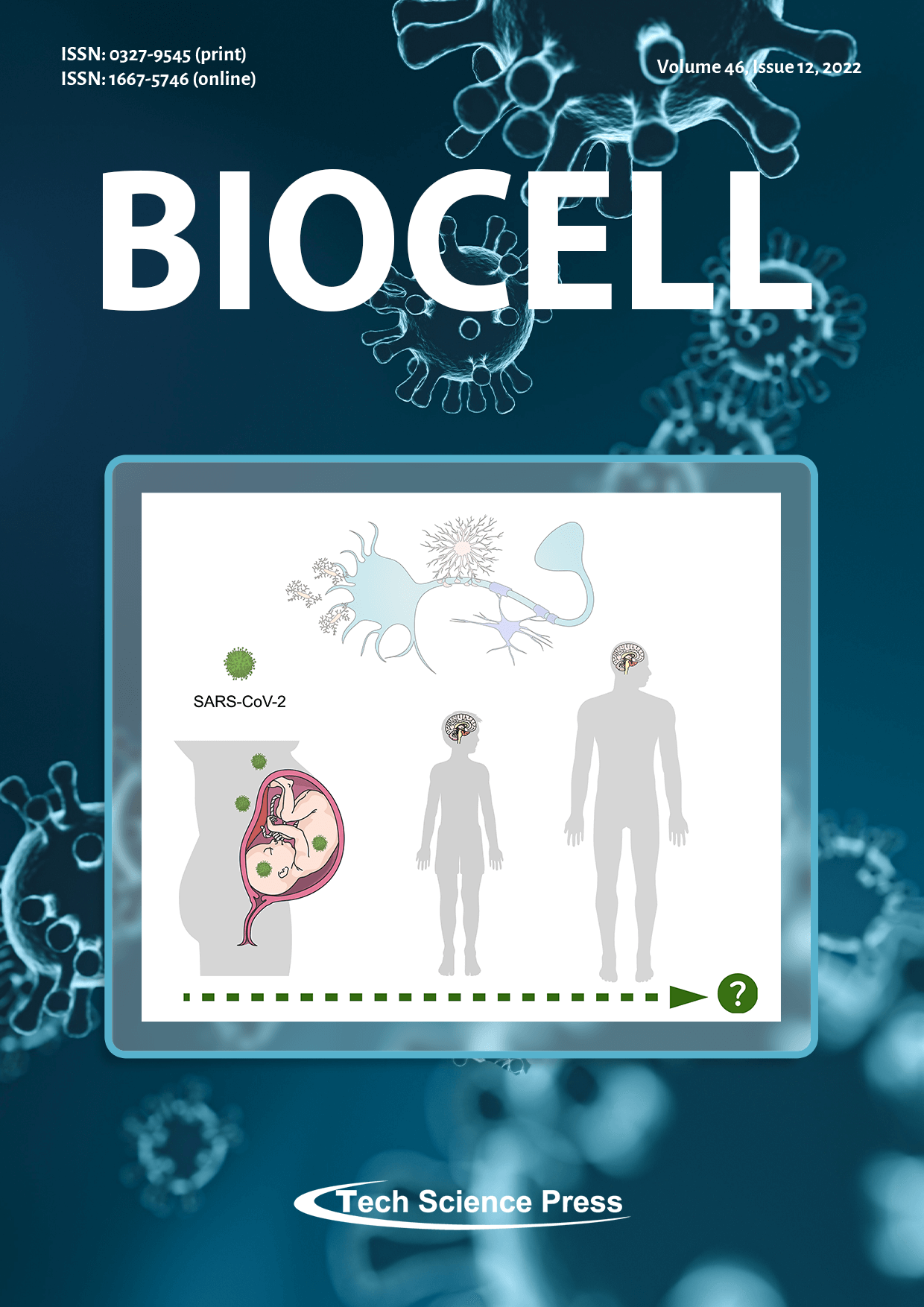
Glial cells play essential roles for brain development and homeostasis. SARS-CoV-2 infection during critical periods of neurodevelopment can alter glial functions, compromising neuronal plasticity (top of the figure). Evidence support that disrupted glial function is associated with a wide range of neuropsychiatric disorders. Based on these relationships, we discuss the impact of SARS-CoV-2 infection during pregnancy as a risk factor for neuropsychiatric consequences in the offspring later in life (bottom of the figure), focusing on the potential role of glial cells.
View this paper