 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Diosgenin inhibited podocyte pyroptosis in diabetic kidney disease by regulating the Nrf2/NLRP3 pathway
1 Department of Nephrology, The First Hospital of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, 410007, China
2 Department of Endocrinology, The First Hospital of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, 410007, China
* Corresponding Author: WENXIAO HU. Email:
BIOCELL 2024, 48(10), 1503-1516. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2024.052692
Received 11 April 2024; Accepted 18 June 2024; Issue published 02 October 2024
Abstract
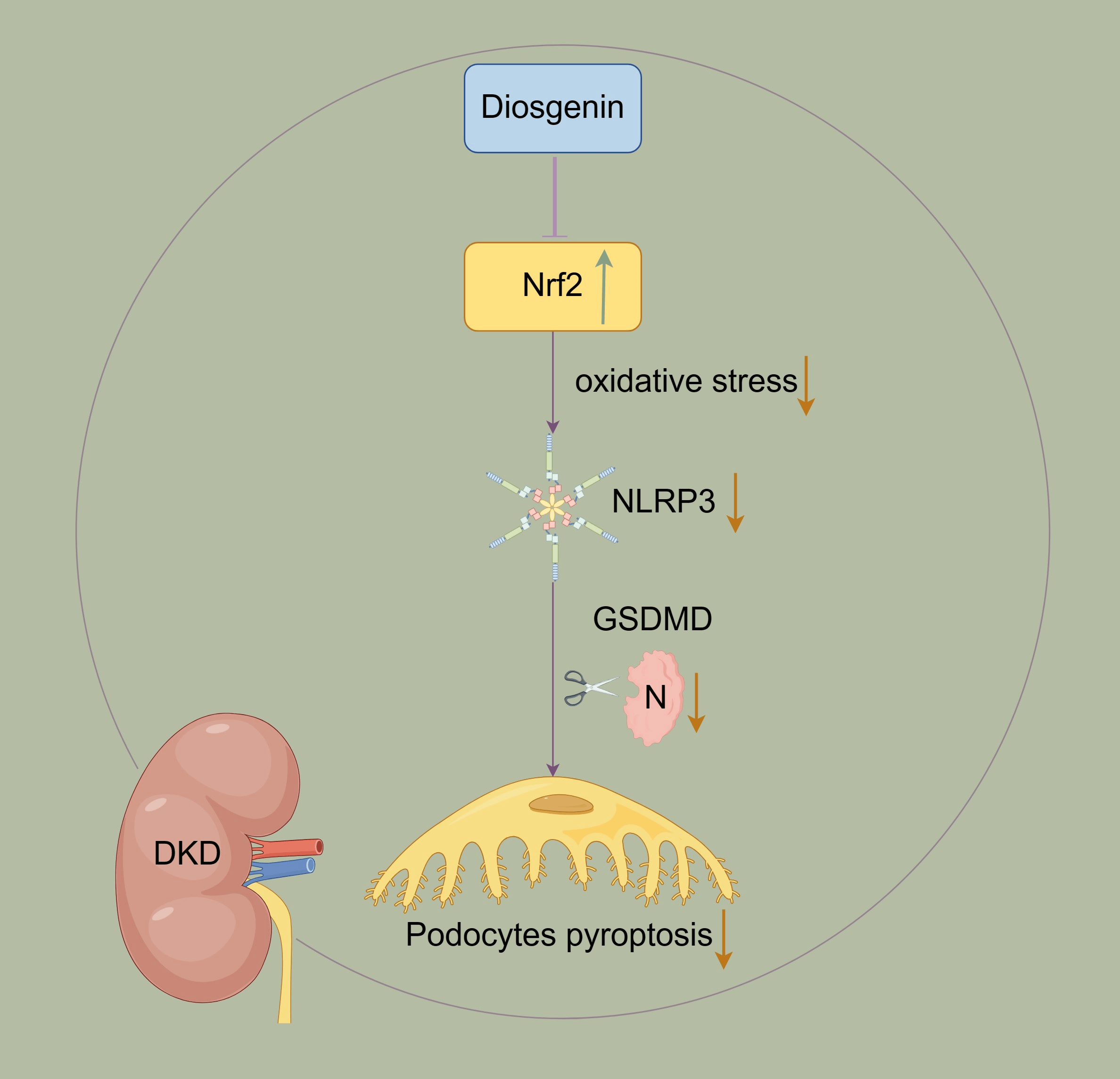
Background: Podocyte injury is crucial in diabetic kidney disease (DKD) progression, and the mechanism remains unclear. The previous studies indicated Diosgenin played a key role in inhibiting podocyte injury progression. However, more research is needed to explore Diosgenin in inhibiting-molecular mechanisms in the process of podocyte injury. Methods: The content of Diosgenin in HeShenwan was detected by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS) method. The podocyte injury model was constructed by high glucose (HG)-induced mpc5 cells. The Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay was utilized to evaluate the activity of mpc5 cells. Pyroptosis in mpc5 cells was assessed using flow cytometry. Molecular docking studies of Diosgenin and Nrf2 were carried out using VINA 1.1.2 software. The levels of Superoxide dismutase (SOD), Malondialdehyde (MDA), Reactive oxygen species (ROS), Interleukin 1β (IL-1β), Interleukin 18 (IL-18), Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and High mobility group protein B1 (HMGB1) were assessed using related kits. The levels of Nod-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3), Nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), Cysteinyl aspartate specific proteinase 1 (Caspase-1), Gasdermin (GSDMD), and Apoptosis-associated speck-like protein contain a CARD (ASC) were detected. Results: The Diosgenin content was the highest in HeShenwan. The addition of Diosgenin enhanced HG-induced mpc5 cell activity and reduced oxidative stress and pyroptosis. Molecular docking results showed that Diosgenin bound to the Nrf2 through hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions, regulating the Nrf2 expression. Overexpression of Nrf2 reduced the levels of NLRP3, reducing oxidative stress and inhibiting pyroptosis in mpc5 cells. Knockdown of Nrf2 reduced HG-induced mpc5 cell activity and increased pyroptosis and oxidative stress. Diosgenin inhibited pyroptosis in mpc5 cells by regulating the Nrf2/NLRP3 pathway. Conclusion: Diosgenin inhibited HG-induced pyroptosis in mpc5 cells by regulating the Nrf2/NLRP3 pathway.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools