 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Inhibition of proliferation, migration, and invasiveness of bladder cancer cells through SAPCD2 knockdown
Department of Urology, Shaoxing People’s Hospital, Shaoxing Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Shaoxing, China
* Corresponding Author: JIAJUN YAN. Email:
BIOCELL 2024, 48(1), 97-109. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2023.045303
Received 23 August 2023; Accepted 23 November 2023; Issue published 30 January 2024
Abstract
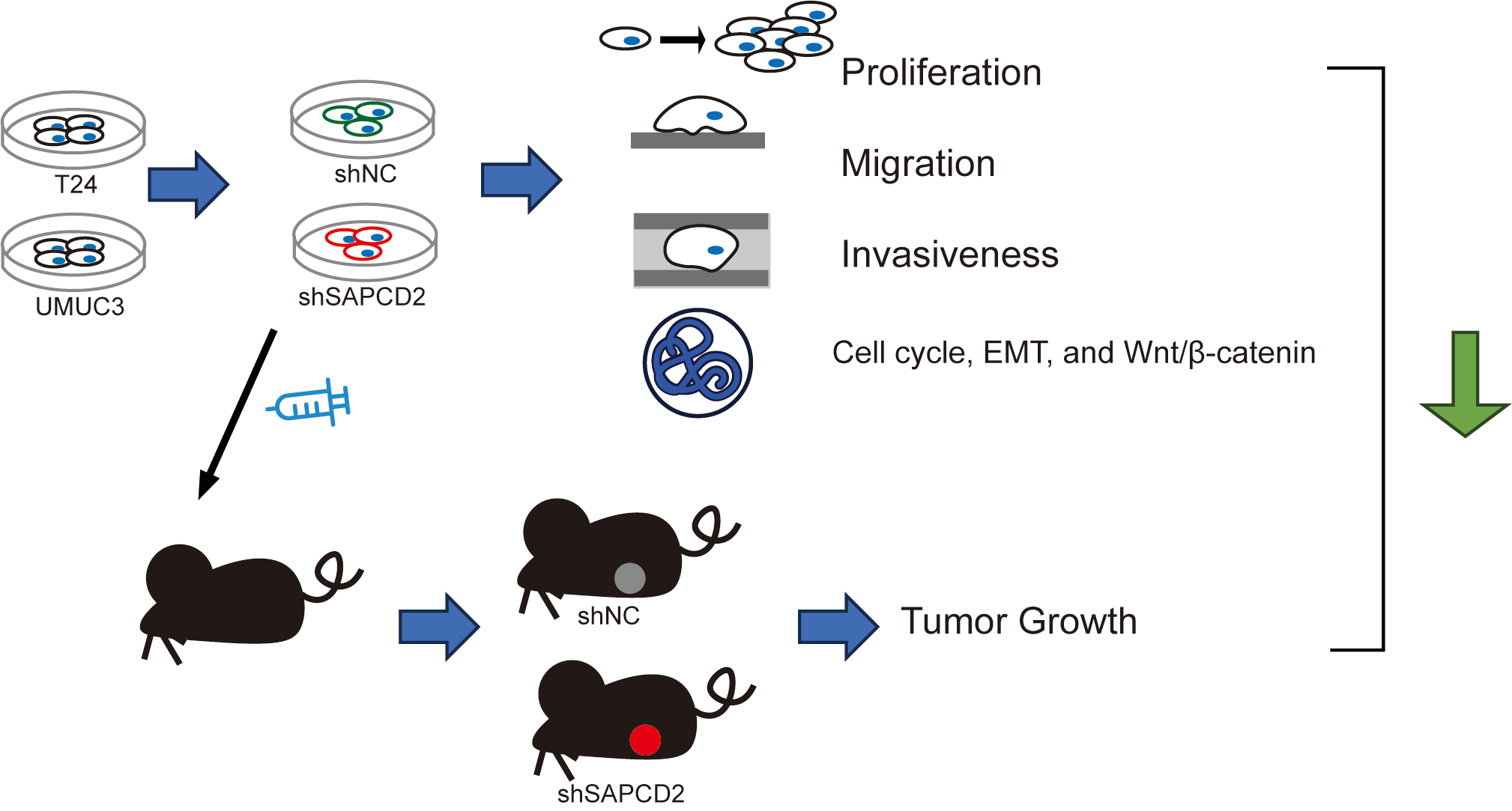
Introduction: Bladder cancer (BC) has a high incidence and mortality rate worldwide. Suppressor anaphase-promoting complex domain containing 2 (SAPCDC2) is over-expressed in a variety of tumors. Objectives: This study investigated the effects of SAPCD2 knockdown on BC cells. Methods: T24 and UMUC3 cell models and the xenografted BC tumor model with SAPCD2 knockdown were established to observe the malignant phenotype of BC cells by cell counting kit-8 assay, colony formation test, wound healing, and Transwell assay, mRNA and proteins expressions were measured with quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction, western blotting, and tissue immunohistochemistry. Lithium chloride agonist on the Wnt/β-catenin pathway was used to clarify the molecular mechanism of SAPCD2 knockdown. Results: SAPCD2 expression was significantly higher in BC cell lines than in SV-HUC-1 cells. SAPCD2 knockdown inhibited viability and cloning, hindered the G0/G1 phase of the cell cycle in UMUC3 and T24 cells, and decreased the migration and invasiveness of BC cells. SAPCD2 knockdown inhibited expression levels of cyclin D1, cyclin B1, N-cadherin, vimentin, Snail, β-catenin, c-Myc, and cyclin-dependent kinase 4, while the P21 and E-cadherin were raised by SAPCD2 knockdown. Furthermore, lithium chloride reversed the effects of SAPCD2 knockdown on the expression levels of the above proteins in UMUC3 and T24 cells. In vivo, SAPCD2 knockdown inhibited the volume, weight, and expression of Ki-67 and β-catenin in tumors and increased the E-cadherin expression. Conclusion: SAPCD2 knockdown inhibits the malignant phenotype of BC via a pathway involving β-catenin.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools