 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Digital Soil Mapping (DSM) Using a GIS-Based RF Machine Learning Model: The Case of Strandzha Mountains (Thrace Peninsula, Türkiye)
1 Department of Geography, Faculty of Arts and Sciences, Tekirdag Namık Kemal University, Tekirdag, 59030, Türkiye
2 Department of Soil Sciences and Plant Nutrition, Faculty of Agriculture, Tekirdag Namık Kemal University, Tekirdag, 59030, Türkiye
* Corresponding Author: Emre Ozsahin. Email:
Revue Internationale de Géomatique 2024, 33, 341-361. https://doi.org/10.32604/rig.2024.054197
Received 21 May 2024; Accepted 14 August 2024; Issue published 13 September 2024
Abstract
This study assessed and mapped the spatial distribution of soil types and properties developed under the forest cover of the Strandzha Mountains of Türkiye. The study was conducted on a micro-scale in the riparian zone of the Balaban River, which characterizes the soils distributed in the mountainous area. The effect of environmental factors on the spatial distribution of soil types and properties was also determined. To gather data, soil sampling, laboratory analysis, data processing and mapping were sequentially performed. These data were analyzed using the Geographical Information System (GIS) based Random Forest (RF) machine learning technique. Digital Soil Mapping (DSM) was developed with satisfactory performance. DSM suggests that the factors affecting the spatial distribution of soil types and properties in the sample area are, from most important to least important, topography (50.77%), climate (28.14%), organisms (8.22%), parent material (7.24%) and time (5.63%). With the contributions of all these factors in different proportions, it was determined that soils belonging to the Entisol and then Inceptisol orders were the most widespread in the sample area. The study results revealed that the GIS-based RF machine-learning technique can be used as a reliable tool for the development of DSM in mountainous terrains.Graphic Abstract
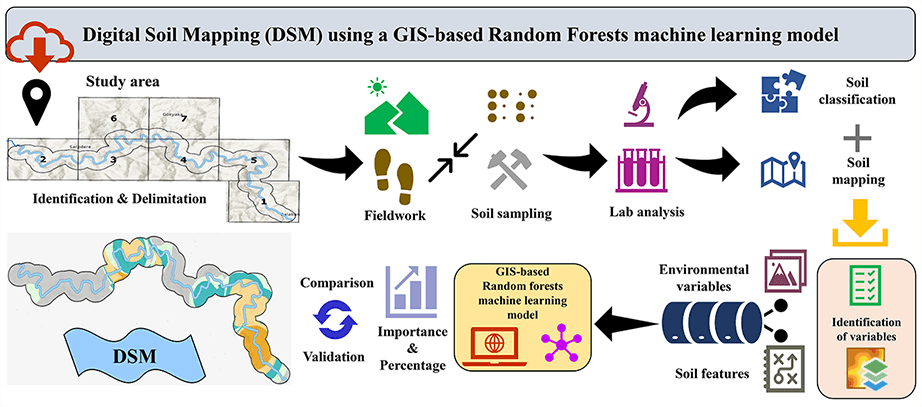
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools