 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Suitability Evaluation for Urban Green Space Areas in Sèmè-Podji District (Southern Benin), Using GIS and AHP Methods
1 Unité de Recherche Horticole et d’Aménagement des Espaces Verts, Laboratoire des Sciences Végétales, Horticoles et Forestières, École d’Horticulture et d’Aménagement des Espaces Verts, Université Nationale d’Agriculture, P.O. Box 43, Kétou, 229, Benin
2 Unité de Recherche en Foresterie et Conservation des BioRessources, Laboratoire de Sciences Végétales, Horticoles et Forestières, École de Foresterie Tropicale, Université Nationale d’Agriculture, P.O. Box 43, Kétou, 229, Benin
* Corresponding Author: Gbodja Houéhanou François Gbesso. Email:
Revue Internationale de Géomatique 2024, 33, 201-220. https://doi.org/10.32604/rig.2024.053500
Received 01 May 2024; Accepted 18 June 2024; Issue published 11 July 2024
Abstract
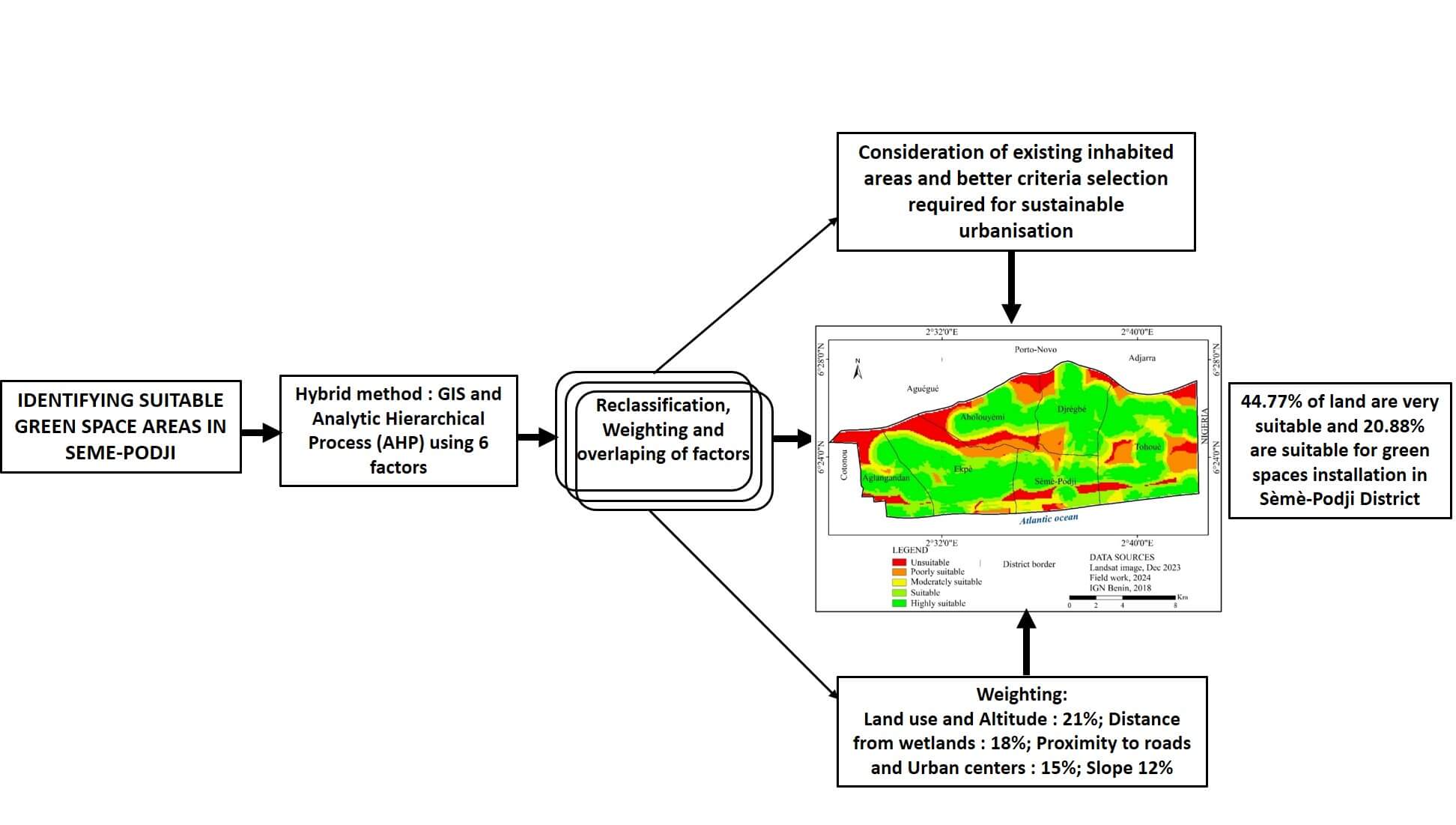
Urban green areas play a vital role in enhancing the social balance, resilience, and environmental sustainability of urban settings. In Benin, while the landscaping sector is expanding, finding appropriate locations for creating green spaces remains a challenge. The purpose of this study was to identify areas conducive to the incorporation of green landscapes into urban planning within the Sèmè-Podji District. The approach used involved a multi-criteria analysis leveraging a combined GIS and Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) framework. Six key factors were considered: land use, elevation, slope, distance to major roads, proximity to urban hubs, and separation from flood-prone zones and water bodies. These were analyzed using the “Spatial Analysis” feature of ArcGIS to create a map highlighting areas suitable for the development of green spaces. The findings reveal that a substantial portion of land, approximately 44.77%, is highly favorable, and 20.88% suitable for landscaping in this district. The weighting of factors combined in this analysis reveals a 21% importance for land use and elevation, while distance from separation from flood-prone zones is given a weight of 18%. Distance to major roads and proximity to urban hubs are weighted at 15%, against 12% for the slope factor. This information provides guidance to decision-makers in selecting suitable sites for green spaces and their integration into the land management of Sèmè-Podji District. The results of this study also provide a scientific basis for addressing similar concerns in other cities.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools