 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Mapping of Land Use and Land Cover (LULC) Using EuroSAT and Transfer Learning
1 Faculty of Computer Science, Selinus University of Sciences and Literature, Ragusa, Italy
2 Deparment of Computer Science and Engineering, Jashore University of Science and Technology, Jashore, Bangladesh
* Corresponding Author: Suman Kunwar. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Geomatics for Environmental Monitoring)
Revue Internationale de Géomatique 2024, 33, 1-13. https://doi.org/10.32604/rig.2023.047627
Received 12 November 2023; Accepted 28 December 2023; Issue published 27 February 2024
Abstract
As the global population continues to expand, the demand for natural resources increases. Unfortunately, human activities account for 23% of greenhouse gas emissions. On a positive note, remote sensing technologies have emerged as a valuable tool in managing our environment. These technologies allow us to monitor land use, plan urban areas, and drive advancements in areas such as agriculture, climate change mitigation, disaster recovery, and environmental monitoring. Recent advances in Artificial Intelligence (AI), computer vision, and earth observation data have enabled unprecedented accuracy in land use mapping. By using transfer learning and fine-tuning with red-green-blue (RGB) bands, we achieved an impressive 99.19% accuracy in land use analysis. Such findings can be used to inform conservation and urban planning policies.Graphic Abstract
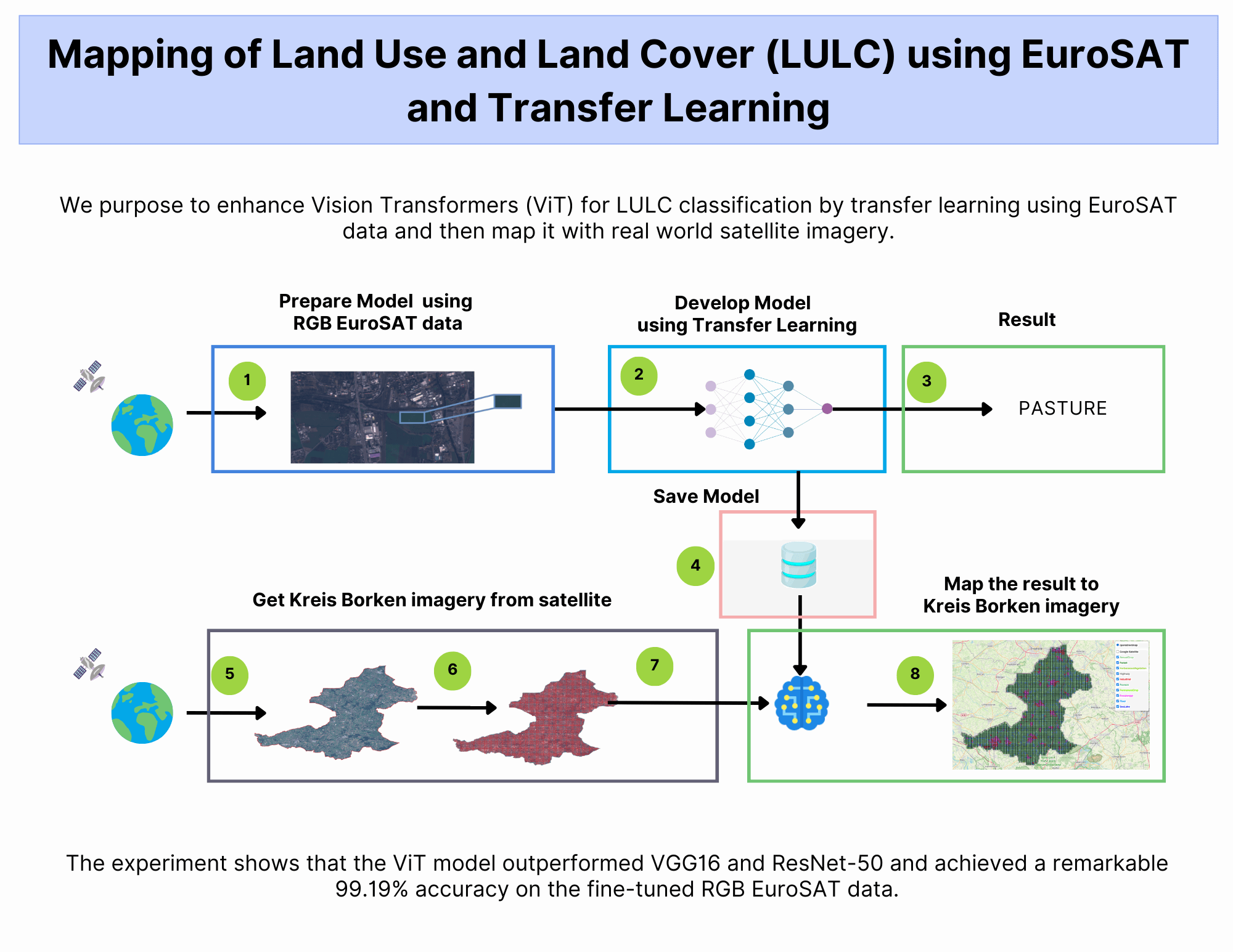
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools