 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Thermal Performance of Entropy-Optimized Tri-Hybrid Nanofluid Flow within the Context of Two Distinct Non-Newtonian Models: Application of Solar-Powered Residential Buildings
1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, College of Engineering in Wadi Alddawasir, Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz University, Wadi Alddawasir, 18413, Saudi Arabia
2 Production Engineering and Mechanical Design Department, Faculty of Engineering, Mansoura University, Mansoura, 35516, Egypt
3 Department of Mathematics and Statistics, Kwara State University, Malete, 23431, Nigeria
4 Department of Pure and Applied Mathematics, Ladoke Akintola University of Technology, Ogbomoso, 210101, Nigeria
5 Department of Mathematics, Saveetha School of Engineering, Saveetha Institute of Medical and Technical Sciences, Saveetha University, Chennai, 602105, India
6 Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, Sakarya University, Serdivan/Sakarya, 54050, Turkey
7 Department of Physical and Chemical Sciences, Federal University of Health Sciences Ila-Orangun, Ila-Orangun, 234101, Nigeria
8 Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Kwara State University, Malete, 23431, Nigeria
9 Fakulti Teknologi dan Kejuruteraan Mekanikal, Universiti Teknikal Malaysia Melaka, Hang Tuah Jaya, Melaka, 76100, Malaysia
* Corresponding Author: Najiyah Safwa Khashi’ie. Email:
Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences 2025, 142(3), 3089-3113. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2025.061296
Received 21 November 2024; Accepted 03 February 2025; Issue published 03 March 2025
Abstract
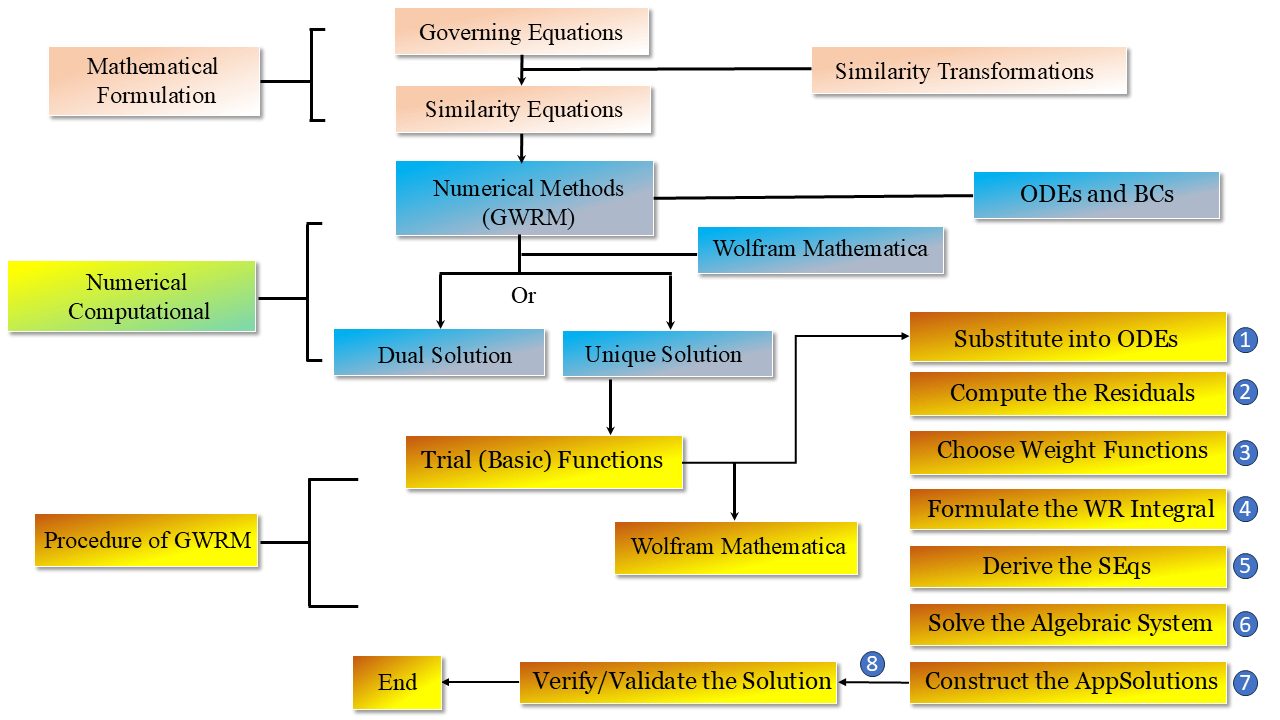
The need for efficient thermal energy systems has gained significant attention due to the growing global concern about renewable energy resources, particularly in residential buildings. One of the biggest challenges in this area is capturing and converting solar energy at maximum efficiency. This requires the use of strong materials and advanced fluids to enhance conversion efficiency while minimizing energy losses. Despite extensive research on thermal energy systems, there remains a limited understanding of how the combined effects of thermal radiation, irreversibility processes, and advanced heat flux models contribute to optimizing solar power performance in residential applications. Addressing these knowledge gaps is critical for advancing the design and implementation of highly efficient thermal energy systems. Owing to its usage, this study investigates the thermal energy and irreversibility processes in the context of solar power systems for residential buildings. Specifically, it explores the influence of thermal radiation and the Cattaneo–Christov heat flux model, considering the interactions over a stretching surface. The study incorporates cross fluid and Maxwell fluid effects into the governing model equations. Utilizing the Galerkin-weighted residual method, the transformed model is solved to understand the impacts on heat distribution. The findings reveal that increased thermal radiation and thermal conductivity significantly enhance heat distribution, offering valuable insights for optimizing solar power system efficiency in residential applications.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools