 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Examining the Quality Metrics of a Communication Network with Distributed Software-Defined Networking Architecture
1 Department of Electrical Engineering, Khwaja Fareed University of Engineering and Information Technology, Rahim Yar Khan, 64200, Pakistan
2 Department of Telecommunication Systems, Bahauddin Zakariya University, Multan, 60000, Pakistan
3 Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Engineering and Technology, Taxila, 47050, Pakistan
4 School of Engineering and Physical Sciences, Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh, EH14 4AS, UK
* Corresponding Author: Khawaja Tahir Mehmood. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Emerging Technologies in Information Security )
Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences 2024, 141(2), 1673-1708. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2024.053903
Received 13 May 2024; Accepted 26 July 2024; Issue published 27 September 2024
Abstract
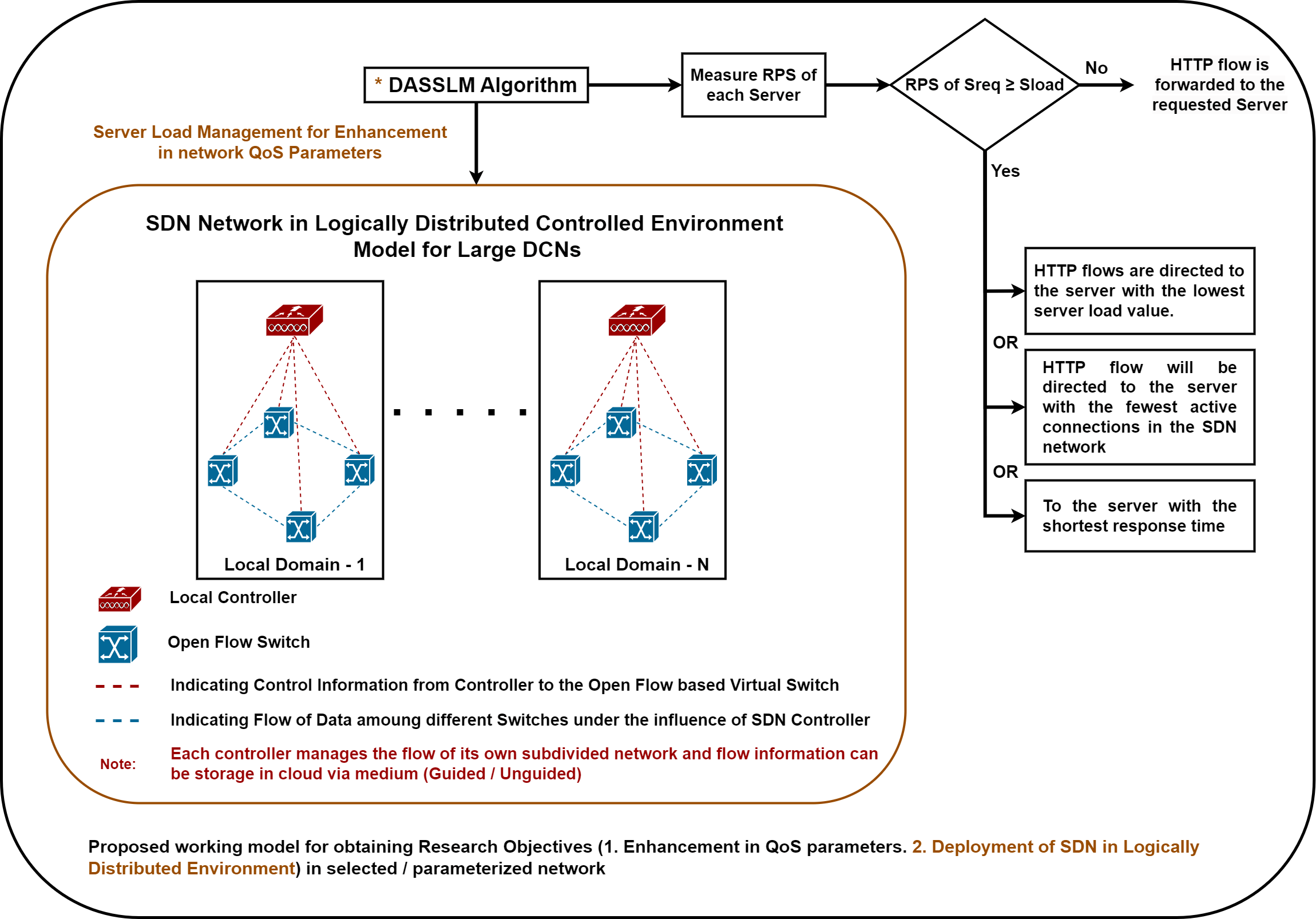
Software-Defined Networking (SDN), with segregated data and control planes, provides faster data routing, stability, and enhanced quality metrics, such as throughput (Th), maximum available bandwidth (Bd(max)), data transfer (DTransfer), and reduction in end-to-end delay (D(E-E)). This paper explores the critical work of deploying SDN in largescale Data Center Networks (DCNs) to enhance its Quality of Service (QoS) parameters, using logically distributed control configurations. There is a noticeable increase in Delay(E-E) when adopting SDN with a unified (single) control structure in big DCNs to handle Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) requests causing a reduction in network quality parameters (Bd(max), Th, DTransfer, D(E-E), etc.). This article examines the network performance in terms of quality matrices (bandwidth, throughput, data transfer, etc.), by establishing a large–scale SDN-based virtual network in the Mininet environment. The SDN network is simulated in three stages: (1) An SDN network with unitary controller-POX to manage the data traffic flow of the network without the server load management algorithm. (2) An SDN network with only one controller to manage the data traffic flow of the network with a server load management algorithm. (3) Deployment of SDN in proposed control arrangement (logically distributed controlled framework) with multiple controllers managing data traffic flow under the proposed Intelligent Sensing Server Load Management (ISSLM) algorithm. As a result of this approach, the network quality parameters in large-scale networks are enhanced.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools