 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
A Hand Features Based Fusion Recognition Network with Enhancing Multi-Modal Correlation
School of Information Engineering, Shenyang University, Shenyang, 110044, China
* Corresponding Author: Wei Wu. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Artificial Intelligence Emerging Trends and Sustainable Applications in Image Processing and Computer Vision)
Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences 2024, 140(1), 537-555. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2024.049174
Received 29 December 2023; Accepted 06 February 2024; Issue published 16 April 2024
Abstract
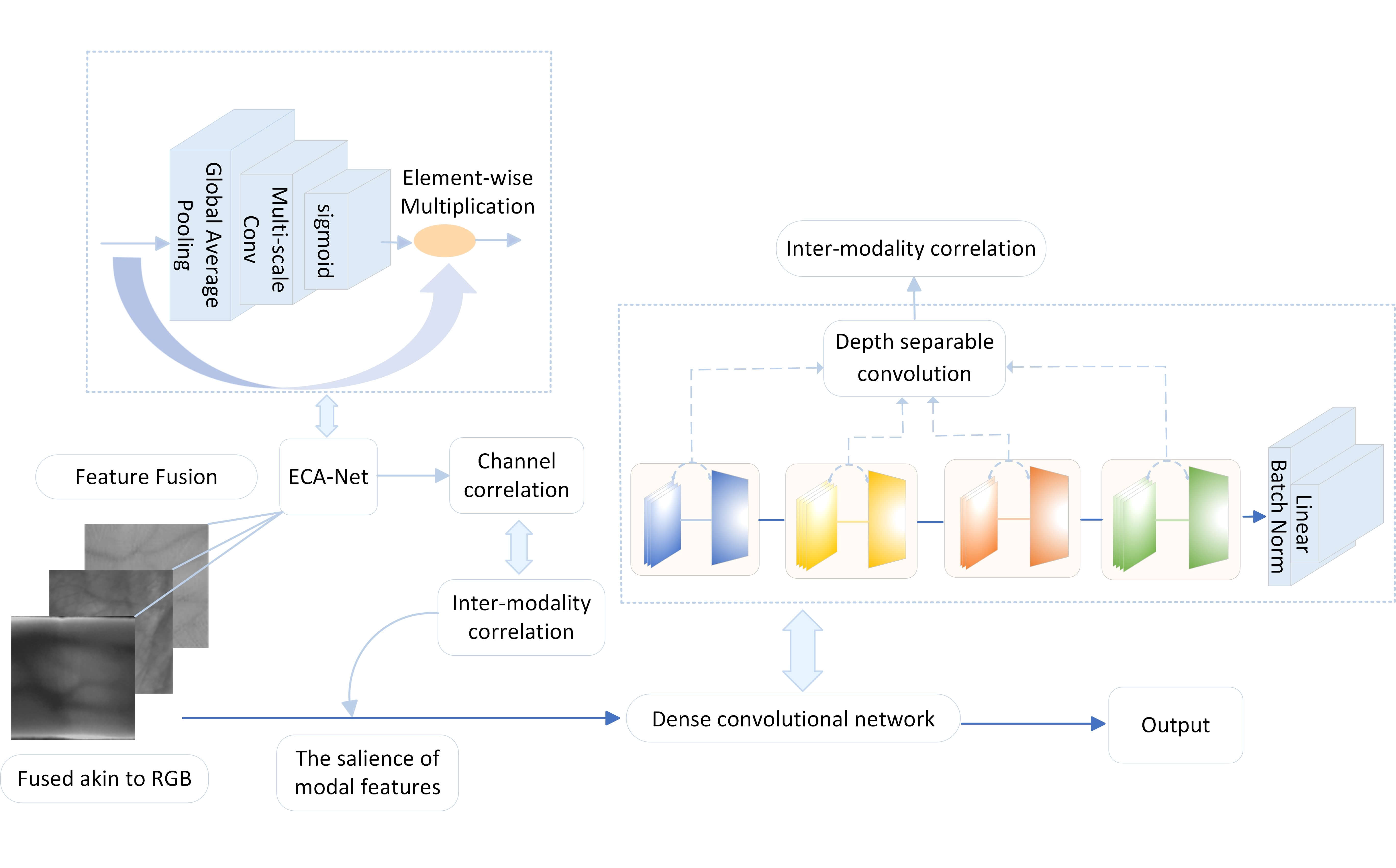
Fusing hand-based features in multi-modal biometric recognition enhances anti-spoofing capabilities. Additionally, it leverages inter-modal correlation to enhance recognition performance. Concurrently, the robustness and recognition performance of the system can be enhanced through judiciously leveraging the correlation among multimodal features. Nevertheless, two issues persist in multi-modal feature fusion recognition: Firstly, the enhancement of recognition performance in fusion recognition has not comprehensively considered the inter-modality correlations among distinct modalities. Secondly, during modal fusion, improper weight selection diminishes the salience of crucial modal features, thereby diminishing the overall recognition performance. To address these two issues, we introduce an enhanced DenseNet multimodal recognition network founded on feature-level fusion. The information from the three modalities is fused akin to RGB, and the input network augments the correlation between modes through channel correlation. Within the enhanced DenseNet network, the Efficient Channel Attention Network (ECA-Net) dynamically adjusts the weight of each channel to amplify the salience of crucial information in each modal feature. Depthwise separable convolution markedly reduces the training parameters and further enhances the feature correlation. Experimental evaluations were conducted on four multimodal databases, comprising six unimodal databases, including multispectral palmprint and palm vein databases from the Chinese Academy of Sciences. The Equal Error Rates (EER) values were 0.0149%, 0.0150%, 0.0099%, and 0.0050%, correspondingly. In comparison to other network methods for palmprint, palm vein, and finger vein fusion recognition, this approach substantially enhances recognition performance, rendering it suitable for high-security environments with practical applicability. The experiments in this article utilized a modest sample database comprising 200 individuals. The subsequent phase involves preparing for the extension of the method to larger databases.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools