 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Blade Wrap Angle Impact on Centrifugal Pump Performance: Entropy Generation and Fluid-Structure Interaction Analysis
1 School of Mechanical Engineering, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Engineering Campus, Nibong Tebal, Penang, 14300, Malaysia
2 Chemical Engineering Department, Faculty of Engineering, Al-Muthanna University, Muthanna, 66001, Iraq
3 Faculty of Mechanical Engineering & Technology, Universiti Malaysia Perlis (UniMAP), Arau, Perlis, 02600, Malaysia
* Corresponding Author: Mohd Sharizal Abdul Aziz. Email:
Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences 2024, 140(1), 109-137. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2024.047245
Received 31 October 2023; Accepted 02 January 2024; Issue published 16 April 2024
Abstract
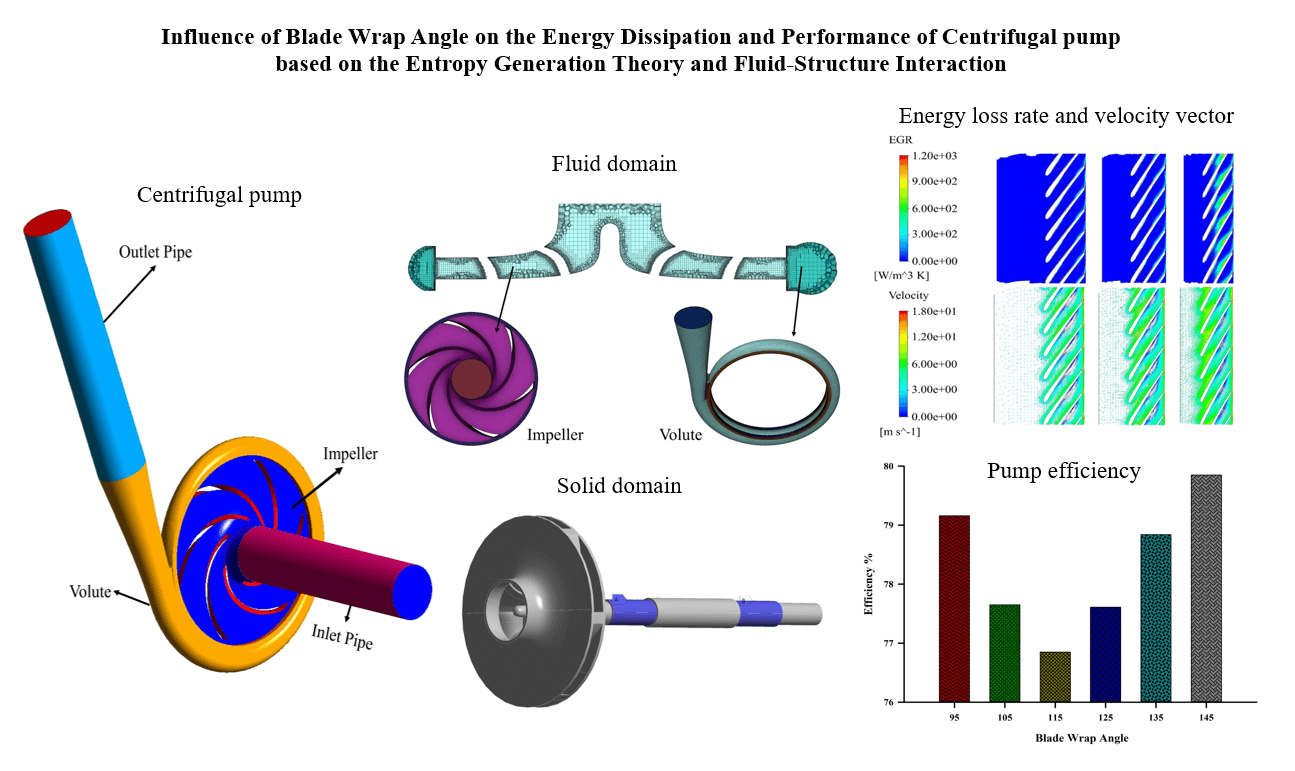
The centrifugal pump is a prevalent power equipment widely used in different engineering patterns, and the impeller blade wrap angle significantly impacts its performance. A numerical investigation was conducted to analyze the influence of the blade wrap angle on flow characteristics and energy distribution of a centrifugal pump evaluated as a low specific speed with a value of 69. This study investigates six impeller models that possess varying blade wrap angles (95°, 105°, 115°, 125°, 135°, and 145°) that were created while maintaining the same volute and other geometrical characteristics. The investigation of energy loss was conducted to evaluate the values of total and entropy generation rates (TEG, EGR). The fluid-structure interaction was considered numerically using the software tools ANSYS Fluent and ANSYS Workbench. The elastic structural dynamic equation was used to estimate the structural response, while the shear stress transport k – ω turbulence model was utilized for the fluid domain modeling. The findings suggest that the blade wrap angle has a significant influence on the efficiency of the pump. The impeller featuring a blade wrap angle of 145° exhibits higher efficiency, with a notable increase of 3.76% relative to the original model. Variations in the blade wrap angle impact the energy loss, shaft power, and pump head. The model with a 145° angle exhibited a maximum equivalent stress of 14.8 MPa and a total deformation of 0.084 mm. The results provide valuable insights into the intricate flow mechanism of the centrifugal pump, particularly when considering various blade wrap angles.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools