 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
A Sharding Scheme Based on Graph Partitioning Algorithm for Public Blockchain
1 Key Laboratory of Computing Power Network and Information Security, Ministry of Education, Shandong Computer Science Center, Qilu University of Technology (Shandong Academy of Sciences), Jinan, 250014, China
2 Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Computer Networks, Shandong Fundamental Research Center for Computer Science, Jinan, 250014, China
3 Mathematical Institute, The Serbian Academy of Sciences and Arts, Belgrade, 11000, Serbia
* Corresponding Author: Shujiang Xu. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: The Bottleneck of Blockchain Techniques: Scalability, Security and Privacy Protection)
Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences 2024, 139(3), 3311-3327. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2023.046164
Received 21 September 2023; Accepted 08 December 2023; Issue published 11 March 2024
Abstract
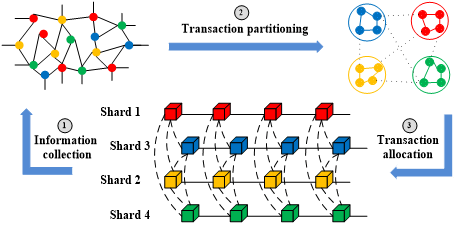
Blockchain technology, with its attributes of decentralization, immutability, and traceability, has emerged as a powerful catalyst for enhancing traditional industries in terms of optimizing business processes. However, transaction performance and scalability has become the main challenges hindering the widespread adoption of blockchain. Due to its inability to meet the demands of high-frequency trading, blockchain cannot be adopted in many scenarios. To improve the transaction capacity, researchers have proposed some on-chain scaling technologies, including lightning networks, directed acyclic graph technology, state channels, and sharding mechanisms, in which sharding emerges as a potential scaling technology. Nevertheless, excessive cross-shard transactions and uneven shard workloads prevent the sharding mechanism from achieving the expected aim. This paper proposes a graph-based sharding scheme for public blockchain to efficiently balance the transaction distribution. By mitigating cross-shard transactions and evening-out workloads among shards, the scheme reduces transaction confirmation latency and enhances the transaction capacity of the blockchain. Therefore, the scheme can achieve a high-frequency transaction as well as a better blockchain scalability. Experiments results show that the scheme effectively reduces the cross-shard transaction ratio to a range of 35%–56% and significantly decreases the transaction confirmation latency to 6 s in a blockchain with no more than 25 shards.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools