 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Interaction Mechanisms between Natural Debris Flow and Rigid Barrier Deflectors: A New Perspective for Rational Design and Optimal Arrangement
1 Department of Geotechnical Engineering, College of Civil Engineering, Tongji University, Shanghai, 200092, China
2 Department of Hydraulic Engineering, College of Civil Engineering, Tongji University, Shanghai, 200092, China
* Corresponding Author: Dianlei Feng. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Recent Advances in Computational Methods for Performance Assessment of Engineering Structures and Materials against Dynamic Loadings)
Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences 2024, 139(2), 1679-1699. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2023.044094
Received 20 July 2023; Accepted 31 October 2023; Issue published 29 January 2024
Abstract
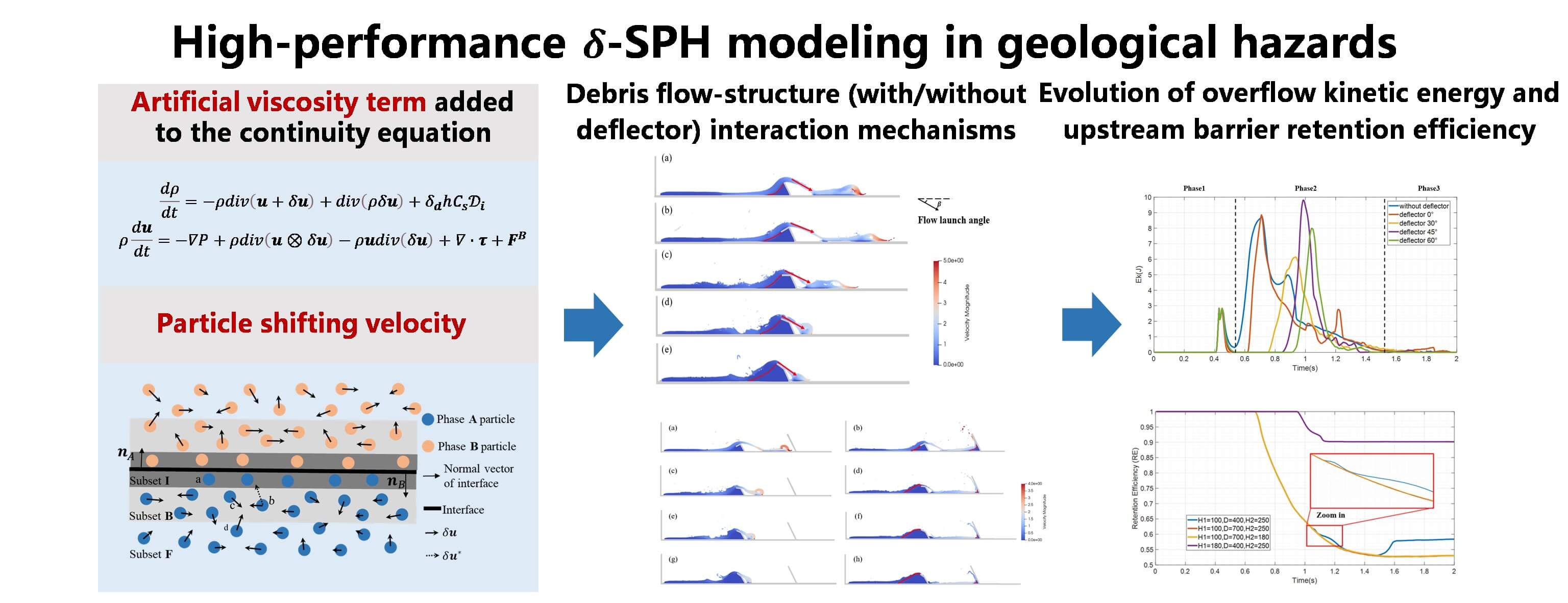
Rigid barrier deflectors can effectively prevent overspilling landslides, and can satisfy disaster prevention requirements. However, the mechanisms of interaction between natural granular flow and rigid barrier deflectors require further investigation. To date, few studies have investigated the impact of deflectors on controlling viscous debris flows for geological disaster prevention. To investigate the effect of rigid barrier deflectors on impact mechanisms, a numerical model using the smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) method with the Herschel–Bulkley model is proposed to simulate the interaction between natural viscous flow and single/dual barriers with and without deflectors. This model was validated using laboratory flume test data from the literature. Then, the model was used to investigate the influence of the deflector angle and multi-barrier arrangements. The optimal configuration of multi-barriers was analyzed with consideration to the barrier height and distance between the barriers, because these metrics have a significant impact on the viscous flow pile-up, run-up, and overflow mechanisms. The investigation considered the energy dissipation process, retention efficiency, and dead-zone formation. Compared with bare barriers with similar geometric characteristics and spatial distribution, rigid barriers with deflectors exhibit superior effectiveness in preventing the overflow and overspilling of viscous debris flow. Recommendations for the rational design of deflectors and the optimal arrangement of multi-barriers are provided to mitigate geological disasters.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools